Abstract
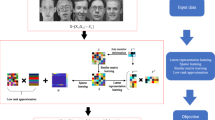
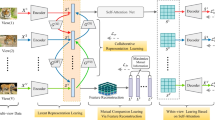
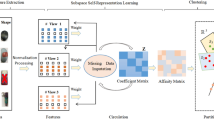
Multi-view clustering has attractive intensive attention and proved to be more effective than single-view clustering. The mining and effective utilization of information complementarity is core of multi-view clustering. In this paper, we propose a novel Auto-Weighted Graph Regularization and Residual Compensation for Multi-view Subspace Clustering (ARMSC) method, which adopts residual representation information to compensate the globally low rank consensus representation. The auto-weighted multi-view graph regularization term is constructed to preserve the local manifold structure of multiple features, which can automatically adjust the weights and the learned weights are adopt to measure the importance of each view’s residual representation for final representation. Specifically, we formulate the graph regularized consistent representation using nuclear norm and a set of group effect residual compensation using Frobenius norm. Finally, we introduce a convex relaxation and alternating direction method to optimize the problem. Comprehensive and ablation experiments on seven real-world data sets illustrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed ARMSC over several state-of-the-art multi-view clustering approaches.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao S, Tron R, Vidal R, Ma Y (2010) Motion segmentation in the presence of outlying, incomplete, or corrupted trajectories. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(10):1832–1845. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2009.191
Chen X, Wang Q, Zhuang S (2021) Ensemble dimension reduction based on spectral disturbance for subspace clustering. Knowl-Based Syst 227:107182
Abavisani M, Patel VM (2018) Multimodal sparse and low-rank subspace clustering. Inf Fus 39:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2017.05.002
Tu B, Yang X, Li N, Zhou C, He D (2020) Hyperspectral anomaly detection via density peak clustering. Pattern Recogn Lett 129:144–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2019.11.022
Chao G, Sun S, Bi J (2021) A survey on multi-view clustering. IEEE Trans Artif Intell 2:146–168. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAI.2021.3065894
Elhamifar E, Vidal R (2012) Sparse subspace clustering: algorithm, theory, and applications. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(11):2765–2781. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2013.57
Liu G, Lin Z, Yan S, Sun J, Yu Y, Ma Y (2013) Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):171–184. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.88
Lu CY, Min H, Zhao ZQ, Zhu L, Huang DS, Yan S (2014) Robust and efficient subspace segmentation via least squares regression. Comput Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33786-4_26
Chao G, Sun J, Lu J, Wang A-L, Langleben DD, Li C-S, Bi J (2019) Multi-view cluster analysis with incomplete data to understand treatment effects. Inf Sci 494:278–293
Yu H, Zhang T, Chen J, Guo C, Lian Y (2018) Web items recommendation based on multi-view clustering. In: 2018 IEEE 42nd annual computer software and applications conference (COMPSAC), vol 1. IEEE, pp 420–425
Xia, R., Pan, Y., Du, L., Yin, J.: Robust multi-view spectral clustering via low-rank and sparse decomposition. In: Proceedings of the national conference on artificial intelligence, pp 2149–2155 (2014)
Li S, Shao M, Fu Y (2018) Multi-view low-rank analysis with applications to outlier detection. ACM Trans Knowl Discov Data 12(3):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1145/3168363
Brbić M, Kopriva I (2017) Multi-view low-rank sparse subspace clustering. Pattern Recogn 73:247–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2017.08.024
Wang X, Guo X, Lei Z, Zhang C, Li S (2017) Exclusivity-consistency regularized multi-view subspace clustering, pp 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.8
Luo S, Zhang C, Zhang W (2018) Consistent and specific multi-view subspace clustering. In: 32nd AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 3730–3737 (2018)
Nie F, Cai G, Li X (2017) Multi-view clustering and semi-supervised classification with adaptive neighbours. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 2408–2414 (2017)
Lin, Z., Liu, R., Su, Z.: Linearized alternating direction method with adaptive penalty for low-rank representation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1109.0367 (2011)
