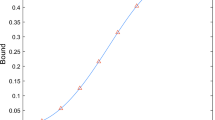
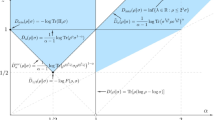
Abstract
In a recent paper, it was shown that the projections of a relativistic spin operator (RSO) massive spin-\({\frac{1}{2}}\) particle on a world-vector which can be in timelike or null tetrad direction are proportional to the helicity or Bargman-Wigner (BW) qubit, respectively. Here we consider Lorentz transformations of two-particle states, which have been constructed both in helicity basis. For convenience, instead of using the superposition of momenta we use only two momentum eigenstates (p 1 and p 2) for each particle. Consequently, in 2D momentum subspace we describe the structure of one particle in terms of the four-qubit system. We present a new approach to quantification of relativistic entanglement based on entanglement witness (EW), which is obtained by a new method of convex optimization. In addition, Lorentz invariance of entanglement using BW qubit is also studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Einstein A., Podolsky B., Rosen N.: Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete?. Phys. Rev. 47, 777 (1935)
Peres A., Scudo P.F., Terno D.R.: Quantum entropy and special relativity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 230402 (2002)
Harshman N.L.: Basis states for relativistic dynamically entangled particles. Phys. Rev. A 71, 022312 (2005)
Lee D., Chang-Young E.: Quantum entanglement under Lorentz boost. New J. Phys. 67, x022312 (2004)
Caban P., Rembielinski J.: Lorentz-covariant reduced spin density matrix and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen–Bohm correlations. Phys. Rev. A 72, 012103 (2005)
Bartlett S.D., Terno D.R.: Relativistically invariant quantum information. Phys. Rev. A 71, 012302 (2005)
Wigner E.P.: On unitary representations of the inhomogeneous Lorentz group. Ann. Math. 40, 149 (1939)
Gingrich R.M., Adami C.: Quantum entanglement of moving bodies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 27 (2002)
Terashimo, H., Ueda, M.: Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen correlation seen from moving observers. Quantum Info. Comput. 3’ 224-228 (2003)
Czachor M.: Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen–Bohm experiment with relativistic massive particles. Phys. Rev. A 55, 72 (1997)
Alsing P.M., Milburn G.J.: Lorentz Invariance of Entanglement. Quantum Info. Comput. 2, 487 (2002)
Ahn D., Lee H.-J., Moon Y.H., Hwang S.W.: Relativistic entanglement and Bell’s inequality. Phys. Rev. A 67, 012103 (2003)
Jafarizadeh M.A., Sufiani R.: Bell-states diagonal entanglement witnesses for relativistic and non-relativistic multispinor systems in arbitrary dimensions. Phys. Rev. A 77, 012105 (2008)
Lamata L., Martin-Delgado M.A.: Relativity and Lorentz invariance of entanglement distillability, E. Solano. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 250502 (2006)
Lamata L., Leon J., Salgado D.: Spin entanglement loss by local correlation transfer to the momentum. Phys. Rev. A 73, 052325 (2006)
Cai J.-M., Zhou Z.-W., Yuan Y.-F., Guo G.-C.: Quantum decoherence modulated by special relativity. Phys. Rev. A 76, 042101 (2007)
Doukas J., Hollenberg L.C.L.: Loss of spin entanglement for accelerated electrons in electric and magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. A 79, 052109 (2009)
Landulfo A.G.S., Matsas G.E.A.: Sudden death of entanglement and teleportation fidelity loss via the Unruh effect. Phys. Rev. A 80, 032315 (2009)
Czachor M., Wilczewski M.: Relativistic BB84, relativistic errors, and how to correct them. Phys. Rev. A 68, 010302(R) (2003)
Czachor, M.: arXiv:1002.0066v3
Czachor M.: Teleportation seen from space-time. Class. Quant. Grav. 25, 205003 (2008)
Czachor, M.: In Photon and Poincare Group, edited by V. V. Dvoeglazov, (Nova, NewYork, 1999) 32, hep-th/9701135
Peres A.: Separability criterion for density matrices A. Peres. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 1413 (1996)
Terhal B.M.: Bell inequalities and the separability criterion. Phys. Lett. A 271, 319 (2000)
Brandao F.G.S.L.: Quantifying entanglement with witness operators. Phys. Rev. A 72, 022310 (2005)
Bertlmann R.A., Durstberger K., Hiesmayr B.C., Krammer Ph.: Optimal entanglement witnesses for qubits and qutrits. Phys. Rev. A 72, 052331 (2005)
Bertlmann R.A., Narnhofer H., Thirring W.: A geometric picture of entanglement and Bell inequalities. Phys. Rev. A. 66, 032319 (2002)
Jafarizadeh M.A., Mahdian M.: Spin-momentum correlation in relativistic single particle quantum states. IJQI 8(3), 517–528 (2010)
Jafarizadeh M.A., Rezaee M., Seyed Yagoobi S.K.A.: Bell states diagonal entanglement witnesses. Phys. Rev. A 72, 062106 (2005)
Jafarizadeh M.A., Rezaee M., Ahadpour S.: Generalized qudit Choi maps. Phys. Rev. A 74, 042335 (2006)
Jafarizadeh M.A., Najarbashi G., Habibian H.: Manipulating multi-qudit entanglement witnesses by using linear programming. Phys. Rev. A 75, 052326 (2007)
Jafarizadeh M.A., Najarbashi G., Akbari Y., Habibian H.: Multi-qubit stabilizer and cluster entanglement witnesses. Eur. Phys. J. D 47, 233 (2008)
Clauser J.F., Horne M.A., Shimony A., Holt R.A.: Proposed experiment to test local hidden-variable theorie. Phys. Rev. Lett. 23, 880 (1969)
Hyllus P., Guehne O., Brus D., Lewenstein M.: Relations between entanglement witnesses and Bell inequalities. Phys. Rev. A 72, 012321 (2005)
Wootters W.K.: Entanglement of formation of an arbitrary state of two qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2245 (1998)
Rudin W.: Functional Analysis. McGraw-Hill, Singapore (1991)
Lewenstein, M., Bru, D., Cirac, J.I., Kraus, B., Kus, M., Samsonowicz, J., Sanpera, A., Tarrach, R.: Separability and distilability in composite quantum systems. J. Mod. Opt. 47, 2841 (2000)
Vianna R.O., Doherty A.C.: Study of the Distillability of Werner States Using Entanglement Witnesses and Robust Semidefinite Programs. Phys. Rev. A 74, 052306 (2006)
Pfeifer W.: The Lie Algebras su(N), An Introduction. Birkhauser, Switzerland (2003)
Fei S.-M., Jost J., Li-Jost X., Wang G.-F.: Entanglement of formation for a class of quantum states. Phys. Lett. A 310, 333–338 (2003)
Penrose R., Rindler W.: Spinors and Space-Time, vol.1: Two-Spinor Calculus and Relativistic Fields. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1984)
Weinberg S.: The Quantum Theory of Fields I. Cambridge University Press, NY (1995)
Boyd S., Vandenberghe L.: Convex Optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Hartmann A.K., Rieger H.: Optimization Algorithms in Physics. Wiley, Berlin (2002)
Chong E.K.P., Zak S.H.: An Introduction to Optimization. 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafarizadeh, M.A., Mahdian, M. Quantifying entanglement of two relativistic particles using optimal entanglement witness. Quantum Inf Process 10, 501–518 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-010-0206-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-010-0206-x