Abstract
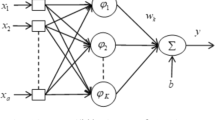
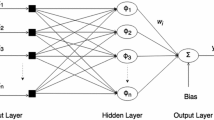
While the conventional standard radial basis function (RBF) networks are based on a single kernel, in practice, it is often desirable to base the networks on combinations of multiple kernels. In this paper, a multi-kernel function is introduced by combining several kernel functions linearly. A novel RBF network with the multi-kernel is constructed to obtain a parsimonious and flexible regression model. The unknown centres of the multi-kernels are determined by an improved k-means clustering algorithm. And orthogonal least squares (OLS) algorithm is used to determine the remaining parameters. The complexity of the newly proposed algorithm is also analyzed. It is demonstrated that the new network can lead to a more parsimonious model with much better generalization property compared with the traditional RBF networks with a single kernel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach FR, Lanckriet GR, Jordan I (2004) Multiple kernel learning, conic duality, and the SMO algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 21st international conference on machine learning
Billings SA, Chen S (1998) The determination of multivariable nonlinear models for dynamic systems using neural networks. In: Leondes CT (ed) Neural network systems techniques and applications. Academic Press, San Diego
Billings SA, Wei HL, Balikhin M (2007) Generalized multiscale radial basis function networks. Neural Netw 20: 1081–1094
Broomhead DS, Lowe D (1988) Multivariable functional interpolation and adaptive networks. Complex Syst 2: 321–355
Chen S (2006) Local regularization assisted orthogonal least regression. Neurocomputing 69: 559–585
Chen S, Billings SA, Luo W (1989) Orthogonal least squares methods and their application to non-linear system identification. Int J Control 50(5): 1873–1896
Chen S, Cowan CF, Grant PM (1991) Orthogonal least squares learning algorithm for radial basis networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 2(2): 302–309
Chen S, Hong X, Harris CJ, Sharkey PM (2004) Sparse modeling using orthogonal forward regression with PRESS statistic and regulation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 34(2): 898–911
Chen S, Wang XX, Harris CJ (2005) Experiments with repeating weighted boosting search for optimization in signal processing applications. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 35(4): 682–693
Gonzalez J, Rojas I, Ortega J, Pomares H, Fernandez J, Diaz AF (2003) Multiobjective evolutionary optimization of the size, shape and position parameters of radial basis function networks for function approximation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 14(6): 1478–1495
Hong X, Harris CJ (2003) Experimental design and model construction algorithms for radial basis function networks. Int J Syst Sci 34(14): 733–745
Huang YS, Bang SY (1997) An efficient method to construct a radial basis function neural network classifier. Neural Netw 10(8): 1495–1503
Huang GB, Saratchandran P, Sundararajan N (2005) A generalized growing and pruning RBF (GGAP-RBF) neural network for function approximation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 16(1): 57–67
Jing XY, Yao YF, Yang JY, Zhang D (2008) A novel face recognition approach based on kernel discriminative common vectors (KDCV) feature extraction and RBF neural network. Neurocomputing 71(13–15): 3044–3048
Karayiannis NB (1999) Reformulated radial basis neural networks trained by gradient descent. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(3): 657–671
Krzanowski WJ, Lai YT (1988) A criterion for determining the number of groups in a data set using sum-of-squares clustering. Biometrics 44(1): 23–34
Kumar R, Das RR, Mishra VN, Dwivedi R (2009) A radial basis function neural network classifier for the discrimination of individual odor using responses of thick-film tin-oxide sensors. IEEE Sens J 9(10): 1254–1261
Lazaro M, Santamaria I, Pataleon C (2003) A new EM-based training algorithm for RBF networks. Neural Netw 16(1): 69–77
Leontaritis IJ, Billings SA (1985) Input–output parametric models for non-linear systems—part I: deterministic non-linear systems. Int J Control 41(2): 303–328
Liaw HC, Shirinzadeh B, Smith J (2009) Robust neural network motion tracking control of piezoelectric actuation systems for micro/nanomanipulation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 20(2): 356–367
Musavi MT, Ahmed W, Chan KH, Faris KB, Hummels DM (1992) On the training of radial basis function classifiers. Neural Netw 5(4): 595–603
Park J, Sandberg IW (1993) Approximation and radial basis function networks. Neural Comput 5(2): 305–316
Poggio T, Edelman S (1990) A network that learns to recognize three dimensional objects. Nature 343: 263–266
Poggio T, Girosi FM (1990) Networks for approximation and learning. Proc IEEE 18(9): 1481–1497
Schwenker F, Kestler HA, Palm G (2001) Three learning phase for radial-basis-function networks. Neural Netw 14(4): 439–458
Smola A (1996) Regression estimation with support vector learning machines. Master’s Thesis, Technische University Műnchen
Smola A, Scholkopf B, Ratsch G (1999) Linear programs for automatic accuracy control in regression. In: Proceedings of the 9th international conference on artificial neural networks
Sonnenburg S, Rätsch G, Schafer C, Schölkopf B (2006) Large scale multiple kernel learning. J Mach Learn Res 7: 1531–1565
Wu Q, Ying Y, Zhou DX (2007) Multi-kernel regularized classifiers. J Complex 23: 108–134
Zhang L, Zhou W, Jiao L (2004) Wavelet support vector machine. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 34(1): 34–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, L., Zhang, M. & Li, H. Sparse RBF Networks with Multi-kernels. Neural Process Lett 32, 235–247 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-010-9153-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-010-9153-x