Abstract
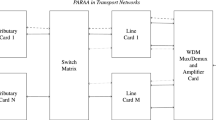
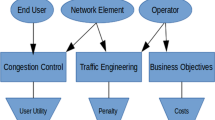
The paper deals with the problem of multilayer resource provisioning in a network in which an operator needs to route traffic flows with different data rates. It is shown that the blocking probability of high data rate requests is usually higher than the blocking probability of other requests. A relevant strategy aimed at solving this problem is proposed, investigated, and compared with the known solution. Numerical results confirm that the proposed strategy is able to substantially reduce the blocking probability of high data rate requests at the cost of increased utilization of the packet switching layer and more complex routing of lightpaths.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Proposed standard: Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks: Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks—Amendment 8: Shortest Path Bridging, IEEE 802.1aq, http://www.ieee802.org/1/pages/802.1aq.html (2011)
Colitti, W. et al.: Adaptive multilayer routing in the next generation GMPLS Internet. Third Int. Conf. Commun. Systems Software and middleware and workshops, 768–775 (2008)
Zhu H. et al.: A novel generic graph model for traffic grooming in heterogeneous WDM mesh networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 11, 285–299 (2003)
Zhu, K., et al.: On-line approaches for provisioning connections of different bandwidth granularities in WDM mesh networks, In: Proceedings of Optical Fiber Communications Conference, 549–551 (2002)
Oki E. et al.: Dynamic multilayer routing schemes in GMPLS-based IP+optical networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 43, 108–114 (2005)
Colitti W. et al.: Multilayer QoS in integrated IP over optical networks. First Int. Conf. Commun. Electron. 1, 1–6 (2006)
Drummond, A., et al.: On-line dynamic traffic grooming algorithms for WDM mesh networks, IEEE International Conference on Communications, 1–5 (2009)
de Santi, J., et al.: Load balancing for holding-time-aware dynamic traffic grooming, IEEE Global Communications Conference, 1–6 (2010)
Szymanski, A., et al.: Performance evaluation of the grade-of-service-based routing strategies for optical networks, IEEE International Conference on Communications, 5252–5257 (2008)
Puype B. et al.: Multilayer traffic engineering for multiservice environments. Photon. Netw. Commun. 18, 150–159 (2009)
Zhu H. et al.: Dynamic traffic grooming in WDM mesh networks using a novel graph model. IEEE Glob. Telecommun. Conf. 3, 2681–2685 (2002)
Szymanski, A., et al.: Route management strategies for grade of service differentiation in optical networks, IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2453–2458 (2006)
Kuchar, A., et al.: Achievements of COST 266 Action and further prospects in research of advanced infrastructure for photonic networks, Proceedings of 2004 6th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks, vol. 1, 37–42 (2004)
Varga A.: Using the OMNeT++ discrete event simulation system in education. IEEE Trans. Educ. 42, 372 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rzasa, J., Lason, A., Szymanski, A. et al. Resource provisioning for multigranular traffic flows in multilayer networks. Photon Netw Commun 23, 60–66 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-011-0336-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-011-0336-9