Abstract
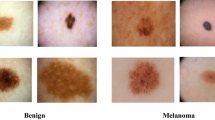
The most aggressive and malignant type of skin cancer is melanoma. When input data is in the form of images, image processing plays a vital role to detect and classifying cancer in the human body. Existing research discovered many weaknesses in complex data models, such as higher feature dimensionality, which required more data for training, resulting in lower detection accuracy, higher computational difficulties, portability, and processing time. Hence, we introduced fractal neural network-based galactic swarm optimization (FNN–GSO) algorithm for the detection of malignant melanoma such as superficial spreading, nodular, and lentigo malignant melanoma. The main aim of this work is to apply a deep learning technique to classify skin lesions for effective treatment and prognostication instead of the gold standard excision biopsy, which is currently used to diagnose this condition. Expert analysis, time consumption, and expensive processing associated with malignant melanoma classification and prediction are minimized in this manner. The proposed work involves four major components such as pre-processing, segmentation, feature extraction, and classification. The raw input images are pre-processed thereby the noise removal and contrast level enhancement are carried out. An adaptive watershed segmentation algorithm performs malignant melanoma segmentation. Following that, image features such as are extracted correctly using the DWT–GLCM feature extraction model. Finally, the malignant melanoma classifications are performed using the FNN–GSO algorithm. The proposed method's performance is evaluated using MATLAB software and different evaluation parameters. The proposed FNN–GSO algorithm demonstrates better classification results than other existing methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palacios‐Ferrer, JL, María Belén G‐O, María G‐G, María ÁG, Caridad D, HouriaBoulaiz JV et al (2021) Metabolomic profile of cancer stem cell‐derived exosomes from patients with malignant melanoma. Mol Oncol 15(2):407–428. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12823
Kassani SH, Peyman H (2019) A comparative study of deep learning architectures on melanoma detection. Tissue Cell 58:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tice.2019.04.009
Alquran H, Isam AQ, Ali MA, Sajidah A, Esraa A, Ammar A, Firas H (2017) The melanoma skin cancer detection and classification using support vector machine. In: 2017 IEEE Jordan conference on applied electrical engineering and computing technologies (AEECT). IEEE, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/AEECT.2017.8257738
Waheed Z, Amna W, Madeeha Z, Farhan R (2017) An efficient machine learning approach for the detection of melanoma using dermoscopic images. In: 2017 International conference on communication, computing and digital systems (C-CODE). IEEE, pp 316–319. https://doi.org/10.1109/C-CODE.2017.7918949
Hekler A, Utikal JS, Enk AH, Berking C, Klode J, Schadendorf D, Jansen P, Franklin C, Holland-Letz T, Krahl D, von Kalle C (2019) Pathologist-level classification of histopathological melanoma images with deep neural networks. Eur J Cancer 115:79–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2019.04.021
Brinker TJ, Hekler A, Hauschild A, Berking C, Schilling B, Enk AH, Haferkamp S, Karoglan A, von Kalle C, Weichenthal M, Sattler E (2019) Comparing artificial intelligence algorithms to 157 German dermatologists: the melanoma classification benchmark. Eur J Cancer 111:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2018.12.016
Brinker TJ, Hekler A, Enk AH, Klode J, Hauschild A, Berking C, Schilling B, Haferkamp S, Schadendorf D, Fröhling S, Utikal JS (2019) A convolutional neural network trained with dermoscopic images performed on par with 145 dermatologists in a clinical melanoma image classification task. Eur J Cancer 111:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2019.02.005
Lee S, Chu YS, Yoo SK, Choi S, Choe SJ, Koh SB, Chung KY, Xing L, Oh B, Yang S (2020) Augmented decision-making for acral lentiginous melanoma detection using deep convolutional neural networks. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 34(8):1842–1850. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.16185
Bakheet S (2017) Ansvm framework for malignant melanoma detection based on optimized hog features. Computation 5(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation5010004
