Abstract
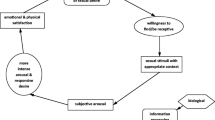
The incidence of dyspareunia at 6 months post-partum is very high. However, effective treatments are limited. Pelvic floor myofascial therapy is a useful method, we investigated the efficacy of it. 72 post-partum women with dyspareunia between 6 weeks and 3 months after delivering from July 2018 to June 2020 were researched. 30 received no treatment and 42 underwent 15 min, twice a week, totally 3 weeks. The scores of FSFI and VAS pain were completed at enrollment and at 6 months. In the observation group, the VAS score had no significant difference at 6 months, but there was a higher FSFI score at 6 months (17.0, IQR 15.3–18.0 vs. 18.4, IQR 15.8–19.9, p = 0.06). But for the treatment group, at the time of 6 moths, VAS scores were significantly lower and FSFI scores were significantly higher (2.0, IQR 1.5–2.8 vs. 7.3, IQR 6.0–8.4, p < .0001 and 20.4, IQR 18.1–21.8 vs. 18.4, IQR 15.8–19.9, p < .01). So pelvic floor myofascisl improves pelvic floor muscle function, exercise appears to have positive effects on female sexual function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. American Psychiatric Association, Washington DC
Hill DA, Taylor CA (2021) Dyspareunia in women. Am Fam Physician 103(10):597–604
McDonald EA, Gartland D, Small R et al (2015) Dyspareunia and childbirth: a prospective cohort study. BJOG 122:672–679. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.13263
Ghaderi F, Bastani P, Hajebrahimi S et al (2019) Pelvic floor rehabilitation in the treatment of women with dyspareunia:a randomized controlled clinical trial. Int Urogynecol J
Zarski AC, Berking M et al (2017) Internet-based guided self-help for vaginal penetration difficulties: results of a randomized controlled pilot trial. J Sex Med 14(2):238–254
Pacik PT (2014) Understanding and treating vaginismus: a multimodal approach. Int Urogynecol J 25:1613–1620
Berghmans B (2018) Physiotherapy for pelvic pain and female sexual dysfunction: an untapped resource. Int Urogynecol J 29(5):631–638
Ensor AW, Newton RA (2014) The role of biofeedback and soft tissue mobilization in the treatment of dyspareunia: a systematic review. J Women Health Phys Ther 38(2):74–80
Morin M, Carroll MS, Bergeron S (2017) Systematic review of the effectiveness of physicaltherapy modalities in women with provoked vestibulodynia. Sex Med Rev 5(3):295–322
Song SH, Jeon H, Kim SW et al (2008) The prevalence and risk factors of female sexual dysfunction in young Korean women: an internet-based survey. J Sex Med 5(7):1694–1701
Parish WL, Laumann EO, Pan S et al (2007) Sexual dysfunctions in urban China: a population-based national survey of men and women. J Sex Med 4:1559–1574
Lou WJ, Chen B, Zhu L et al (2017) Prevalence and factors associated with female sexual dysfunctionin Beijing, China. Chin Med J (Engl) 130(12):1389–1394
Polland AR, Davis M, Zeymo A, Iglesia CB (2019) Association between comorbidities and female sexual dysfunction: findings from the third National Survey of sexual attitudes and lifestyles(Natsal-3). Int Urogynecol J 30(3):377–383
Brin MF, Vapanek JM (1997) Treatment of vaginismus with botulinum toxin injections. Lancet 349(947):252–253
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by Guangzhou combines traditional Chinese medicine with western medicine Science and technology Project Fund 20162A011013
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, F., Liu, H., Langchi, H. et al. Pelive Floor Myofascisl Therapy is Associated with Improved VAS Pain Scores and FSFI Scores in Women with Dyspareunia 6 Months Post-partum. Neural Process Lett 55, 259–263 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10609-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10609-4