Abstract
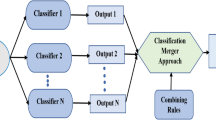
We present a two stage sequential ensemble where data samples whose output from the first classifier fall in a low confidence output interval (LCOI) are processed by a second stage classifier. Training is composed of three processes: training the first classifier, determining the LCOI of the first classifier, and training the second classifier upon the data items whose output fall in the LCOI. The LCOI is determined varying a threshold on the false positive rate (FPR) and false negative rate (FNR) curves. We have tested the approach on a database of feature vectors for the classification of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and control subjects extracted from structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI) data. In this paper, we focus on the combinations obtained when the first classifier is a relevance vector machine (RVM). Obtained results improve over previous results for this database.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADNI: (2011) Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement 7(2): 208–
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxel-Based morphometry—the methods. Neuroimage 11(6): 805–821
Baron JC, Chetelat G, Desgranges B, Perchey G, Landeau B, de la Sayette V, Eustache F (2001) In vivo mapping of gray matter loss with Voxel-based morphometry in mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 14(2): 298–309
Bowd C, Medeiros FA, Zhang Z, Zangwill LM, Hao J, Lee T-W, Sejnowski TJ, Weinreb RN, Goldbaum MH (2005) Relevance vector machine and support vector machine classifier analysis of scanning laser polarimetry retinal nerve fiber layer measurements. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46(4): 1322–1329
Breiman L (1996) Bagging predictors. Mach Learn 24(2): 123–140
Busatto G (2008) Voxel-based morphometry in Alzheimers’ disease. Expert Rev Neurother 8(11): 1691–1702
Busatto GF, Garrido GEJ, Almeida OP, Castro CC, Camargo CHP, Cid CG, Buchpiguel CA, Furuie S, Bottino CM (2003) A voxel-based morphometry study of temporal lobe gray matter reductions in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24(2): 221–231
Busatto GF, Garrido GE, Almeida OP, Castro CC, Camargo CH, Cid CG, Buchpiguel CA, Furuie S, Bottino CM (2003) A voxel-based morphometry study of temporal lobe gray matter reductions in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24(2): 221–231
Caesarendra W, Widodo A, Pham HT, Yang B-S (2010) Machine degradation prognostic based on RVM and ARMA/GARCH model for bearing fault simulated data. In: Prognostics and health management conference, 2010. PHM ’10, Portland, Oregon, pp 1–6
Chen S, Gunn SR, Harris CJ (2001) The relevance vector machine technique for channel equalization application. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12(6): 1529–1532
Dos Santos EM, Sabourin R, Maupin P (2009) Overfitting cautious selection of classifier ensembles with genetic algorithms. Inf Fusion 10(2): 150–162
Demir B, Erturk S (2007) Hyperspectral data classification using RVM with pre-segmentation and RANSAC. In: Geoscience and remote sensing symposium, 2007. IGARSS 2007. IEEE International, pp 1763–1766
Freund Y, Schapire RE (1995) A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. In: EuroCOLT ’95: proceedings of the second European conference on computational learning theory. Springer-Verlag, London, UK, pp 23–37
Frisoni GB, Testa C, Zorzan A, Sabattoli F, Beltramello A, Soininen H, Laakso MP (2002) Detection of grey matter loss in mild Alzheimer’s disease with voxel based morphometry. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73(6): 657–664
García-Pedrajas N, García-Osorio C (2011) Constructing ensembles of classifiers using supervised projection methods based on misclassified instances. Expert Syst Appl 38(1): 343–359
