Abstract
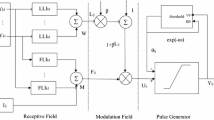
In this paper, we use Unit-linking PCNN (Pulse Coupled Neural Network), the simplified model of PCNN consisting of spiking neurons, to code a 2-dimensional image into a 1-dimensional time sequence called global Unit-linking PCNN image icon or time signature, including features of the original image and having the translation, rotation, and scale invariance. Dividing an image into multiple parts can obtain local Unit-linking PCNN image icons corresponding to the image’s local regions, which can reflect the local changes of the image. In the meantime, the global and the local Unit-linking PCNN image icons are used in navigation, object detection, and image authentication. In navigation, global Unit-linking PCNN image icon shows qualified performance especially in non-stationary-video navigation. Object detection using global Unit-linking PCNN image icon, is independent of variances of translation, rotation, and scale, and object segmentation is avoided. In image authentication, using local Unit-linking PCNN image icon can authenticate correctly some juggled images failed to authenticate by using local histogram or local mean intensity, and can locate the juggled positions in the juggled images with some accuracy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Eckhorn R, Reitboeck HJ, Arndt M and Dicke PW (1990). Feature linking via synchronization among distributed assemblies: simulation of results from cat cortex. Neural Comput 2: 293–307
Eckhorn R, Bauer R, Jordan W, Brosch M, Kruse W, Munk M and Reitboeck HJ (1988). Coherent oscillations: a mechanism of feature linking in the visual cortex? Multiple electrode and correlation analyses in the cat. Biol Cybern 60(2): 121–130
Gray CM, Konig P, Engel AK and Singer W (1989). Oscillatory responses in cat visual cortex exhibitioner-columnar synchronization which reflects global stimulus properties. Nature 338: 334–337
Johnson JL and Ritter D (1993). Observation of periodic waves in a pulse-coupled neural network. Opt Lett 18: 1253–1255
Johnson JL and Padgett ML (1999). PCNN models and applications. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(3): 480–498
Kuntimad G and Ranganath HS (1999). Perfect image segmentation using pulse coupled neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(3): 591–598
Broussard RP, Rogers SK, Oxley ME and Tarr GL (1999). Physiologically motivated image fusion for object detection using a pulse coupled neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(3): 554–563
Kinser JM (1999). Foveation by a pulse-coupled neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(3): 621–625
Caulfield HJ and Kinser JM (1999). Finding shortest path in the shortest time using PCNN’s. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(3): 604–606
Gu XD, Yu DH and Zhang LM (2004). Image thinning using pulse coupled neural network. Pattern Recognit Lett 25(9): 1075–1084
Gu XD, Yu DH and Zhang LM (2005). Image shadow removal using pulse coupled neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 16(3): 692–698
Maass W (1997). Fast sigmoid networks via spiking neurons. Neural Comput 9: 279–304
Hopfield JJ (1995). Pattern recognition computation using action potential timing for stimulus representation. Nature 376: 33–36
Sejnowski TJ (1995). Time for a new neural code?. Nature 376: 31–32
Johnson JL (1994). Pulse-coupled neural nets: translation, rotation, scale, distortion and intensity signal invariance for images. Appl Optics 33: 6239–6253
Muresan RC (2003). Pattern recognition using pulse-couple neural networks and discrete Fourier transforms. Neurocomputing 51: 487–493
Weng JY, Zhang YL and Hwang WS (2003). Candid covariance-free incremental principal component analysis. IEEE Trans PAMI 25(8): 1034–1040
Hwang WS and Weng JY (2000). Hierarchical discriminant regression. IEEE Trans PAMI 22(11): 1277–1293
Schneider M, Chang SF (1996) A robust digital content based digital signature for image authentication. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Image Processing, Lausanne, Switzerland, pp. 227–230
Lou DC and Liu JL (2000). Fault resilient and compression tolerant digital signature for image authentication. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 46(1): 31–39
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, X. Feature Extraction using Unit-linking Pulse Coupled Neural Network and its Applications. Neural Process Lett 27, 25–41 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-007-9057-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-007-9057-6