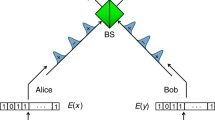
We show how the techniques developed for long distance quantum key distribution in optical fibers can be used to demonstrate other quantum information processing and communication protocols. We present a fiber optics realization of the Deutsch–Jozsa and Bernstein–Vazirani algorithms. We describe a method, called “error filtration”, for reducing errors in quantum communication channels, and present an experimental implementation thereof. We discuss the cryptographic primitive of string flipping, and present an experimental implementation which has higher security than achievable using any classical protocol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. H. Bennett and G. Brassard, Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing, in Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, (IEEE, New York, 1984. Bangalore, India, 1984), pp. 175–179.
Deutsch D. (1985). Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 400, 97
Nielsen M.A., Chuang I.L. (2004). Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Stucki D., Gisin N., Guinnard O., Ribordy G., Zbinden H. (2002). New J. Phys. 4, 41
Gobby C., Yuan Z.L., Shields A. (2004). Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 3762–3764
Ribordy G., Gautier J-D., Gisin N., Guinnard O., Zbinden H. (1998). Elect. Lett. 34, 2116–2117
Deutsch D., Jozsa R. (1992). Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 439, 553
Bernstein E., Vazirani U.V. (1997). SIAM J. Comput. 26: 1411
Terhal B.M., Smolin J.A. (1998). Phys. Rev. A 58, 1822–1826
Brainis E., Lamoureux L.-P., Cerf N.J., Emplit Ph., Haelterman M., Massar S. (2003). Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 157902
Shor P. (1995). Phys. Rev. A 52: 2493
Bennett et al.C.H. (1996). Phys. Rev. Lett. 76: 722
Gisin N., Linden N., Massar S., Popescu S. (2005). Phys. Rev. A 72: 012338
Lamoureux L.-P., Brainis E., Cerf N.J., Emplit Ph., Haelterman M., Massar S. (2005). Phys. Rev. Lett., 94: 230501
Lamoureux L.P., Brainis E., Amans D., Barrett J., Massar S. (2005). Phys. Rev. Lett. 94: 050503
J. Barrett and S. Massar, Cheat Sensitive String Flipping, in preparation (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massar, S. Fiber Optics Protocols for Quantum Communication. Quantum Inf Process 5, 441–449 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-006-0029-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-006-0029-y
Keywords
- Quantum information
- quantum communication
- optical fibers
- Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm
- Bernstein-Vazirani algorithm
- error Filtration
- quantum coin tossing