Abstract
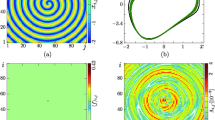
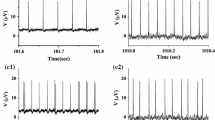
This paper, a novel 3D generalized Hopfield neural network is proposed and investigated in order to generate and highlight some unknown behaviors related to such type of neural network. This generalized model is constructed by exploiting the effect of an external stimulus on the dynamics of a simplest 3D autonomous Hopfield neural network reported to date. The stability of the model around its ac-equilibrium point is studied. We note that the model has three types of stability depending on the value of the external stimulus. The stable node-focus, the unstable saddle focus, and the stable node characterize the stability of the equilibrium point of the model. Traditional nonlinear analyses tools are used to highlight and support several complex phenomena such as remerging Feigenbaum trees, the coexistence of up to two, four and six disconnected stable states when the amplitude of the external stimulus is set to zero. Furthermore, for some values of the frequency and amplitudes of the external stimulus, bursting oscillations occur. This latter behavior is characterized by the fact that oscillations switch between quiescent states and spiking states, repetitively. The transformed phase portraits are used to support the bursting mode of oscillations found. Finally, PSpice simulations enable to support the results of the theoretical studies.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Hopfield JJ (1984) Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of 2-state neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81(10):3088–3092
Laskowski Ł (2013) A novel hybrid-maximum neural network in stereo-matching process. Neural Comput Appl 23(7):2435–2450
Pajeras G, Cruz JM, Aranda J (1998) Relaxation by Hopfield network in stereo image matching. Pattern Recognit 31(5):561–574
Brosch T, Neumann H (2014) Computing with a canonical neural circuits model with pool normalization and modulating feedback. Neural Comput 26(12):2735–2789
Wen S, Zeng Z, Huang T, Meng Q, Yao W (2015) Lag synchronization of switched neural networks via neural activation function and applications in image encryption. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26(7):1493–1502
Yang J, Wang LD, Wang Y, Guo TT (2017) A novel memristive Hopfield neural network with application in associative memory. Neurocomputing 227:142–148
Chen D, Li S, Wu Q (2018) Rejecting chaotic disturbances using a super-exponential-zeroing neurodynamic approach for synchronization of chaotic sensor systems. Sensors (Basel) 19(1):E74. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010074
Chen D, Li S, Wu Q, Luo X (2019) New disturbance rejection constraint for redundant robot manipulators: an optimization perspective. IEEE Trans Ind Inform. https://doi.org/10.1109/tii.2019.2930685
Chen D, Li S, Lin F, Wu Q (2019) New super-twisting zeroing neural-dynamics model for tracking control of parallel robots: a finite-time and robust solution. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcyb.2019.2930662
Njitacke ZT, Kengne J, Fotsin HB (2018) A plethora of behaviors in a memristor based Hopfield neural networks (HNNs). Int J Dyn Control. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-018-0435-x
Bao B, Qian H, Xu Q, Chen M, Wang J, Yu Y (2017) Coexisting behaviors of asymmetric attractors in hyperbolic-type memristor based hopfield neural network. Front Comput Neurosci 11(81):1–14
Njitacke ZT, Kengne J (2018) Complex dynamics of a 4D Hopfield neural networks (HNNs) with a nonlinear synaptic weight: coexistence of multiple attractors and remerging Feigenbaum trees. Int J Electron Commun (AEÜ) 93:242–252
Danca MF, Kuznets L (2017) Hidden chaotic sets in a Hopfield neural system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 103:144–150