Chaudhuri K, Kakade S, Livescu K, Sridharan K (2009) Multi-view clustering via canonical correlation analysis. In: Proceedings of the 26th annual international conference on machine learning, pp 129–136. https://doi.org/10.1145/1553374.1553391
Liang Y, Huang D, Wang C-D (2019) Consistency meets inconsistency: a unified graph learning framework for multi-view clustering. In: 2019 IEEE international conference on data mining (ICDM). IEEE, pp 1204–1209
Nie F, Li J, Li X (2016) Parameter-free auto-weighted multiple graph learning: a framework for multiview clustering and semi-supervised classification. In: Proceedings of the 25h international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1881–1887
Nie F, Li J, Li X (2017) Self-weighted multiview clustering with multiple graphs. In: 16th international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 2564–2570. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2017/357
Nie F, Wang X, Jordan M, Huang H (2016) The constrained Laplacian rank algorithm for graph-based clustering. In: The 30th AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1969–1976. https://doi.org/10.5555/3016100.3016174
Hao W, Yan Y, Bing L, Hamido F (2019) A study of graph-based system for multi-view clustering. Knowl-Based Syst 163:1009–1019
Zheng Q, Zhu J, Li Z, Pang S, Wang L, Jun Y (2019) Feature concatenation multi-view subspace clustering. Knowl-Based Syst 379:89–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.074
Xia R, Pan Y, Du L, Yin J (2014) Robust multi-view spectral clustering via low-rank and sparse decomposition. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 28
Zhang C, Fu H, Hu Q, Cao X, Yuan X, Tao D, Dong X (2018) Generalized latent multi-view subspace clustering. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42:86–99
Zhang C, Hu Q, Fu H, Zhu P, Cao X (2017) Latent multi-view subspace clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4279–4287
Chen Y, Wang S, Zheng F, Cen Y (2020) Graph-regularized least squares regression for multi-view subspace clustering. Knowl-Based Syst 194:105482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105482
Zhang G-Y, Chen X-W, Zhou Y-R, Wang C-D, Huang D (2021) Consistency-and inconsistency-aware multi-view subspace clustering. In: International conference on database systems for advanced applications. Springer, pp 291–306
Ji P, Zhang T, Li H, Salzmann M, Reid I (2017) Deep subspace clustering network. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 24–33
Zhu W, Peng B (2020) Sparse and low-rank regularized deep subspace clustering. Knowl-Based Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106199
Abavisani M, Patel VM (2018) Deep multimodal subspace clustering networks. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 12(6):1601–1614
Cai D, Chen X (2014) Large scale spectral clustering via landmark-based sparse representation. IEEE Trans Cybern 45(8):1669–1680
Huang D, Wang C-D, Wu J-S, Lai J-H, Kwoh C-K (2019) Ultra-scalable spectral clustering and ensemble clustering. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 32(6):1212–1226
Ng AY, Jordan MI, Weiss Y (2001) On spectral clustering: Analysis and an algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 14th international conference on neural information processing systems: natural and synthetic, pp 849–856
Nie F, Wang X, Huang H. (2014) Clustering and projected clustering with adaptive neighbors. In: ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery data mining, pp 977–986. https://doi.org/10.1145/2623330.2623726
You C, Li C-G, Robinson DP, Vidal R (2016) Oracle based active set algorithm for scalable elastic net subspace clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3928–3937
Lin Z, Liu R, Su Z (2011) Linearized alternating direction method with adaptive penalty for low-rank representation. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 612–620
Lu CS (2007) Solution of the matrix equation \(ax+xb = c\). Electron Lett 7(8):185–186
Yang J, Yin W, Zhang Y, Wang Y (2009) A fast algorithm for edge-preserving variational multichannel image restoration. SIAM J Imag Sci 2(2):569–592
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Chen, X. & Chen, W. Auto-Weighted Graph Regularization and Residual Compensation for Multi-view Subspace Clustering. Neural Process Lett 54, 3851–3871 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10789-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10789-7