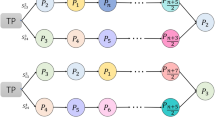
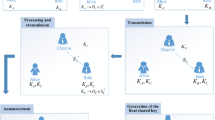
Abstract
Two conditions must be satisfied in a secure quantum key agreement (QKA) protocol: (1) outside eavesdroppers cannot gain the generated key without introducing any error; (2) the generated key cannot be determined by any non-trivial subset of the participants. That is, a secure QKA protocol can not only prevent the outside attackers from stealing the key, but also resist the attack from inside participants, i.e. some dishonest participants determine the key alone by illegal means. How to resist participant attack is an aporia in the design of QKA protocols, especially the multi-party ones. In this paper we present the first secure multiparty QKA protocol against both outside and participant attacks. Further more, we have proved its security in detail.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Menezes, A.J., van Oorscot, P.C., Vanstone, S.A.: Key establishment protocols. In: Handbook of Applied Cryptography. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1997)
Mitchell C.J., Ward M., Wilson P.: Key control in key agreement protocols. Electron. Lett. 34(10), 980–981 (1998)
Ateniese G., Steiner M., Tsudik G.: New multiparty authentication services and key agreement protocols. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 18(4), 628 (2000)
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings of 35th Annual Symposium on the Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 124–134, Santa Fe (1994)
Grover, L.K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of 28th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 212–219, New York (1996)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public-key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal, pp. 175–179, Bangalore (1984)
Jackson D.J., Hockney G.M.: Securing QKD links in the full Hilbert space. Quantum Inf. Process. 4, 35–47 (2005)
Brandt H.E.: Unambiguous state discrimination in quantum key distribution. Quantum Inf. Process. 4, 387–398 (2005)
Gao F., Guo F.Z., Wen Q.Y., Zhu F.C.: On the information-splitting essence of two types of quantum key distribution protocols. Phys. Lett. A 355, 172–175 (2006)
Huang W., Guo F.Z., Huang Z., Wen Q.Y., Zhu F.C.: Three-particle QKD protocol against a collective noise. Opt. Commun. 284(1), 536–540 (2011)
Liu B., Gao F., Wen Q.Y.: Single-photon multiparty quantum cryptographic protocols with collective detection. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 47, 1383–1390 (2011)
El Allati A., El Baz M., Hassouni Y.: Quantum key distribution via tripartite coherent states. Quantum Inf. Process. 10, 589–602 (2011)
Cleve R., Gottesman D., Lo H.K.: How to share a quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 648–651 (1999)
Hillery M., Buzěk V., Berthiaume A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829–1834 (1999)
Karlsson A., Koashi M., Imoto N.: Quantum entanglement for secret sharing and secret splitting. Phys. Rev. A 59, 162–168 (1999)
Gao F., Qin S.J., Wen Q.Y.: A simple participant attack on the Bradler–Dusek protocol. Quantum Inf. Comput. 7, 329–334 (2007)
Qin S.J., Gao F., Wen Q.Y., zhu F.C.: Cryptanalysis of the Hillery–Buzek–Berthiaume quantum secret-sharing protocol. Phys. Rev. A 76, 062324 (2007)
Song T.T., Zhang J., Gao F., Wen Q.Y., Zhu F.C.: Participant attack on quantum secret sharing based on entanglement swapping. Chin. Phys. B 18, 1333 (2009)
Guo F.Z., Qin S.J., Gao F., Lin S., Wen Q.Y., Zhu F.C.: Participant attack on a kind of MQSS schemes based on entanglement swapping. Eur. Phys. J. D 56, 445 (2010)
Yang Y., Wang Y., Chai H., Teng Y., Zhang H.: Member expansion in quantum (t,n) threshold secret sharing schemes. Opt. Commun. 284, 3479–3482 (2011)
Shi R.H., Zhong H.: Multiparty quantum secret sharing with the pure entangled two-photon states. Quantum Inf. Process. 11, 161–169 (2012)
Long G., Liu X.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum- key- distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Boström K., Felbinger T.: Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 187902 (2002)
Deng F., Long G., Liu X.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042317 (2003)
Gao F., Qin S.J., Wen Q.Y., Zhu F.C.: Cryptanalysis of multiparty controlled quantum secure direct communication using Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger state. Opt. Commun. 283, 192 (2010)
Yang Y.G., Cao W.F., Wen Q.Y.: Secure quantum private comparison. Phsy. Scr. 80, 065002 (2009)
Chen X.B., Xu G., Niu X.X., Wen Q.Y., Yang Y.X.: An efficient protocol for the private comparison of equal information based on the triplet entangled state and single-particle measurement. Opt. Commun. 283, 1161–1165 (2009)
Liu W., Wang Y.B., Jiang Z.T.: An efficient protocol for the quantum private comparison of equality with W state. Opt. Commun. 284, 3160–3163 (2011)
Tseng H.Y., Lin J., Hwang T.: New quantum private comparison protocol using EPR pairs. Quantum Inf. Process. 11, 373–384 (2011)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Jia, H.Y., Huang, W., Zhang, W.W., Wen, Q.Y.: Efficient quantum private comparison employing single photons and collective detection. Quantum Inf. Process. (2012). doi:10.1007/s11128-012-0439-y
Gao F., Wen Q.Y., Zhu F.C.: Comment on: “Quantum exam”. Phys. Lett. A 360, 748 (2007)
Gao F., Guo F.Z., Wen Q.Y., Zhu F.C.: Comment on “Experimental Demonstration of a Quantum Protocol for Byzantine Agreement and Liar Detection”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 208901 (2008)
Gisin N., Ribordy G., Tittel W., Zbinden H.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145–195 (2002)
Tajima A., Tanaka A., Maeda W., Takahashi S., Tomita A.: Practical quantum cryptosystem for metro area applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 13, 1031–1038 (2007)
Zhou N., Zeng G., Xiong J.: Quantum key agreement protocol. Electron. Lett. 40, 1149 (2004)
Chong S.K., Tsai C.W., Hwang T.: Improvement on quantum key agreement protocol with maximally entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50, 1793–1802 (2011)
Chong S.K., Hwang T.: Quantum key agreement protocol based on BB84. Opt. Commun. 283, 1192–1195 (2010)
Shi, R.H., Zhong, H.: Multi-party quantum key agreement with bell states and bell measurements. Quantum Inf. Process. doi:10.1007/s11128-012-0443-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W. et al. Multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles. Quantum Inf Process 12, 1797–1805 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-012-0492-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-012-0492-6