Abstract
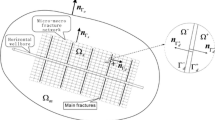
In this paper, two-grid finite element method for the steady dual-permeability-Stokes fluid flow model is proposed and analyzed. Dual-permeability-Stokes interface system has vast applications in many areas such as hydrocarbon recovery process, especially in hydraulically fractured tight/shale oil/gas reservoirs. Two-grid method is popular and convenient to solve a large multiphysics interface system by decoupling the coupled problem into several subproblems. Herein, the two-grid approach is used to reduce the coding task substantially, which provides computational flexibility without losing the approximate accuracy. Firstly, we solve a global problem through standard Pk − Pk− 1 − Pk − Pk finite elements on the coarse grid. After that, a coarse grid solution is applied for the decoupling between the interface terms and the mass exchange terms to solve three independent subproblems on the fine grid. The three independent parallel subproblems are the Stokes equations, the microfracture equations, and the matrix equations, respectively. Four numerical tests are presented to validate the numerical methods and illustrate the features of the dual-permeability-Stokes model.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Discacciati, M., Miglio, E., Quarteroni, A.: Mathematical and numerical models for coupling surface and groundwater flows. Appl. Numer. Math. 43, 57–74 (2002)
Layton, W., Tran, H., Trenchea, C.: Analysis of long time stability and errors of two partitioned methods for uncoupling evolutionary groundwater surface water flows. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51, 248–272 (2013)
Nassehi, V.: Modelling of combined Navier-Stokes and Darcy flows in crossflow membrane filtration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 53, 1253–1265 (1998)
Yao, J., Huang, Z., Li, Y., Wang, C., Lv, X.: Discrete Fracture-Vug Network Model for Modeling Fluid Flow in Fractured Vuggy Porous Media. Society of Petroleum Engineers, International Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition, Beijing, China (2010)
Discacciati, M.: Domain Decomposition Methods for the Coupling of Surface and Groundwater Flows. Ph.d. dissertation École Polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (2004)
Girault, V., Rivière, B.: DG approximation of coupled Navier-Stokes and Darcy equations by Beaver-Joseph-Saffman interface condition. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 2052–2089 (2009)
Layton, W.J., Schieweck, F., Yotov, I.: Coupling fluid flow with porous media flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40, 2195–2218 (2003)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., Hu, X., Hua, F., Wang, X., Zhao, W.: Finite element approximation for Stokes-Darcy flow with Beavers-Joseph interface conditions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 4239–4256 (2010)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., Hua, F., Wang, X.: Coupled Stokes-Darcy model with Beavers-Joseph interface boundary condition. Comm. Math. Sci. 8, 1–25 (2010)
Olgac, U., Kurtcuoglu, V., Poulikakos, D.: Computational modeling of coupled blood-wall mass transport of LDL: effects of local wall shear stress. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 294, 909–919 (2008)
Prosi, M., Zunino, P., Perktold, K., Quarteroni, A.: Mathematical and numerical models for transfer of low-density lipoproteins through the arterial walls: a new methodology for the model set up with applications to the study of disturbed lumenal flow. J. Biomech. 38, 903–917 (2005)
Sun, N., Wood, N., Hughes, A., Thom, A., Xu, X.-Y.: Effects of transmural pressure and wall shear stress on LDL accumulation in the arterial wall: a numerical study using a multilayered model. Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 292, 3148–3157 (2007)
Kong, F.D., Cai, X.-C.A.: Highly scalable multilevel Schwarz method with boundary geometry preserving coarse spaces for 3D elasticity problems on domains with complex geometry, SIAM. J. Sci. Comput. 38, C73–C95 (2016)