Sanchez-Reyes L-M, Juvenal R-R, Sebastián S-C, Gloria N-R, Gerardo Israel P-S (2020) A high-accuracy mathematical morphology and multilayer perceptron-based approach for melanoma detection. Appl Sci 10(3):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031098
İlkin S, Tuğrul HG, Fidan KG, Hikmetcan Ö, Mehmet AA, Suhap Ş (2021) hybSVM: bacterial colony optimization algorithm based SVM for malignant melanoma detection. Eng Sci Technol Int J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2021.02.002
Ali AA, Al-Marzouqi H (2017) Melanoma detection using regular convolutional neural networks. In: 2017 International conference on electrical and computing technologies and applications (ICECTA). IEEE, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECTA.2017.8252041
Khan MA, Tallha A, Muhammad S, Aamir S, Khursheed A, Musaed A, Syed IH, Abdualziz A (2018) An implementation of normal distribution based segmentation and entropy controlled features selection for skin lesion detection and classification. BMC Cancer 18(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4465-8
Sundararaj V, Muthukumar S, Kumar RS (2018) An optimal cluster formation based energy efficient dynamic scheduling hybrid MAC protocol for heavy traffic load in wireless sensor networks. Comput Secur 77:277–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2018.04.009
Vinu S (2016) An efficient threshold prediction scheme for wavelet based ECG signal noise reduction using variable step size firefly algorithm. Int J Intell Eng Syst 9(3):117–126. https://doi.org/10.22266/ijies2016.0930.12
Sundararaj V (2019) Optimised denoising scheme via opposition-based self-adaptive learning PSO algorithm for wavelet-based ECG signal noise reduction. Int J Biomed Eng Technol 31(4):325. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBET.2019.103242
Sundararaj V, Anoop V, Dixit P, Arjaria A, Chourasia U, Bhambri P, Rejeesh MR, Sundararaj R (2020) CCGPA‐MPPT: cauchy preferential crossover‐based global pollination algorithm for MPPT in photovoltaic system. Prog Photovolt Res Appl 28(11):1128–1145. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.3315
Rejeesh MR, Thejaswini P (2020) MOTF: Multi-objective optimal trilateral filtering based partial moving frame algorithm for image denoising. Multim Tools Appl 79(37):28411–28430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09234-5
Gowthul Alam MM, Baulkani S (2019) Local and global characteristics-based kernel hybridization to increase optimal support vector machine performance for stock market prediction. Knowl Inf Syst 60(2):971–1000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-018-1263-1
Alam MG, Baulkani S (2016) A hybrid approach for web document clustering using K-means and artificial bee colony algorithm. Int J Intell Eng Syst 9(4):11–20. https://doi.org/10.22266/ijies2016.1231.02
Gowthul Alam MM, Baulkani S (2019) Geometric structure information based multi-objective function to increase fuzzy clustering performance with artificial and real-life data. Soft Comput 23(4):1079–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3124-y
Vinu S, Selvi M (2021) Opposition grasshopper optimizer based multimedia data distribution using user evaluation strategy. Multim Tools Appl 80:29875–29891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11123-4
Parsian A, Mehdi R, Noradin G (2017) A hybrid neural network-gray wolf optimization algorithm for melanoma detection
Azmi NFM, Sarkan HM, Yahya Y, Chuprat S (2016) ABCD rules segmentation on malignant tumor and benign skin lesion images. In: 2016 3rd international conference on computer and information sciences (ICCOINS). IEEE, pp 66–70. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCOINS.2016.7783190
Vocaturo E, Ester Z, Pierangelo V (2018) Image pre-processing in computer vision systems for melanoma detection. In: 2018 IEEE international conference on bioinformatics and biomedicine (BIBM). IEEE, pp 2117–2124. https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM.2018.8621507
Tinnathi S, Sudhavani G (2021) An efficient copy move forgery detection using adaptive watershed segmentation with AGSO and hybrid feature extraction. J Vis Commun Image Represen 74(2021):102966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2020.102966
Huang Z, Jiang S, Yang Z, Ding Y, Wang W, Yan Yu (2016) Automatic multi-organ segmentation of prostate magnetic resonance images using watershed and nonsubsampled contourlet transform. Biomed Signal Process Control 25:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2015.11.002
