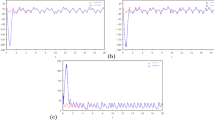
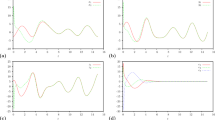
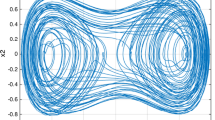
Abstract
A method using sliding mode control (SMC) and wavelet neural networks (WNN) is proposed, investigated and exploited for synchronizing master and slave chaotic systems with uncertain model and unknown interference. In this paper, integral sliding surface and applying WNN for approximating uncertain model and unknown interference are further developed for designing adaptive sliding mode controller. Mexican hat wavelet function is used as activation function in WNN. The adaptive laws of network parameters are derived in the sense of Lyapunov stability analysis so that the tracking errors and convergence of the weights can be guaranteed. The error of synchronization of master–slave chaotic systems can be reached desired level in limited time by using Li function in SMC. Illustrative examples are provided and analyzed to substantiate the efficacy of proposed method for solving the problem of synchronizing master and slave chaotic systems.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Ott E, Grebogi C, Yorke JA (1990) Controlling chaos. Phys Rev Lett 64(11):1196–1199
Chen HK (2005) Global chaos synchronization of new chaotic systems via nonlinear control. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 23(4):1245–1251
Cao J, Ho DWC, Yang Y (2009) Projective synchronization of a class of delayed chaotic systems via impulsive control. Phys Lett A 373(35):3128–3133
Yassen MT (2006) Chaos control of chaotic dynamical systems using backstepping design. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 27(2):537–548
Aghababa MP, Feizi H (2012) Design of a sliding mode controller for synchronizing chaotic systems with parameter and model uncertainties and external disturbances. Trans Inst Meas Control 34(8):990–997
Ouannas A, Odibat Z, Shawagfeh N et al (2017) Universal chaos synchronization control laws for general quadratic discrete systems. Appl Math Model 45:636–641
Yih-Yuh C (1996) Randomly synchronizing chaotic systems: condensed matter and statistical physics. Progress Theoret Phys 96(4):683–692
Khadra A, Liu XZ, Shen X (2005) Impulsively synchronizing chaotic systems with delay and applications to secure communication. Automatica 41(9):1491–1502
Naderi B, Kheiri H, Heydari A et al (2016) Optimal synchronization of complex chaotic t-systems and its application in secure communication. J Control Autom Electr Syst 27(4):379–390
Carroll TL, Pecora LM (2002) Synchronizing chaotic circuits. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst 38(4):453–456
Junwei S, Xingtong Z, Jie F et al (2018) Autonomous memristor chaotic systems of infinite chaotic attractors and circuitry realization. Nonlinear Dyn 94(4):2879–2887
Li WL (2008) On control and synchronization in chaotic and hyperchaotic systems via linear feedback control. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 13(7):1246–1255
Haeri M, Emadzadeh A (2007) Synchronizing different chaotic systems using active sliding mode control. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 31(1):119–129
Tavazoei MS, Haeri M (2007) Determination of active sliding mode controller parameters in synchronizing different chaotic systems. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 32(2):583–591
Fuh CC (2009) Optimal control of chaotic systems with input saturation using an input-state linearization scheme. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 14(8):3424–3431
Tan X, Zhang J, Yang Y (2003) Synchronizing chaotic systems using backstepping design. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 16(1):37–45
Li GH, Zhou SP, Yang K (2006) Generalized projective synchronization between two different chaotic systems using active backstepping control. Phys Lett A 355(4):326–330
Chen HH, Sheu GJ, Lin YL et al (2009) Chaos synchronization between two different chaotic systems via nonlinear feedback control. Nonlinear Anal Theory Methods Appl 70(12):4393–4401
Mobayen S (2018) Chaos synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems using composite nonlinear feedback based integral sliding mode control. ISA Trans 77:100–111