Kong, F.D., Cai, X.-C.A.: Scalable nonlinear fluid-structure interaction solver based on a Schwarz preconditioner with isogeometric unstructured coarse spaces in 3D. J. Comput. Phys. 340, 498–518 (2017)
Abbasi, M., Madani, M., Sharifi, M., Kazemi, A.: Fluid flow in fractured reservoirs: Exact analytical solution for transient dual porosity model with variable rock matrix block size. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 164, 571–583 (2018)
Abdelazim, R., Rahman, S.S.: Estimation of permeability of naturally fractured reservoirs by pressure transient analysis: an innovative reservoir characterisation and flow simulation. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 145, 404–422 (2016)
Ranjbar, E., Hassanzadeh, H., Chen, Z.: Effect of fracture pressure depletion regimes on the dual-porosity shape factor for flow of compressible fluids in fractured porous media. Adv. Water Res. 34, 1681–1693 (2011)
Chen, Z.X.: Transient flow of slightly compressible fluids through doubleporosity, double-permeability systems-a state-of-the-art review. Transp. Porous Med. 4, 147–184 (1989)
Chen, H.-Y., Teufel, L.W.: Coupling Fluid Flow and Geomechanics in Dual-Porosity Modeling of Naturally Fractured reservoir-Model Description and Comparison, SPE-59043-MS, SPE International Petroleum Conference and Exhibition 1-3 February, Villahermosa, Mexico (2000)
Sofla, S.J.D., Pouladi, B., Sharifi, M., Shabankareian, B., Moraveji, M.K.: Experimental and Simulation study of gas diffusion effect during gas injection into naturally fractured reservoirs. J. Nat Gas Sci. Eng. 33, 438–447 (2016)
Abushaikha, A.S., Gosselin, O.R.: Matrix-Fracture Transfer Function in Dual-Media Flow Simulation: Review, Comparison and Validation, SPE-113890-MS, Europec/EAGE Conference and Exhibition 9-12 June 2008, Rome, Italy (2008)
Douglas, C.C., Bai, B., He, X.-M., Wei, M., Hou, J.: A data assimilation enabled model for coupling dual porosity flow with free flow, 17th International Symposium on Distributed Computing and Applications for Business Engineering and Science (2018)
Hou, J., Qiu, M., He, X.-M., Gu, C., Wei, M., Bai, B.A.: Dual-porosity-stokes model and finite element method for coupling dual-porosity flow and free flow. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 38, B710–B739 (2016)
Bello, R.O., Wattenbarger, R.A.: Rate transient analysis in naturally fractured shale gas reservoirs, SPE-114591, Society of Petroleum Engineers, CIPC/SPE Gas Technology Symposium 2008 Joint Conference, Calgary, Alberta, Canada (2008)
Carlson, E.S., Mercer, J.C.: Devonian shale gas production: Mechanisms and simple models. J. Petro. Technol. 43, 476–482 (1991)
Shan, L., Hou, J., Yan, W., Chen, J.: Partitioned time stepping method for a dual-porosity-Stokes model. J. Sci. Comput. 79, 389–413 (2019)
Al-Ghamdi, A., Ershaghi, I.: Pressure transient analysis of dually fractured reservoirs, SPE-26959-PA. SPE J. 1, 1–8 (1996)
Mahbub, M.A.A., He, X.-M., Nasu, N.J., Qiu, C., Zheng, H.: Coupled and decoupled stabilized mixed finite element methods for nonstationary dual-porosity-Stokes fluid flow model. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 120, 803–833 (2019)
Barenblatt, G.I., Zheltov, I.P., Kochina, I.N.: Basic concepts in the theory of seepage of homogeneous liquids in fissured rocks [strata]. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 24, 1286–1303 (2016)
Warren, J.E., Root, P.J.: The behavior of naturally fractured reservoirs. Soc. Petrol. Eng. J. 3, 245–255 (1963)
Lim, K.T., Aziz, K.: Matrix-fracture transfer shape factors for dual-porosity simulators. J. Petro. Sci. Eng. 13, 169–178 (1995)
Ranjbar, E., Hassanzadeh, H.: Matrix-fracture transfer shape factor for modeling flow of a compressible fluid in dual-porosity media. Adv. Water Resour. 34, 627–639 (2011)
De Swaan, A.: Analytic solutions for determining naturally fractured reservoir properties by well testing. Soc. Petro. Eng. 16, 117–122 (1976)