Jierong C, Rajapakse JC (2008) Segmentation of clustered nuclei with shape markers and marking function. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56(3):741–748. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2008.2008635
Koyuncu CF, Ece A, Tulin E, Rengul C‐A, Cigdem G‐D (2016) Iterative h‐minima‐based marker‐controlled watershed for cell nucleus segmentation. Cytomet Part A 89(4):338–349. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.22824
Çevik T, Alshaykha AMA, Çevik N (2016) Performance analysis of GLCM-based classification on wavelet transform-compressed fingerprint images. In: 2016 sixth international conference on digital information and communication technology and its applications (DICTAP). IEEE, pp 131–135. https://doi.org/10.1109/DICTAP.2016.7544014
Haralick RM (1979) Statistical and structural approaches to texture. Proc IEEE 67(5):786–804. https://doi.org/10.1109/PROC.1979.11328
Fathima MM, Manimegalai D, Thaiyalnayaki S (2013) Automatic detection of tumor subtype in mammograms based On GLCM and DWT features using SVM. In: 2013 international conference on information communication and embedded systems (ICICES). IEEE, pp 809–813. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICES.2013.6508213
Chen SS, Keller JM, Crownover RM (1993) On the calculation of fractal features from images. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 15(10):1087–1090. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.254066
Roberto GF, Alessandra L, Leandro AN, Marcelo ZN (2021) Fractal neural network: a new ensemble of fractal geometry and convolutional neural networks for the classification of histology images. Expert Syst Appl 166(2021):114103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114103
Yamashita R, Nishio M, Do RKG, Togashi K (2018) Convolutional neural networks: an overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 9(4):611–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-018-0639-9
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2017) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun ACM 60(6):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
Ab Wahab MN, Nefti-Meziani S, Atyabi A (2015) A comprehensive review of swarm optimization algorithms. PLoS ONE 10(5):e0122827. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122827
Marini F, Walczak B (2015) Particle swarm optimization (PSO). A tutorial. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 149:153–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2015.08.020
Pandey D, Pandey BK, Wairya S (2021) Hybrid deep neural network with adaptive galactic swarm optimization for text extraction from scene images. Soft Comput 25(2):1563–1580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05245-4
Muthiah-Nakarajan V, Noel MM (2016) Galactic Swarm Optimization: a new global optimization metaheuristic inspired by galactic motion. Appl Soft Comput 38:771–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.10.034
Iaquinta P, Miriam I, Luciano C, Turano S, Sergio P, Francesco D, Ivana P, Pierangelo V, Ester Z (2017) eIMES 3D: an innovative medical images analysis tool to support diagnostic and surgical intervention. Proc Comput Sci 110(2017):459–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.06.122
Dańczak-Pazdrowska A, Pazdrowski J, Polańska A, Basta B, Schneider A, Kowalczyk MJ, Golusiński P, Golusiński W, Adamski Z, Żaba R, Masternak MM (2021) Profiling of microRNAs in actinic keratosis and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma patients. Arch Dermatol Res 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-021-02221-2
Bi L, Jinman K, Euijoon A, Ashnil K, Dagan F, Michael F (2019) Step-wise integration of deep class-specific learning for dermoscopic image segmentation. Pattern Recogn 85:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.08.001
Bi L, Jinman K, Euijoon A, Ashnil K, Michael F, Dagan F (2017) Dermoscopic image segmentation via multistage fully convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(9):2065–2074. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2017.2712771
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karuppiah, S.P., Sheeba, A., Padmakala, S. et al. An Efficient Galactic Swarm Optimization Based Fractal Neural Network Model with DWT for Malignant Melanoma Prediction. Neural Process Lett 54, 5043–5062 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10847-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10847-0