Ji DH, Jeong SC, Ju HP et al (2012) Robust adaptive backstepping synchronization for a class of uncertain chaotic systems using fuzzy disturbance observer. Nonlinear Dyn 69(3):1125–1136
Lin D, Wang X, Nian F et al (2010) Dynamic fuzzy neural networks modeling and adaptive backstepping tracking control of uncertain chaotic systems. Neurocomputing 73(16–18):2873–2881
Barker AE (2012) Adaptive modified function projective synchronization of general uncertain chaotic complex systems. Phys Scr 85(3):438–445
Mobayen S, Tchier F (2017) Synchronization of a class of uncertain chaotic systems with lipschitz nonlinearities using state-feedback control design: a matrix inequality approach. Asian J Control 20(1):71–85
Mobayen S (2018) Design of novel adaptive sliding mode controller for perturbed Chameleon hidden chaotic flow. Nonlinear Dyn 92:1539–1553
Mofid Omid, Mobayen Saleh (2018) Adaptive synchronization of fractional-order quadratic chaotic flows with nonhyperbolic equilibrium. J Vib Control 24(21):4971–4987
Saleh M, Jun M (2018) Robust finite-time composite nonlinear feedback control for synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems with nonlinearity and time-delay. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 114:46–54
Sun J, Wu Y, Cui G et al (2017) Finite-time real combination synchronization of three complex-variable chaotic systems with unknown parameters via sliding mode control. Nonlinear Dyn 88(3):1677–1690
Sun J, Wang Y, Wang Y et al (2016) Finite-time synchronization between two complex-variable chaotic systems with unknown parameters via nonsingular terminal sliding mode control. Nonlinear Dyn 85(2):1105–1117
Yan JJ, Liao TL (2017) Discrete sliding mode control for hybrid synchronization of continuous Lorenz systems with matched/unmatched disturbances. Trans Inst Meas Control 40(5):1417–1424
Fu YY, Wu CJ, Ko CN et al (2011) Radial basis function networks with hybrid learning for system identification with outliers. Appl Soft Comput 11(3):3083–3092
Fernández-Navarro F, Hervás-Martínez C, Sanchez-Monedero J et al (2011) MELM-GRBF: a modified version of the extreme learning machine for generalized radial basis function neural networks. Neurocomputing 74(16):2502–2510
Zhang Y, Yang Y, Tan N et al (2011) Zhang neural network solving for time-varying full-rank matrix Moore-Penrose inverse. Computing 92(2):97–121
Liao B, Zhang Y (2014) From different ZFs to different ZNN models accelerated via Li activation functions to finite-time convergence for time-varying matrix pseudoinversion. Neurocomputing 133(8):512–522
Shuai L, Li Y, Zheng W (2013) A class of finite-time dual neural networks for solving quadratic programming problems and its k k mathContainer Loading Mathjax -winners-take-all application. Neural Netw 39(39):27–39
Wang H, Han ZZ, Xie QY et al (2009) Finite-time chaos synchronization of unified chaotic system with uncertain parameters. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 14(5):2239–2247
Cordova J, Yu W (2012) Two types of haar wavelet neural networks for nonlinear system identification. Neural Process Lett 35(3):283–300
Pindoriya NM, Singh SN, Singh SK (2008) An adaptive wavelet neural network-based energy price forecasting in electricity markets. IEEE Trans Power Syst 23(3):1423–1432
Zhang Q (1997) Using wavelet network in nonparametric estimation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 8(2):227
Pai Ming-Chang (2016) RBF-based discrete sliding mode control for robust tracking of uncertain time-delay systems with input nonlinearity. Complexity 21(6):194–201
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank anonymous peer reviewer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, G., Yang, Z. & Peng, K. Synchronizing Chaotic Systems with Uncertain Model and Unknown Interference Using Sliding Mode Control and Wavelet Neural Networks. Neural Process Lett 50, 2547–2565 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-019-10034-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-019-10034-8