Bao B, Qian H, Wang J, Xu Q, Chen M, Wu H, Yu Y (2017) Numerical analyses and experimental validations of coexisting multiple attractors in Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3808-3
Njitacke ZT, Kengne J (2019) Nonlinear dynamics of three-neurons-based hopfield neural networks (HNNs): remerging Feigenbaum trees, coexisting bifurcations and multiple attractors. J Circuits Syst Comput 28(7):1950121
Xu Q, Song Z, Bao H, Chen M, Bao B (2018) Two-neuron-based non-autonomous memristive Hopfield neural network: numerical analyses and hardware experiments. Int J Electron Commun (AEÜ) 96:66–74
Njitacke ZT, Kengne J, Kamdjeu Kengne L (2017) Antimonotonicity, chaos and multiple coexisting attractors in a simple hybrid diode-based jerk circuit. Chaos Solitons Fractals 105:77–91
Njitacke ZT, Kengne J, Wafo Tapche R, Pelap FB (2018) Uncertain destination dynamics of a novel memristive 4D autonomous system Chaos. Solitons Fractals 107:177–185
Njitacke ZT, Kengne J, Fotsin HB, Negou AN, Tchiotsop D (2016) Coexistence of multiple attractors and crisis route to chaos in a novel memristive diode bidge-based Jerk circuit. Chaos Solitons Fractals 91:180–197
Kengne J, Njitacke ZT, Negou AN, Fouodji MT, Fotsin HB (2015) Coexistence of multiple attractors and crisis route to chaos in a novel chaotic jerk circuit. Int J Bifurc Chaos 25(4):1550052
Kengne J, Njitacke ZT, Kamdoum VT, Negou AN (2015) Periodicity, chaos, and multiple attractors in a memristor-based Shinriki’s circuit. Chaos Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 25:103126
Xu Q, Zhang QL, Qian Hui WuHG, Bao BC (2018) Crisis induced coexisting multiple attractors in a second-order non-autonomous memristive diode bridge-based circuit. Int J Circ Theor. https://doi.org/10.1002/cta.2492
Wolf A, Swift JB, Swinney HL, Vastano JA (1985) Determining lyapunov exponents from a time series. Phys D Nonlinear Phenom 16(3):285–317
Kengne J, Jafari S, Njitacke ZT, Yousefi Azar Khanian M, Cheukem A (2017) Dynamic analysis and electronic circuit implementation of a novel 3D autonomous system without linear terms. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2017.04.017
Dawson SP, Grebogi C, Yorke JA, Kan I, Koçak H (1992) Antimonotonicity: inevitable reversals of period-doubling cascades. Phys Lett A 162:249–254
Bier M, Boutis TC (1984) Remerging Feigenbaum trees in dynamical systems. Phys Lett A 104:239–244
Dawson SP (1993) Geometric mechanism for antimonotonicity in scalar maps with two critical points. Phys Rev E 48:1676–1680
Xu Y, Jia Y, Ge MY, Lu LL, Yang LJ, Zhan X (2018) Effects of ion channel blocks on electrical activity of stochastic Hodgkin–Huxley neural network under electromagnetic induction. Neurocomputing 283:196–204
Gu H (2013) Biological experimental observations of an unnoticed chaos as simulated by the Hindmarsh–Rose model. PLoS ONE 8(12):e81759
Gu HG, Pan BB, Chen GR, Duan LX (2014) Biological experimental demonstration of bifurcations from bursting to spiking predicted by theoretical models. Nonlinear Dyn 78(1):391–407
Wu XY, Ma J, Yuan LH, Liu Y (2014) Simulating electric activities of neurons by using PSPICE. Nonlinear Dyn 75(1–2):113–126
Mineeja KK, Ignatius RP (2018) Spatiotemporal activities of a pulse-coupled biological neural network. Nonlinear Dyn 92(4):1881–1897
Izhikevich EM (2000) Neural excitability, spiking and bursting. Int J Bifurc Chaos 10(6):1171–1266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabekoueng Njitacke, Z., Laura Matze, C., Fouodji Tsotsop, M. et al. Remerging Feigenbaum Trees, Coexisting Behaviors and Bursting Oscillations in a Novel 3D Generalized Hopfield Neural Network. Neural Process Lett 52, 267–289 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-020-10264-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-020-10264-1