Arbogast, T., Douglas Jr., J., Hornung, U.: Derivation of the double porosity model of single phase flow via homogenization theory. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 21, 823–836 (1990)
Guo, C., Wei, M., Chen, H., He, X.-M., Bai, B.: Improved numerical simulation for shale gas reservoirs, OTC-24913, Offshore Technology Conference Asia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, March 25–28 (2014)
Guo, C., Wang, J., Wei, M., He, X.-M., Bai, B.: Multi-stage fractured horizontal well numerical simulation and its application in tight shale reservoirs, SPE-176714, SPE Russian Petroleum Technology Conference, Moscow, Russia, October 26–28 (2015)
Seale, R.A., Athans, J.: An effective openhole horizontal completion system for multistage fracturing and stimulation, Society of Petroleum Engineers, SPE Tight Gas Completions Conference, Texas, USA (2008)
Brohi, I.G., Pooladi-Darvish, M., Aguilera, R.: Modeling fractured horizontal wells as dual porosity composite reservoirs-Application to tight gas, shale gas and tight oil cases, SPE-144057, Society of Petroleum Engineers, SPE Western North American Region Meeting, Anchorage, AK (2011)
Bourbiaux, B., Granet, S., Landereau, P., Noetinger, B., Sarda, S., Sabathier, J.C.: Scaling up matrix-fracture transfers in dual-porosity models: Theory and application, SPE-56557, Society of Petroleum Engineers, SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston TX (1999)
Aguilera, R.: Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. Pennwell Publishing Company, Tulsa, OK (1995)
Chen, C.-C., Serra, K., Reynolds, A.C., Raghavan, R.: Pressure transient analysis methods for bounded naturally fractured reservoirs. Soc. Petro. Eng. J. 25, 451–464 (1985)
Wang, W., Yuan, B., Su, Y., Sheng, G., Yao, W., Gao, H., Wang, K.A.: Composite dual-porosity fractal model for channel-fractured horizontal wells. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 12, 104–116 (2018)
Cordero, J.A.R., Sanchez, E.C.M., Roehl, D.: Integrated discrete fracture dual porosity-dual permeability models for fluid flow in deformable fractured media. J. Petrol. Sci Eng. 175, 644–653 (2019)
Mahbub, M.A.A., Shi, F., Nasu, N.J., Wang, Y., Zheng, H.: Mixed stabilized finite element method for the stationary Stokes-dual-permeability fluid flow model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 358, 1–31 (2020)
Mahbub, M.A.A., He, X.-M., Nasu, N.J., Qiu, C., Wang, Y., Zheng, H.: A Coupled multiphysics model and a decoupled stabilized finite element method for the closed-loop geothermal system. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 42, B951–B982 (2020)
Carneiro, J.F.: Numerical simulations on the influence of matrix diffusion to carbon sequestration in double porosity fissured aquifers. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Con. 3, 431–443 (2009)
Cicek, O.: Compositional and non-isothermal simulation of CO2 sequestration in naturally fractured reservoirs/coalbeds: Development and verification of the model, SPE-84341, PE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver CO (2003)
Gerke, H.H., Van Genuchten, M.T.: Evaluation of a first-order water transfer term for variably saturated dual-porosity flow models. Water Resour. Res. 29, 1225–1238 (1993)
Haws, N.W., Rao, P.S.C., Simunek, J., Poyer, I.C.: Single-porosity and dual-porosity modeling of water flow and solute transport in subsurface-drained fields using effective field-scale parameters. J. Hydrol. 313, 257–273 (2005)
Shaik, A.R., Rahman, S.S., Tran, N.H., Tran, T.: Numerical simulation of Fluid-Rock coupling heat transfer in naturally fractured geothermal system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 31, 1600–1606 (2011)
Boubendir, Y., Tlupova, S.: Domain decomposition methods for solving Stokes-Darcy problems with bondary integrals. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 35, B82–B106 (2013)
