Abstract
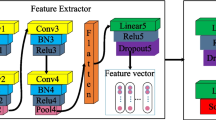
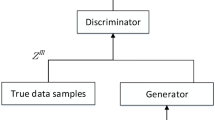
The success of intelligent fault diagnosis comes from one important assumption: the test data are consistent with the training data in data distribution. However, in the actual factory environment, the difference in data distribution due to changing working conditions will cause the performance of the trained model to seriously degrade. To address the problems, a transfer capsule network based on domain-adversarial training (DATTCN) is proposed. Specifically, it extracts fault features through wide convolution and multi-scale convolution, and performs fault classification through capsule networks. And the purpose of enhancing the diagnostic performance of the target domain is realized through adversarial training. In the fault identification of the Case Western Reserve University data set under varying working conditions, the DATTCN algorithm almost reaches 100% accuracy, and it is 92.3% on the Paderborn University data set. The accuracy of the DATTCN algorithm exceeds other advanced algorithms, fully verifying the effectiveness of the DATTCN algorithm.





Similar content being viewed by others

Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The dataset generated in this paper is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
The custom software code generated during the current study is not publicly available due to confidentiality policy.
References
You D, Gao X, Katayama S (2015) WPD-PCA-based laser welding process monitoring and defects diagnosis by using FNN and SVM. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62:628–636. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2014.2319216
Zhu J, Hu T, Jiang B, Yang X (2020) Intelligent bearing fault diagnosis using PCA–DBN framework. Neural Comput Appl 32:10773–10781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04612-z
Zhang S, Wang M, Li W, Luo J, Lin Z (2019) Deep learning with emerging new labels for fault diagnosis. IEEE Access 7:6279–6287. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2886078
Shao H, Xia M, Han G, Zhang Y, Wan J (2021) Intelligent fault diagnosis of rotor-bearing system under varying working conditions with modified transfer convolutional neural network and thermal images. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 17:3488–3496. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.3005965
Ganin Y, Ustinova E, Ajakan H, Germain P, Larochelle H, Laviolette F, Marchand M, Lempitsky V (2016) Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. J Mach Learn Res 17:2096–2030
Guo L, Lei Y, Xing S, Yan T, Li N (2019) Deep convolutional transfer learning network: a new method for intelligent fault diagnosis of machines with unlabeled data. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66:7316–7325. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2018.2877090
Zhang W, Li X, Ma H, Luo Z, Li X (2021) Open-set domain adaptation in machinery fault diagnostics using instance-level weighted adversarial learning. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 17:7445–7455. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2021.3054651
Li JP, Huang RY, He GL, Liao YX, Wang Z, Li WH (2021) A two-stage transfer adversarial network for intelligent fault diagnosis of rotating machinery with multiple new faults. IEEE-ASME Trans Mechatron 26:1591–1601. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMECH.2020.3025615
Sabour S, Frosst N, Hinton GE (2017) Dynamic routing between capsules. In: Proceedings of 31st annual conference on neural information processing systems (NIPS).
Li F, Tang T, Tang B, He Q (2021) Deep convolution domain-adversarial transfer learning for fault diagnosis of rolling bearings. Measurement 169:108339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108339
Han T, Ma R, Zheng J (2021) Combination bidirectional long short-term memory and capsule network for rotating machinery fault diagnosis. Measurement 176:109208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109208
Huang R, Li J, Wang S, Li G, Li W (2020) A robust weight-shared capsule network for intelligent machinery fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 16:6466–6475. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.2964117
Pan SJ, Yang Q (2010) A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 22:1345–1359. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2009.191
Al-Moslmi T, Omar N, Abdullah S, Albared M (2017) Approaches to cross-domain sentiment analysis: a systematic literature review. IEEE Access 5:16173–16192. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2690342
Wang M, Deng W (2018) Deep visual domain adaptation: A survey. Neurocomputing 312:135–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.083
Koga Y, Miyazaki H, Shibasaki R (2020) A method for vehicle detection in high-resolution satellite images that uses a region-based object detector and unsupervised domain adaptation. Remote Sensing 12:575. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030575
Shao S, McAleer S, Yan R, Baldi P (2019) Highly accurate machine fault diagnosis using deep transfer learning. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 15:2446–2455. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2018.2864759
Zhang W, Li X, Ma H, Luo Z (2021) Li X (2021) Federated learning for machinery fault diagnosis with dynamic validation and self-supervision. Knowl-Based Syst 213:106679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106679
Long M, Cao Y, Wang J, Jordan M (2021) Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: Proceedings of International conference on machine learning, pp 97–105
Long M, Zhu H, Wang J, Jordan MI (2017) Deep transfer learning with joint adaptation networks. In: Proceedings of international conference on machine learning, pp 2208–2217
Li X, Zhang W, Ding Q, Sun J-Q (2019) Multi-Layer domain adaptation method for rolling bearing fault diagnosis. Signal Process 157:180–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.12.005
Wen L, Gao L, Li X (2019) A new deep transfer learning based on sparse auto-encoder for fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems 49:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2017.2754287
Yang B, Lei Y, Jia F, Xing S (2019) An intelligent fault diagnosis approach based on transfer learning from laboratory bearings to locomotive bearings. Mech Syst Sig Process 122:692–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.12.051
Li X, Zhang W (2021) Deep learning-based partial domain adaptation method on intelligent machinery fault diagnostics. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 68:4351–4361. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.2984968
Zhang W, Peng G, Li C, Chen Y, Zhang Z (2017) A new deep learning model for fault diagnosis with good anti-noise and domain adaptation ability on raw vibration signals. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17020425
Kingma D, Ba J (2014) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: Proceedings of international conference on learning representations
Case Western Reserve University Bearing Data Center Website (2000) http://csegroups.case.edu/bearingdatacenter/home
Lessmeier C, Kimotho JK, Zimmer D, Sextro W (2016) Condition monitoring of bearing damage in electromechanical drive systems by using motor current signals of electric motors: a benchmark data set for data-driven classification. In: Proceedings of European conference of the prognostics and health management society
Wang Y, Ning D, Feng S (2020) A novel capsule network based on wide convolution and multi-scale convolution for fault diagnosis. Appl Sci 10:3659
Zhang M, Wang D, Lu W, Yang J, Li Z, Liang B (2019) A deep transfer model with wasserstein distance guided multi-adversarial networks for bearing fault diagnosis under different working conditions. IEEE Access 7:65303–65318. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2916935
Li Y, Wang N, Shi J, Hou X, Liu J (2018) Adaptive batch normalization for practical domain adaptation. Pattern Recognit 80:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.03.005
Funding
This work was supported by Shanghai Informatization Development Special Project (Grant No. 202001012), Shanghai Industrial Internet Innovation and Development Project (Grant No. 2020-GYHLW-02010), and Science and Technology Project Fund of East China Branch of State Grid Corporation (Grant No. ZWDL211578).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW: Conceptualization, methodology, software, visualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. DN: Conceptualization, visualization, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition. JL: Software, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Ning, D. & Lu, J. A Novel Transfer Capsule Network Based on Domain-Adversarial Training for Fault Diagnosis. Neural Process Lett 54, 4171–4188 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10803-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10803-y