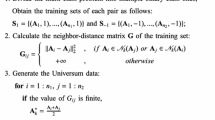Abstract
The existing matrixized learning machines (MLMs) use bilateral weight vectors on both side of one pattern as the constraints to manipulate matrix-based datasets directly. However, MLM might be challenged while the input pattern is a vector whose features are independent from each others. The traditional solution is to transform the vector into its all corresponding matrix forms, which is not only irrational, but also requiring extra computation in preprocessing. To overcome the problem, this paper proposes a novel matrixized learning model that utilizes an efficient clustering-based interpolation strategy to mapping the original vector-based pattern to an unique matrix. The proposed method first selects the most typical features defined as \(candidate\hbox {s}\) from each dimension of all patterns in the same class through a fast clustering method, and then measures the relationship between the features of each training pattern and the \(candidate\hbox {s}\) to generate a new matrix named the candidate-matrix in turn. Afterwards, the candidate-matrix is combined with the pattern to form the corresponding final matrix. At last, all final matrices are collected to form the new training set for the subsequent matrixized classifier. Named FCIMLM for short, the proposed matrixized method is proved more effective and efficient than the traditional MLM under the same structural risk minimum framework through the designed experiments on 21 vector-based benchmark datasets from UCI repository. The main contributions of this paper are: (1) proposing a new matrixized learning model with a more efficient matrixization process using a feature-based fast clustering strategy; (2) combining the feature-clustering-based interpolation to the matrix-pattern-oriented classifier for the first time; (3) extending the existing MLM design techniques.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
The basic MATLAB code of FCIMLM can be freely downloaded from this website: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1ntkjBVb, please click the button with download symbol to get the wrapped .rar file.
References
An L, Bhanu B (2014) Face image super-resolution using 2D CCA. Signal Process 103:184–194
Bache K, Lichman M (2013) UCI machine learning repository. http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml. Accessed Nov 2014
Chen S, Wang Z, Tian Y (2007) Matrix-pattern-oriented Ho–Kashyap classifier with regularization learning. Pattern Recognit 40(5):1533–1543
Demšar J (2006) Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J Mach Learn Res 7:1–30
Duda R, Hart P, Stork D (1999) Pattern classification. Wiley, New York
Everson RM, Fieldsend JE (2006) Multi-class ROC analysis from a multi-objective optimisation perspective. Pattern Recognit Lett 27(8):918–927
Fernández A, Del Jesus MJ, Herrera F (2010) Multi-class imbalanced data-sets with linguistic fuzzy rule based classification systems based on pairwise learning. In: Computational intelligence for knowledge-based systems design. Springer, Berlin, pp 89–98
Ferri C, Hernández-Orallo J, Salido MA (2003) Volume under the ROC surface for multi-class problems. In: Machine learning: ECML 2003. Springer, Berlin, pp 108–120
Galar M, Fernández A, Barrenechea E, Bustince H, Herrera F (2012) A review on ensembles for the class imbalance problem: bagging-, boosting-, and hybrid-based approaches. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C 42(4):463–484
Gao Q, Hao X, Zhao Q, Shen W, Ma J (2013) Feature extraction using two-dimensional neighborhood margin and variation embedding. Comput Vis Image Underst 117(5):525–531
García-Pedrajas N, Pérez-Rodríguez J, de Haro-García A (2013) Oligois: scalable instance selection for class-imbalanced data sets. IEEE Trans Cybern 43(1):332–346
Ghanem AS, Venkatesh S, West G (2010) Multi-class pattern classification in imbalanced data. In: Proceedings of the 20th international conference on pattern recognition, pp 2881–2884
Ho Y, Kashyap RL (1965) An algorithm for linear inequalities and its applications. IEEE Trans Electron Comput EC–14(5):683–688
Hou C, Nie F, Zhang C, Yi D, Wu Y (2014) Multiple rank multi-linear SVM for matrix data classification. Pattern Recognit 47(1):454–469
Leski J (2003) Ho–Kashyap classifier with generalization control. Pattern Recognit Lett 24(14):2281–2290
Li M, Yuan B (2005) 2D-LDA: a statistical linear discriminant analysis for image matrix. Pattern Recognit Lett 26(5):527–532
Li X, Tang Y (2014) Two-dimensional nearest neighbor classification for agricultural remote sensing. Neurocomputing 142:182–189
Noushath S, Hemantha Kumar G, Shivakumara P (2006) (2D) 2LDA: an efficient approach for face recognition. Pattern Recognit 39(7):1396–1400
Pele O, Taskar B, Globerson A, Werman M (2013) The pairwise piecewise-linear embedding for efficient non-linear classification. In: Proceedings of the 30th international conference on machine learning, pp 205–213
Rodriguez A, Laio A (2014) Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks. Science 344(6191):1492–1496
Vapnik V (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Wan M, Li M, Yang G, Gai S, Jin Z (2014) Feature extraction using two-dimensional maximum embedding difference. Inf Sci 274:55–69
Wang Z, Lu MZ, Zhu YJ, Gao DQ (2014) IMAT: matrix learning machine with interpolation mapping. Electron Lett 50(24):1836–1838
Xu QS, Liang YZ (2001) Monte Carlo cross validation. Chemom Intell Labor Syst 56(1):1–11
Yan H, Lu J, Zhou X, Shang Y (2014) Multi-feature multi-manifold learning for single-sample face recognition. Neurocomputing 143:134–143
Yang J, Zhang D, Frangi AF, Yang J (2004) Two-dimensional PCA: a new approach to appearance-based face representation and recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26(1):131–137
Zhang D, Zhou ZH (2005) (2D) 2PCA: two-directional two-dimensional pca for efficient face representation and recognition. Neurocomputing 69(1):224–231
Zhou ZH, Liu XY (2010) On multi-class cost-sensitive learning. Comput Intell 26(3):232–257
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by Natural Science Foundations of China under Grant Nos. 61272198 and 21176077, Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission under Grant No. 14ZZ054, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Intelligent Information Processing of China under Grant No. IIPL-2012-003, and Provincial Key Laboratory for Computer Information Processing Technology of Soochow University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Wang, Z. & Gao, D. Matrixized Learning Machine with Feature-Clustering Interpolation. Neural Process Lett 44, 291–306 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-015-9458-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-015-9458-x