He, X.-M., Li, J., Lin, Y., Ming, J.A.: Domain decomposition method for the steady-state Navier-Stokes-Darcy model with Beavers-Joseph interface condition. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 37, S264–S290 (2015)
Discacciati, M., Quarteroni, A., Valli, A.: Robin-robin domain decomposition methods for the Stokes-Darcy coupling. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45, 1246–1268 (2007)
Jiang, B.: A parallel domain decomposition method for coupling of surface and groundwater flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 198, 947–957 (2009)
Cao, Y., Gunzburger, M., He, X.-M., Wang, X.: Parallel, non-iterative, multi-physics domain decomposition methods for time-dependent Stokes-Darcy systems. Math. Comput. 83, 1617–1644 (2014)
Qiu, C., He, X.-M., Li, J., Lin, Y.: A domain decomposition method for the time-dependent Navier-Stokes-Darcy model with Beavers-Joseph interface condition and defective boundary condition. J. Comput. Phys. 411, 109400 (2020)
Marquez, A., Meddahi, S., Sayas, F.J.A.: Decoupled preconditioning technique for a mixed Stokes-Darcy model. J. Sci. Comput. 57, 174–192 (2013)
Mu, M., Zhu, X.H.: Decoupled schemes for a non-stationary mixed Stokes-Darcy model. Math. Comput. 79, 707–731 (2010)
Shan, L., Zheng, H., Layton, W.J.A.: Decoupling method with different subdomain time steps for the nonstationary Stokes-Darcy model. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Eqns. 29, 549–583 (2013)
Shan, L., Zheng, H.: Partitioned time stepping method for fully evolutionary Stokes-Darcy flow with the Beavers-Joseph interface conditions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51, 813–839 (2013)
Gunzburger, M., He, X.-M., Li, B.: On Stokes-Ritz projection and multistep backward differentiation schemes in decoupling the Stokes-Darcy Model. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 56, 397–427 (2018)
Xu, J.: Two-grid discretization techniques for linear and nonlinear PDEs. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 33, 1759–1777 (1996)
Xu, J.A.: Novel two-grid method for semi-linear equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 15, 231–237 (1994)
Mu, M., Xu, J.A.: Two grid method of a mixed Stokes-Darcy model for coupling fluid flow with porous media flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45, 1801–1813 (2007)
Cai, M.C., Mu, M., Xu, J.C.: Numerical solution to a mixed Navier-Stokes/Darcy model by the two-grid approach. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 3325–3338 (2009)
Zuo, L.Y., Hou, Y.A.: Decoupling two-grid algorithm for the mixed Stokes-Darcy model with the Beavers-Joseph interface condition. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Eqns. 3, 1066–1082 (2014)
Zhang, T., Yuan, J.Y.: Two novel decoupling algorithms for the steady Stokes-Darcy model based on two-grid discretizations. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst.-Ser. B 19, 849–865 (2014)
Jia, H., Jia, H., Huang, Y.A.: Modified two-grid decoupling method for the mixed Navier-Stokes/Darcy Model. Comput. Math. Appl. 72, 1142–1152 (2014)
You, J., Zheng, H., Shi, F., Zhao, R.: Two-grid finite element method for the stabilization of mixed Stokes-Darcy model. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst.-Ser. B. 24, 387–402 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Zheng, H., Hou, Y., Shan, L.: Optimal error estimates of both coupled and two-grid decoupled methods for a mixed Stokes-Stokes model. Appl. Numer. Math. 133, 116–129 (2018)
Chen, C., Li, K., Chen, Y., Huang, Y.: Two-grid finite element methods combined with Crank-Nicolson scheme for nonlinear Sobolev equations. Adv. Comput. Math. 45, 611–630 (2019)
Nasu, N.J., Mahbub, M.A.A., Hussain, S., Zheng, H.: Two-level finite element approximation for Oseen viscoelastic fluid flow. Mathematics 6, 71 (2018)
Cai, M.C., Mu, M.A.: Multilevel decoupled method for a mixed Stokes/Darcy model. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 236, 2452–2465 (2012)