García-Sebastián M, Savio A, Graña M, Villanúa J (2009) On the use of morphometry based features for Alzheimer’s disease detection on MRI. In: Cabestany J, Sandoval F, Prieto A, Corchado JM (eds) Bio-inspired systems: computational and ambient intelligence/IWANN 2009 (Part I). LNCS 5517, Salamanca, Spain, pp 957–964
Kittler J, Hatef M, Duin RPW, Matas J (1998) On combining classifiers. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20(3): 226–239
Kuncheva LI, Rodríguez JJ (2010) Classifier ensembles for FMRI data analysis: an experiment. Magn Reson Imaging 28(4): 583–593
Lima CAM, Coelho ALV, Chagas S (2009) Automatic EEG signal classification for epilepsy diagnosis with relevance vector machines. Expert Syst Appl 36(6): 10054–10059
Marcus DS, Wang TH, Parker J, Csernansky JG, Morris JC, Buckner RL (Sep 2007) Open access series of imaging studies (OASIS): cross-sectional MRI data in young, middle aged, nondemented, and demented older adults. J Cogn Neurosci 19(9):1498–1507
Ozer S, Haider MA, Langer DL, van der Kwast TH, Evans AJ, Wernick MN, Trachtenberg J, Yetik IS (2009) Prostate cancer localization with multispectral MRI based on relevance vector machines. In: Biomedical imaging: from nano to macro, 2009. ISBI ’09. IEEE international symposium on, Boston, MA, USA, pp 73–76
Savio A, García-Sebastián M, Graña M, Villanúa J (2009a) Results of an adaboost approach on Alzheimer’s disease detection on MRI. In: Mira J, Ferrández JM, Alvarez JR, dela Paz F, Tolede FJ (eds) Bioinspired applications in artificial and natural computation. LNCS 5602, IWINAC 2009, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, pp 114–123
Savio A, García-Sebastián M, Hernández C, Graña M, Villanúa J (2009b) Classification results of artificial neural networks for Alzheimer’s disease detection. In: Emilio C, Hujun Y (eds) Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning—IDEAL 2009. LNCS 5788, Burgos, Spain, pp 641–648
Savio A, Garcia-Sebastian MT, Chyzhyk D, Hernandez C, Grana M, Sistiaga A, Lopez de Munain A, Villanua J (2011) Neurocognitive disorder detection based on feature vectors extracted from vbm analysis of structural MRI. Comput Biol Med 41:600–610
Scahill RI, Schott JM, Stevens JM, Rossor MN, Fox NC (2002) Mapping the evolution of regional atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease: unbiased analysis of fluid-registered serial MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(7): 4703
Selvathi D, Ram Prakash RS, Thamarai Selvi S (2007) Performance evaluation of kernel based techniques for brain MRI data classification. In: Conference on computational intelligence and multimedia applications, 2007. International Conference on, Sivakasi, Tamilnadu, India, vol 2, pp 456–460
Silva C, Ribeiro B (2006) Two-level hierarchical hybrid SVM-RVM classification model. In: Machine learning and applications, 2006. ICMLA ’06. 5th International conference on, pp 89–94
Tipping ME (2001) Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. J Mach Learn Res 1(3): 211–244
Tipping ME, Anita F, Avenue JJT, Avenue JJT (2003) Fast marginal likelihood maximisation for sparse Bayesian models. Proceedings of the ninth international workshop on artificial intelligence and statistics, Key West, FL, USA, pp 3–6
Traven HGC (1991) A neural-network approach to statistical pattern classification by semiparametric estimation of a probability density funcitons. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 2: 366–377
Tsai C-F, Lin Y-C, Yen DC, Chen Y-M (2011) Predicting stock returns by classifier ensembles. Appl Soft Comput 11(2):2452–2459 (the impact of soft computing for the progress of artificial intelligence]
Ulas A, Semerci M, Yildiz OT, AlpaydIn E (2009) Incremental construction of classifier and discriminant ensembles. Inf Sci 179(9): 1298–1318
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Termenon, M., Graña, M. A Two Stage Sequential Ensemble Applied to the Classification of Alzheimer’s Disease Based on MRI Features. Neural Process Lett 35, 1–12 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-011-9200-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-011-9200-2