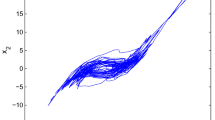
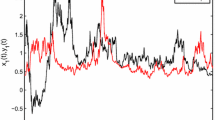
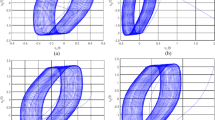
Abstract
This paper is devoted to study the finite time lag synchronization problem of memristive mixed delays neural networks with switching jumps and parameter mismatch. The main objective of this paper is to design simple linear feedback control such as the drive response systems can realize synchronization in the finite time. Several theoretical aspects are addressed, mean Filippov differential inclusion and set-valued map. Based on the Gronwall’s inequality and properties of differential operation, a new finite time lag synchronization scheme is proposed to guarantee that coupled memristive mixed delays neural networks are in a state of lag synchronization in finite time. In addition, finite lag synchronization criteria of two identical memristive mixed delays neural networks are also considered. Finally, numerical examples are presented to illustrate the effectiveness of the our proposed theorems.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chua LO (1971) Memristor—the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans Circuit Theory 18:507–519
Chua LO, Kang SM (1976) Memristive devices and systems. Proc IEEE 64(2):209–223
Strukov DB, Snider GS, Stewart DR, Williams RS (2008) The missing memristor found. Nature 453:80–83
Tour JM, He T (2008) Electronics: the fourth element. Nature 453:42–43
Sharifi MJ, Banadaki YM (2010) General SPICE models for memristor and application to circuit simulation of memristor-based synapses and memory cells. J Circuits Syst Comput 19:407–424
Itoh M, Chua LO (2008) Memristor oscillators. Int J Bifurc Chaos 18(11):3183–3206
Nie X, Zheng WX, Cao J (2015) Multistability of memristive Cohen–Grossberg neural networks with non-monotonic piecewise linear activation functions and time-varying delays. Neural Netw 71:27–36
Itoh M, Chua LO (2009) Memristor cellular automata and memristor discrete-time cellular neural networks. Int J Bifurc Chaos 19(11):3605–3656
Wang X, Chen Y, Xi H, Li H, Dimitrov D (2009) Spintronic memristor through spin-torque-induced magnetization motion. IEEE Electron Device Lett 30(3):294–297
Pershin YV, Ventra MD (2010) Experimental demonstration of associative menmory with memristive neural networks. Neural Netw 23:881–886
Jo SH, Chang T, Ebong I, Bhadviya BB (2010) Nanocsale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett 10:1297–1301
Hu J, Wang J (2010) Global uniform asymptotic stability of memristor-based recurrent neural networks with time delays. Int Joint Conf Neural Netw 1–8. doi:10.1109/IJCNN.2010.5596359
Kim H, Sah MP, Yang C, Roska T, Chua LO (2012) Memristor bridge synapses. Proc IEEE 100(6):2061–2070
Mu C, Ni Z, Sun C et al (2017) Air-breathing hypersonic vehicle tracking control based on adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(3):584–598
Ding W, Chaoxu M (2017) Developing nonlinear adaptive optimal regulators through an improved neural learning mechanism. Sci China Inf Sci 60(5):058201
Tang Y, Xing X, Karimi HR et al (2016) Tracking control of networked multi-agent systems under new characterizations of impulses and its applications in robotic systems. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(2):1299–1307
Tang Y, Gao H, Zhang W et al (2015) Leader-following consensus of a class of stochastic delayed multi-agent systems with partial mixed impulses. Automatica 53:346–354
Wu X, Tang Y, Zhang W (2016) Stability analysis of stochastic delayed systems with an application to multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 61(12):4143–4149
Yang X, Ho DW (2016) Synchronization of delayed memristive neural networks: robust analysis approach. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(12):3377–3387
Li N, Cao JD (2016) Lag synchronization of memristor-based coupled neural networks via-measure. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(3):686–697
Ding SB, Wang ZS (2016) Lag quasi-synchronization for memristive neural networks with switching jumps mismatch. Neural Comput Appl 1–12. doi:10.1007/s00521-016-2291-y
Wang X, Li C, Huang T, Duan S (2014) Global exponential stability of a class of memristive neural networks with time-varying delays. Neural Comput Appl 24(7–8):1707–1715
Yang X, Cao J, Liang J (2016) Exponential synchronization of memristive neural networks with delays: interval matrix method. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 1–11. doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2561298
Abdurahman A, Jiang H, Teng Z (2015) Finite-time synchronization for memristor-based neural networks with time-varying delays. Neural Netw 69:20–28
Bao HB, Cao JD (2016) Finite-time generalized synchronization of nonidentical delayed chaotic systems. Nonlinear Anal 21(3):306–324
Liao CW, Lu CY (2011) Design of delay-dependent state estimator for discrete-time recurrent neural networks with interval discrete and infinite-distributed time-varying delays. Cogn Neurodyn 5(2):133–143
Liu Y, Zhang D, Lu J et al (2016) Global-stability criteria for quaternion-valued neural networks with unbounded time-varying delays. Inf Sci 360:273–288
Liu X, Ho DW, Yu WW, Cao JD (2014) A new switching design to finite-time stabilization of nonlinear systems with applications to neural networks. Neural Netw 57:94–102
Mu C, Sun C (2015) A new finite time convergence condition for super twisting observer based on Lyapunov analysis. Asian J Control 17(3):1050–1060
Mu C, Xu W, Sun C (2016) On switching manifold design for terminal sliding mode control. J Franklin Inst 353(7):1553–1572
Liu Y, Zhang D, Lu J (2017) Global exponential stability for quaternion-valued recurrent neural networks with time-varying delays. Nonlinear Dyn 87(1):553–565
Wen S, Zeng Z, Huang T et al (2015) Lag synchronization of switched neural networks via neural activation function and applications in image encryption. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26(7):1493–1502
Yang X, Cao J, Qiu J (2015) pth moment exponential stochastic synchronization of coupled memristor-based neural networks with mixed delays via delayed impulsive control. Neural Netw 65:80–91
Yang XS, Cao DJ, Yu WW (2014) Exponential synchronization of memristive Cohen–Grossberg neural networks with mixed delays. Cogn Neurodyn 8(3):239–249
Mu C, Sun C, Song A et al (2016) Iterative GDHP-based approximate optimal tracking control for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing 214:775–784
Aubin JP, Frankowska H (2009) Set-valued analysis. Springer, New York
Forti M, Nistri P, Quincampoix M (2004) Generalized neural network for nonsmooth nonlinear programming problems. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 51(9):1741–1754
Forti M, Nistri P, Papini D (2005) Global exponential stability and global convergence in finite time of delayed neural networks with infinite gain. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 16(6):1449–1463
Chua L (2011) Resistance switching memories are memristors. Appl Phys A 102(4):765–783
Chen J, Zeng Z, Jiang P (2014b) Global Mittag–Leffler stability and synchronization of memristor-based fractional-order neural networks. Neural Netw 51:1–8
Wang LM, Shen Y, Yin Q, Zhang GD (2015) Adaptive synchronization of memristor-based neural networks with time-varying delays. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26(9):2033–2042
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China under Grant No. BK20161126 and the Graduate Innovation Project of Jiangsu Province under Grant No. KYLX16\(_{-}\)0778.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Yang, Y., Wang, F. et al. Finite-Time Lag Synchronization for Memristive Mixed Delays Neural Networks with Parameter Mismatch. Neural Process Lett 47, 365–389 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-017-9653-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-017-9653-z