Abstract
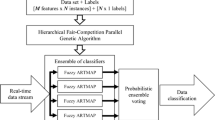
In this paper, a framework for designing optimum pattern classifiers is proposed. The fuzzy ARTMAP (FAM) is first used as a base classifier. Multiple FAM classifiers form an ensemble to improve classification accuracy. Multi-objective genetic algorithms (GAs) are then used to search for the best combinations of variables, for the FAM classifiers. Based on the population of potential solutions, another GA selects the best combination of FAM classifiers to create an ensemble. Individual decisions are combined using a probabilistic voting scheme. To increase the inter-classifier diversity, a hierarchical parallel GA variant and a negative correlation method is employed during the genetic optimization phase for the ensemble evaluation. The proposed framework is evaluated using benchmark and real-world data sets, and the results compared with literature. Results positively indicate the proposed framework is effective in undertaking data classification tasks.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Georgiopoulos M, Koufakou A, Anagnostopoulos GC, Kasparis T (2001) Overtraining in fuzzy ARTMAP: myth or reality? In: Proceedings of the 2001 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN 2001), vol 2. pp 1186–1190
Dvzeroski S, Zenko B (2004) Is combining classifiers with stacking better than selecting the best one? Mach Learn 54(3):255–273
Hu JJ, Goodman ED (2002) The hierarchical fair competition (HFC) model for parallel evolutionary algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation. IEEE, pp 49–54
Loghmanian SMR, Jamaluddin H, Ahmad R, Yusof R, Khalid M (2012) Structure optimization of neural network for dynamic system modeling using multi-objective genetic algorithm. Neural Comput Appl 21(6):1281–1295
Ahmad F, Isa NAM, Hussain Z, Sulaiman SN (2013) A genetic algorithm-based multi-objective optimization of an artificial neural network classifier for breast cancer diagnosis. Neural Comput Appl 23(5):1427–1435
Chou CW, Chien CF, Gen M (2014) A multiobjective hybrid genetic algorithm for TFT-LCD module assembly scheduling. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 11(3):692–705
Carrano EG, Soares LA, Takahashi RH, Saldanha RR, Neto OM (2006) Electric distribution network multiobjective design using a problem-specific genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 21(2):995–1005
Celli G, Ghiani E, Mocci S, Pilo F (2005) A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm for the sizing and siting of distributed generation. IEEE Trans Power Syst 20(2):750–757
Leng G, McGinnity TM, Prasad G (2006) Design for self-organizing fuzzy neural networks based on genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 14(6):755–766
Ding S, Zhang Y, Chen J, Jia W (2013) Research on using genetic algorithms to optimize Elman neural networks. Neural Comput Appl 23(2):293–297
Nguyen HD, Yoshihara I, Yamamori K, Yasunaga M (2007) Implementation of an effective hybrid GA for large-scale traveling salesman problems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B 37(1):92–99
Dehuri S, Cho SB (2010) A hybrid genetic based functional link artificial neural network with a statistical comparison of classifiers over multiple datasets. Neural Comput Appl 19(2):317–328
Tsai JT, Liu TK, Chou JH (2004) Hybrid Taguchi-genetic algorithm for global numerical optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 8(4):365–377
Tu Z, Lu Y (2004) A robust stochastic genetic algorithm (StGA) for global numerical optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 8(5):456–470
Carpenter GA, Grossberg S, Reynolds J (1991) ARTMAP: a self-organizing neural network architecture for fast supervised learning and pattern recognition. In: Proceedings of the 1991 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN 1991) vol 1. pp 863–868
Carpenter GA, Grossberg S, Marzukon N, Reynolds JH, Rosen DB (1992) Fuzzy ARTMAP: a neural network architecture for incremental supervised learning of analog multidimensional maps. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 3(5):698–713
Williamson JR (1996) Gaussian ARTMAP: a neural network for fast incremental learning of noisy multidimensional maps. Neural Netw 9(5):881–897
Carpenter GA, Milenova BL, Noeske BW (1998) Distributed ARTMAP: a neural network for fast distributed supervised learning. Neural Netw 11(5):793–813
Gómez-Sánchez E, Dimitriadis YA, Cano-Izquierdo JM, López-Coronado J (2002) muARTMAP: use of mutual information for category reduction in Fuzzy ARTMAP. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 13(1):58–69
Zhang Y, Ji H, Zhang W (2014) TPPFAM: use of threshold and posterior probability for category reduction in fuzzy ARTMAP. Neurocomputing 124:63–71
Carpenter GA, Gaddam SC (2010) Biased ART: a neural architecture that shifts attention toward previously disregarded features following an incorrect prediction. Neural Netw 23(3):435–451
Dagher I, Georgiopoulos M, Heileman GL, Bebis G (1999) An ordering algorithm for pattern presentation in fuzzy ARTMAP that tends to improve generalization performance. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(4):768–778
