Abstract
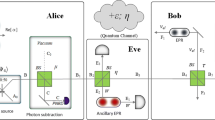
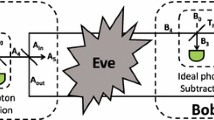
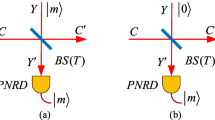
Motivated by a fact that the non-Gaussian operation may increase entanglement of an entangled system, we suggest a photon-monitoring attack strategy in the entanglement-based (EB) continuous-variable quantum key distribution (CVQKD) using the photon subtraction operations, where the entangled source originates from the center instead of one of the legal participants. It shows that an eavesdropper, Eve, can steal large information from participants after intercepting the partial beams with the photon-monitoring attach strategy. The structure of the proposed CVQKD protocol is useful in simply analyzing how quantum loss in imperfect channels can decrease the performance of the CVQKD protocol. The proposed attack strategy can be implemented under current technology, where a newly developed and versatile no-Gaussian operation can be well employed with the entangled source in middle in order to access to mass information in the EB CVQKD protocol, as well as in the prepare-and-measure (PM) CVQKD protocol.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nielsen, M., Chuang, I.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Scarani, V., Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H., Cerf, N.J., Dusek, M., Lutkenhaus, N., Peev, M.: The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1301 (2009)
Weedbrook, C., Pirandola, S., Garcáa-Patrón, R., Cerf, N.J., Ralph, T.C., Shapiro, J.H., Lloyd, S.: Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 621 (2012)
Grosshans, F., Van Assche, G., Wenger, J., Tualle-Brouri, R., Cerf, N.J., Grangier, P.: Virtual entanglement and reconciliation protocols for quantum cryptography with continuous variables. Nature 421, 238 (2003)
García-Patrón, R., Cerf, N.J.: Unconditional optimality of Gaussian attacks against continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 190503 (2006)
Navascués, M., Grosshans, F., Acín, A.: Optimality of Gaussian attacks in continuous-variable quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 190502 (2006)
Renner, R., Cerf, N.J.: de Finetti representation theorem for infinite-dimensional quantum systems and applications to quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 110504 (2009)
Grosshans, F., Grangier, P.: Continuous variable quantum cryptography using coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 057902 (2002)
Furrer, F., Franz, T., Bert, M., Leverrier, A., Scholz, V.B., Tomamichel, M., Werner, R.F.: Continuous variable quantum key distribution: finite-key analysis of composable security against coherent attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 100502 (2012)
Weedbrook, C., Lance, A.M., Bowen, W.P., Symul, T., Ralph, T.C., Lam, P.K.: Quantum cryptography without switching. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 170504 (2004)
Leverrier, A., García-Patrón, R., Renner, R., Cerf, N.J.: Security of continuous-variable quantum key distribution against general attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 030502 (2013)
Madsen, L.S., Usenko, V.C., Lassen, M., Filip, R., Andersen, U.L.: Continuous variable quantum key distribution with modulated entangled states. Nat. Commun. 3, 1083 (2012)
Leverrier, A., Grangier, P.: Unconditional security proof of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution with discrete modulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 180504 (2009)
Jouguet, P., Kunz-Jacques, S., Leverrier, A.: Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a Gaussian modulation. Phys. Rev. A 84, 062317 (2011)
Yang, J., Xu, B., Guo, H.: Source monitoring for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 86, 042314 (2012)
Takahashi, H., Neergaard-Nielsen, J.S., Takeuchi, M., Takeoka, M., Hayasaka, K., Furusawa, A., Sasaki, M.: Entanglement distillation from Gaussian input states. Nat. Photon. 4, 178 (2010)
Leverrier, A., Grangier, P.: Continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution protocols with a non-Gaussian modulation. Phys. Rev. A 83, 042312 (2011)
Kim, H.-J., Lee, S.-Y., Ji, S.-W., Nha, H.: Quantum linear amplifier enhanced by photon subtraction and addition. Phys. Rev. A 85, 013839 (2012)
Lee, S.-Y., Ji, S.-W., Kim, H.-J., Nha, H.: Enhancing quantum entanglement for continuous variables by a coherent superposition of photon subtraction and addition. Phys. Rev. A 84, 012302 (2011)
García-Patrón, R., Cerf, N.:Quantum information with optical continuous variables: from bell tests to key distribution/information Quantique avec Variables Continues Optiques: des Tests de Bell à la Distribution de Clé
Huang, P., He, G., Fang, J., Zeng, G.: Performance improvement of continuous-variable quantum key distribution via photon subtraction. Phys. Rev. A 87, 012317 (2013)
Peres, A.: Separability criterion for density matrices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 1413 (1996)
Vidal, G., Werner, R.F.: Computable measure of entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032314 (2002)
Weedbrook, C.: Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with entanglement in the middle. Phys. Rev. A 87, 022308 (2013)
Grosshans, F., Cerf, N.J., Wenger, J., Tualle-Brouri, R., Grangier, P.: Virtual entanglement and reconciliation protocols for quantum cryptography with continuous variables. Quantum Inf. Comput. 3, 535 (2003)
Kitagawa, A., Takeoka, M., Sasaki, M., Chefles, A.: Entanglement evaluation of non-Gaussian states generated by photon subtraction from squeezed states. Phys. Rev. A 73, 042310 (2006)
Ourjoumtsev, A., Dantan, A., Tualle-Brouri, R., Grangier, P.: Increasing entanglement between Gaussian states by coherent photon subtraction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 030502 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61272495, 61379153), the postdoctoral science foundation of China (2013M542119), and partly by Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (13A010) and the construct program of the key discipline in Hunan province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Huang, P., Guo, Y. et al. Photon-monitoring attack on continuous-variable quantum key distribution with source in middle. Quantum Inf Process 13, 2745–2757 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0821-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0821-z