Hou, Y.: Optimal error estimates of a decoupled scheme based on two-grid finite element for mixed Stokes-Darcy model. Appl. Math. Lett. 57, 90–96 (2016)
Du, G., Li, Q., Zhang, Y.: A two-grid method with backtracking for the mixed Navier–Stokes/Darcy model. Numer. Methods Partial Differential Equations 36, 1601–1610 (2020)
Zuo, L., Du, G.A.: Parallel two-grid linearized method for the coupled Navier-Stokes-Darcy problem. Numer. Algorithms 77, 151–165 (2018)
Babuška, I., Gatica, G.N.A.: Residual-based a posteriori error estimator for the Stokes-Darcy coupled problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 48, 498–523 (2010)
Gatica, G.N., Meddahi, S., Oyarzú, R.A.: Conforming mixed finite-element method for the coupling of fluid flow with porous media flow. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 29, 86–108 (2009)
Kanschat, G., Riviére, B.: A strongly conservative finite element method for the coupling of Stokes and Darcy flow. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 5933–5943 (2010)
Lipnikov, K., Vassilev, D., Yotov, I.: Discontinuous Galerkin and mimetic finite difference methods for coupled Stokes-Darcy flows on polygonal and polyhedral grids. Numer. Math. 126, 321–360 (2014)
Li, R., Gao, Y., Li, J., Chen, Z.: Discontinuous finite volume element method for a coupled non-stationary Stokes-Darcy problem. J. Sci. Comput. 74, 693–727 (2018)
Li, R., Li, J., He, X.-M., Chen, Z.A.: Stabilized finite volume element method for a coupled Stokes-Darcy problem. Appl. Numer. Math. 133, 2–24 (2018)
Ervin, V.J., Jenkins, E.W., Sun, S.: Coupling nonlinear Stokes and Darcy flow using mortar finite elements. Appl. Numer. Math. 61, 1198–1222 (2011)
Galvis, J., Sarkis, M.: Non-matching mortar discretization analysis for the coupling Stokes-Darcy equations. Electron. Trans. Numer. Anal. 26, 350–384 (2007)
He, X.-M., Jiang, N., Qiu, C.: An artificial compressibility ensemble algorithm for a stochastic Stokes-Darcy model with random hydraulic conductivity and interface conditions. Int. J. Numer. Methods. Eng. 121, 712–739 (2020)
Li, Y., Hou, Y., Rong, Y.A.: Second-order artificial compression method for the evolutionary Stokes-Darcy system. Numer. Algorithm 84, 1019–1048 (2020)
Beavers, G., Joseph, D.: Boundary conditions at a naturally permeable wall. J. Fluid Mech. 30, 197–207 (1967)
Saffman, P.: On the boundary condition at the surface of a porous media. Stud. Appl. Math. 50, 93–101 (1971)
Li, R., Li, J., Chen, Z.X., Gao, Y.L.A.: Stabilized finite element method based on two local Gauss integrations for a coupled Stokes-Darcy problem. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 292, 92–104 (2016)
Hecht, F., Le Hyaric, A., Ohtsuka, K., Pironneau, O.: FreeFem++, Finite elements software, http://www.freefem.org/ff++/
Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Huang, Y., Fu, L.: Two-grid methods of expanded mixed finite-element solutions for nonlinear parabolic problems. Appl. Numer. Math. 144, 204–222 (2019)
Goswami, D., Damázio, P.D.A.: Two-grid finite element method for time-dependent incompressible Navier-Stokes equations with non-smooth initial data. Numer. Math. Theory Methods Appl. 8, 549–581 (2015)
Shi, D., Yang, H.: Unconditional optimal error estimates of a two-grid method for semilinear parabolic equation. Appl. Math. Comput. 310, 40–47 (2017)
Chen, C., Liu, W.: Two-grid finite volume element methods for semilinear parabolic problems. Appl. Numer. Math. 60, 10–18 (2010)
Funding
All authors are partially supported by NSF of China (Grant No. 11971174), NSF of Shanghai (Grant No. 19ZR1414300), and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant No. 18dz2271000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasu, N.J., Mahbub, M.A.A., Hussain, S. et al. Two-grid finite element method for the dual-permeability-Stokes fluid flow model. Numer Algor 88, 1703–1731 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-021-01091-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-021-01091-z