Palaniappan R, Eswaran C (2009) Using genetic algorithm to select the presentation order of training patterns that improves simplified fuzzy ARTMAP classification performance. Appl Soft Comput 9(1):100–106
Granger E, Henniges P, Oliveira L, Sabourin R (2006) Particle swarm optimization of fuzzy ARTMAP parameters. In: Proceedings of the 2006 international joint conference on neural networks. pp 2060–2067
Mohamed MA, Hegazy AEF, Badr AA (2011) Evolutionary fuzzy ARTMAP approach for breast cancer diagnosis. Int J Comput Sci Netw Secur 11(4):77–84
Hansen LK, Salamon P (1990) Neural network ensembles. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel 12(10):993–1001
Loo CK, Cheong SF, Seldon M, Mand A, Muthu K, Liew WS, Lim E (2012) Genetic-optimized classifier ensemble for cortisol salivary measurement mapping to electrocardiogram features for stress evaluation. In: PRICAI 2012: trends in artificial intelligence. pp 274–284
Lee H, Kim E, Pedrycz W (2012) A new selective neural network ensemble with negative correlation. Appl Intell 37(4):488–498
Liu Y, Yao X, Higuchi T (2000) Evolutionary ensembles with negative correlation learning. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 4(4):380–387
Lin X, Yacoub S, Burns J, Simske S (2003) Performance analysis of pattern classifier combination by plurality voting. Pattern Recogn Lett 24(12):1959–1969
Loo CK, Rao MVC (2005) Accurate and reliable diagnosis and classification using probabilistic ensemble simplified Fuzzy ARTMAP. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 17(11):1589–1593
Frank A, Asuncion A (2011) UCI machine learning repository. http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml. Accessed March 2012
Zhang Y, Burer S, Street WN (2006) Ensemble pruning via semi-definite programming. J Mach Learn Res 7:1315–1338
Ordóñez FJ, Ledezma A, Sanchis A (2008) Genetic approach for optimizing ensembles of classifiers. In: FLAIRS conference. pp 89–94
Chen H, Yao X (2010) Multiobjective neural network ensembles based on regularized negative correlation learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 22(12):1738–1751
Verma B, Rahman A (2012) Cluster-oriented ensemble classifier: impact of multicluster characterization on ensemble classifier learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 24(4):605–618
Woloszynski T, Kurzynski M, Podsiadlo P, Stachowiak GW (2012) A measure of competence based on random classification for dynamic ensemble selection. Inf Fusion 13(3):207–213
Wei H, Lin X, Xu X, Li L, Zhang W, Wang X (2014) A novel ensemble classifier based on multiple diverse classification methods. 2014 11th international conference on fuzzy systems and knowledge discovery. pp 301–305
Xue X, Yao M, Wu Z, Yang J (2014) Genetic ensemble of extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 129:175–184
Sachnev V, Ramasamy S, Sundaram S, Kim HJ, Hwang HJ (2015) A cognitive ensemble of extreme learning machines for steganalysis based on risk-sensitive hinge loss function. Cogn Comput 7(1):103–110
Georgiopoulos M, Fernlund H, Bebis G, Heileman GL (1996) Order of search in fuzzy ART and fuzzy ARTMAP: effect of the choice parameter. Neural Netw 9(9):1541–1559
Carpenter GA, Gjaja MN (1994) Fuzzy ART choice functions. In: Proceedings of the 1993 world congress on neural networks (WCNN 1994), vol 4. pp 133–142
Anagnostopoulos GC, Bharadwaj M, Georgiopoulos M, Verzi SJ, Heileman GL (2003) Exemplar-based pattern recognition via semi-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 2003 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN 2003), vol 4. pp 2782–2787
Kirschbaum C, Pirke K-M, Hellhammer DH (1993) The trier social stress test-a tool for investigating psychobiological stress responses in a laboratory setting. Neuropsychobiology 28:76–81
Malik M, Bigger JT, Camm AJ, Kleiger RE, Malliani A, Moss AJ, Schwartz PJ (1996) Heart rate variability standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Eur Heart J 17(3):354–381
Zhong Y, Wang H, Ju KH, Jan K-M, Chon KH (2004) Nonlinear analysis of the separate contributions of autonomic nervous systems to heart rate variability using principal dynamic modes. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51(2):255–262
Choi J, Gutierrez-Osuna R (2009) Using heart rate monitors to detect mental stress. In: 6th international workshop on wearable and implantable body sensor networks. pp 219–223
Engert V, Vogel S, Efanov SI, Duchesne A, Corbo V, Ali N, Pruessner JC (2011) Investigation into the cross-correlation of salivary cortisol and alpha-amylase responses to psychological stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36(9):1294–1302
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by University of Malaya High Impact Research Grant UM.C/625/1/HIR/MOHE /FCSIT/10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liew, W.S., Seera, M. & Loo, C.K. Hierarchical Parallel Genetic Optimization Fuzzy ARTMAP Ensemble. Neural Process Lett 44, 451–470 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-015-9467-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-015-9467-9