Abstract
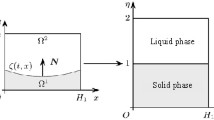
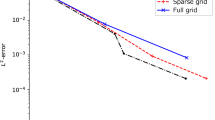
In this paper, a one-dimensional two-phase inverse Stefan problem is studied. The free surface is considered unknown here, which is more realistic from the practical point of view. The problem is ill-posed since small errors in the input data can lead to large deviations from the desired solution. To obtain a stable numerical solution, we propose a method based on discrete mollification combined with space marching. We use the integration matrix in Bernstein polynomial basis for the discrete mollification method. Through this method, our numerical integration does not involve any direct function integration and only contains algebraic calculations. Furthermore, the stability and convergence of the process are proved. Finally, the results of this paper are illustrated and examined through some numerical examples. The numerical examples supporting our theoretical analysis are provided and discussed.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodaghi, S., Zakeri, A., Amiraslani, A.: A numerical scheme based on discrete mollification method using Bernstein basis polynomials for solving the inverse onedimensional Stefan problem Inverse Problems in Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1080/17415977.2020.1733996 (2020)
Sazhin, S.S., Krutitskii, P.A., Gusev, I.G., Heikal, M.R.: Transient heating of an evaporating droplet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 53, 2826–2836 (2010)
Back, J.M., McCue, S.W., Hsieh, M.H.-N., Moroney, T.J.: The effect of surface tension and kinetic undercooling on a radially-symmetric melting problem. Appl. Math. Comput. 229, 41–52 (2014)
Herrero, M.A., Velazquez, J.J.L.: On the melting of ice balls. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 28, 1–32 (1997)
McCue, S.W., Wu, B., Hill, J.M.: Classical two-phase Stefan problem for spheres. Proc. R. Soc. A 464, 2055–2076 (2008)
McCue, S.W., Hsieh, M., Moroney, T.J., Nelson, M.I.: Asymptotic and numerical results for a model of solvent-dependent drug diffusion through polymeric spheres. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 71, 2287–2311 (2011)
Pedroso, R.I., Domoto, G.A.: Perturbation solutions for spherical solidification of saturated liquids. J. Heat Transfer 95, 42–46 (1973)
Riley, D.S., Smith, F.T., Poots, G.: The inward solidification of spheres and circular cylinders. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 17, 1507–1516 (1974)
Soward, A.M.: A unified approach to Stefan’s problem for spheres. Proc. R. Soc. A 373, 131–147 (1980)
Stewartson, K., Waechter, R.T.: On Stefan’s problem for spheres. Proc. R. Soc. A 348, 415–426 (1976)
Tabakova, S., Feuillebois, F., Radev, S.: Freezing of a supercooled spherical droplet with mixed boundary conditions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 466, 1117–1134 (2010)
Vynnycky, M.: On the onset of air-gap formation in vertical continuous casting with superheat. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 73, 69–76 (2013)
Vynnycky, M.: A mathematical model for air-gap formation in vertical continuous casting: the effect of superheat. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 62, 495–498 (2009)
Acosta, C.D., Mejia, C.E.: Stabilization of explicit methods for convection diffusion equations by discrete mollification. Comput. Math. Appl. 55, 368–380 (2008)
Bakal, A., Timbers, G., Hayakawa, K.: Solution of the characteristic equation involved in the transient heat conduction for foods approximated by an infinite slab, Can Inst. Food Techtlol. 76 (1970)
Bollati, J., Semitiel, J., Tarzia, D.A.: Heat balance integral methods applied to the one-phase Stefan problem with a convective boundary condition at the fixed face. Appl. Math. Comput. 331, 1–19 (2018)
Coles, C., Murio, D.A.: Identification of parameters in the 2-D IHCP. Comput. Math. Appl. 40, 939–956 (2000)
Conti, M.: Density change effects on crystal growth from the melt. Phys. Rev. E 64, 051601 (2001)
Crank, J.: Free and Moving Boundary Problems. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1984)
Goldman, N.L.: Inverse Stefan Problem. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1997)
Gupta, S.C.: The Classical Stefan Problem. Basic Concepts, Modelling and Analysis. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2003)
Johansson, T., Lesnic, D., Reeve, T.: A meshless method for an inverse two-phase one dimensional nonlinear Stefan problem. Math. Comput. Simul. 101, 61–77 (2014)
Libbrecht, K.G.: The physics of snow crystals. Rep. Prog. Phys. 68, 855 (2005)
Lin, W.S.: Steady ablation on the surface of a two-layer composite, vol. 48. A. M. Meirmanov, The Stefan Problem, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, 1992 (2005)
Mejia, C.E., Murio, D.A.: Mollified hyperbolic method for coefficient identification problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 26(5), 1–12 (1993)
Mejia, C.E., Acosta, C.D., Saleme, K.I.: Numerical identification of a nonlinear diffusion coefficient by discrete mollification. Comput. Math. Appl. 62, 2187–2199 (2011)
Mejia, C.E., Murio, D.A.: Numerical solution of generalized IHCP by discrete mollification. Comput. Math. Appl. 32(2), 33–50 (1996)
Mitchell, S.L., Vynnycky, M.: Finite-difference methods with increased accuracy and correct initialization for one-dimensional Stefan problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 215, 1609–1621 (2009)
Murio, D.A.: Mollification and space marching. In: Woodbury, K (ed.) Inverse Engineering Handbook, CRC Press (2002)
Namenanee, K., McKenzie, J., Kosa, E., Schwab, M., Sunsaneewitayakul, B., Vasavakul, T., Khunnawat, C., Ngarmukos, T.: A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J. Amer. College Cardiology 43(11), 2044–2053 (2004)
Salva, N.N., Tarzia, D.A.: Explicit solution for a Stefan problem with variable latent heat and constant heat flux boundary conditions. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 379, 240–244 (2011)
Sharifi, N., Bergman, T.L., Allen, M.J., Faghri, A.: Melting and solidification enhancement using a combined heat pipe, foil approach. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Tran. 78, 930–941 (2015)
Slota, D.: Direct and inverse one-phase Stefan problem solved by the variational iteration method. Comput. Math. Appl. 54, 113–1146 (2007)
Slota, D.: Homotopy perturbation method for solving the two-phase inverse Stefan problem. Numer. Heat Transfer PartA 59, 755–68 (2011)
Rubinstein, L.I.: The Stefan Problem. AMS, Providence (1971)
Tayler, A.B.: Mathematical Models in Applied Mechanics. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2001)
Trueba, J.L., Voller, V.R.: Analytical and numerical solution of a generalized Stefan problem exhibiting two moving boundaries with application to ocean delta formation. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 366, 538–549 (2010)
Wrobel, L.C.: A Boundary Element Solution to Stefan’s Problem. In: Brebbia, C.A., Futagami, T., Tanaka, M. (eds.) Boundary Elements V, Computational Mechanics Publications, pp 173–182. Springer, Berlin (1983)
El Badia, A., Moutazaim, F.: A one-phase inverse Stefan problem. Inverse Prob. 15, 1507–1522 (1999)
Cannon, J.R., Douglas, J.: The Cauchy problem for the heat equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 4(3), 317–336 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bodaghi, S., Zakeri, A., Amiraslani, A. et al. Discrete mollification in Bernstein basis and space marching scheme for numerical solution of an inverse two-phase one-dimensional Stefan problem. Numer Algor 90, 1569–1592 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-021-01242-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-021-01242-2