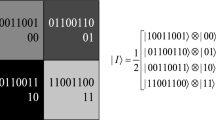
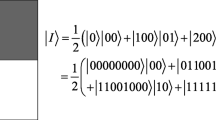Abstract
Quantum morphology operations are proposed based on the novel enhanced quantum representation model. Two kinds of quantum morphology operations are included: quantum binary and grayscale morphology operations. Dilation and erosion operations are fundamental to morphological operations. Consequently, we focus on quantum binary and flat grayscale dilation and erosion operations and their corresponding circuits. As the basis of designing of binary morphology operations, three basic quantum logic operations AND, OR, and NOT involving two binary images are presented. Thus, quantum binary dilation and erosion operations can be realized based on these logic operations supplemented by quantum measurement operations. As to the design of flat grayscale dilation and erosion operations, the searching for maxima or minima in a certain space is involved; here, we use Grover’s search algorithm to get these maxima and minima. With respect that the grayscale is represented by quantum bit string, the quantum bit string comparator is used as an oracle in Grover’s search algorithm. In these quantum morphology operations, quantum parallelism is well utilized. The time complexity analysis shows that quantum morphology operations’ time complexity is much lower or equal to the classical morphology operations.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University, Cambrige (2000)
Tseng, C.C., Hwang, T.M.: Quantum circuit design of \(8\times 8\) discrete cosine transforms using its fast computation flow graph. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, ISCAS, pp. 828–831 (2005)
Fijany, A., Wiliams, C.P.: Quantum Wavelet Transform: Fast Algorithm and Complete Circuits. Springer, Berlin (1999)
Venegas-Andraca, S.E., Bose, S.: Storing, processing and retrieving an image using quantum mechanics. In: AeroSense 2003, International Society for Optics and Photonics, pp. 137–147 (2003)
Yuan, S.Z., Mao, X., Xue, Y.L., et al.: SQR: a simple quantum representation of infrared images. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(6), 1353–1379 (2014)
Le, P.Q., Dong, F., Hirota, K.: A flexible representation of quantum images for polynomial preparation, image compression and processing operations. Quantum Inf. Process. 10, 63–84 (2011)
Zhang, Y., Lu, K., Gao, Y., Wang, M.: NEQR: a novel enhanced quantum representation of digital images. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 2833–2860 (2013)
Childs, A.M., Leung, D.W., Nielsen, M.A.: Unified derivations of measurement-based schemes for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 71(032318), 1–14 (2005)
Le, P.Q., Iliyasy, A.M., Dong, F., Hirota, K.: Fast geometric transformations on quantum images. IAENG Int. J. Appl. Math. 40(3), 113–123 (2010)
Le, P.Q., Iliyasy, A.M., Dong, F., Hirota, K.: Efficient color transformations on quantum images. JACIII 15(6), 698–706 (2011)
Iliyasu, A.M., Le, P.Q., Dong, F., Hirota, K.: Watermarking and authentication of quantum images based on restricted geometric transformations. Inf. Sci. 186(1), 126–149 (2011)
Iliyasu, A.M., Le, P.Q., Dong, F., Hirota, K.: A framework for representing and producing movies on quantum computers. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 9(6), 1459–1497 (2011)
Barenco, A., Bennett, C.H., Cleve, R., et al.: Elementary gates for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 52(5), 3457–3488 (1995)
Gonzalez, R.C., Wood, R.E.: Digital Image Processing, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (2002)
Gómez-Muñoz, J.L.: A free Mathematica ‘Quantum’ add-on, Version 2.3.0. http://homepage.cem.itesm.mx/lgomez/quantum/ (2011)
Mertens, S.: Computational complexity for physicists. Comput. Sci. Eng. 4(3), 31–47 (2002)
Oliveira, D.S., Ramos, R.V.: Quantum bit string comparator: circuits and applications. Quantum Comput. Comput. 7(1), 17–26 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20121102130001), the Innovation Foundation of BUAA for Ph.D. Graduates, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61103097).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, S., Mao, X., Li, T. et al. Quantum morphology operations based on quantum representation model. Quantum Inf Process 14, 1625–1645 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0862-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0862-3