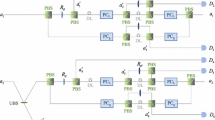
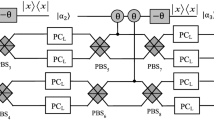
Abstract
Hyperentanglement has attracted much attention in recent years for its promising applications. Various schemes on topics of manipulating, concentrating, and purifying hyperentangled photons have been discussed widely using nonlinear optics. However, the fidelities and experimental feasibilities are unsatisfied due to the low efficiency of the nonlinear optical process. In order to overcome this problem, we present an one-step hyperentanglement purification protocol with linear optics for non-local photon systems in mixed polarization- and spatial-mode- hyperentangled states. Errors in both polarization and spatial-mode degrees of freedom can be purified simultaneously with the assistance of W-states. We also discuss the efficiencies and experimental feasibilities of this linear optics-based protocol.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and einstein-podolsky-rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70(13), 1895 (1993)
Bennett, C.H., Wiesner, S.J.: Communication via one-and two-particle operators on einstein-podolsky-rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69(20), 2881 (1992)
Liu, X., Long, G., Tong, D., Li, F.: General scheme for superdense coding between multiparties. Phys. Rev. A 65(2), 022304 (2002)
Raussendorf, R., Briegel, H.J.: A one-way quantum computer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86(22), 5188 (2001)
Kwiat, P.G.: Hyper-entangled states. J. Mod. Opt. 44(11–12), 2173–2184 (1997)
Mair, A., Vaziri, A., Weihs, G., Zeilinger, A.: Entanglement of the orbital angular momentum states of photons. Nature 412(6844), 313–316 (2001)
Fiorentino, M., Wong, F.N.: Deterministic controlled-not gate for single-photon two-qubit quantum logic. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93(7), 070502 (2004)
Ali-Khan, I., Broadbent, C.J., Howell, J.C.: Large-alphabet quantum key distribution using energy-time entangled bipartite states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(6), 060503 (2007)
Menicucci, N.C., Flammia, S.T., Pfister, O.: One-way quantum computing in the optical frequency comb. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101(13), 130501 (2008)
Barreiro, J.T., Wei, T.C., Kwiat, P.G.: Beating the channel capacity limit for linear photonic superdense coding. Nat. Phys. 4(4), 282–286 (2008)
Ramelow, S., Ratschbacher, L., Fedrizzi, A., Langford, N., Zeilinger, A.: Discrete tunable color entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103(25), 253601 (2009)
Yan, H., Zhang, S., Chen, J., Loy, M., Wong, G.K., Du, S.: Generation of narrow-band hyperentangled nondegenerate paired photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106(3), 033601 (2011)
Wang, C., Deng, F.G., Li, Y.S., Liu, X.S., Long, G.L.: Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum superdense coding. Phys. Rev. A 71(4), 044305 (2005)
Kwiat, P.G., Weinfurter, H.: Embedded bell-state analysis. Phys. Rev. A 58(4), R2623 (1998)
Walborn, S., Pádua, S., Monken, C.: Hyperentanglement-assisted bell-state analysis. Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042313 (2003)
Schuck, C., Huber, G., Kurtsiefer, C., Weinfurter, H.: Complete deterministic linear optics bell state analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(19), 190501 (2006)
Barbieri, M., Vallone, G., Mataloni, P., De Martini, F.: Complete and deterministic discrimination of polarization bell states assisted by momentum entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 75(4), 042317 (2007)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G.: Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal bell-state analysis with hyperentanglement. Phys. Rev. A 81(3), 032307 (2010)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G.: One-step deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82(4), 044305 (2010)
Li, X.H.: Deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82(4), 044304 (2010)
Deng, F.G.: One-step error correction for multipartite polarization entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 83(6), 062316 (2011)
Wang, T.J., Wang, C.: Parallel quantum computing teleportation for spin qubits in quantum dot and microcavity coupled system. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 21(3), 1–7 (2015)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B., Smolin, J.A., Wootters, W.K.: Purification of noisy entanglement and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76(5), 722 (1996)
Deutsch, D., Ekert, A., Jozsa, R., Macchiavello, C., Popescu, S., Sanpera, A.: Quantum privacy amplification and the security of quantum cryptography over noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(13), 2818 (1996)
Pan, J.W., Simon, C., Brukner, Č., Zeilinger, A.: Entanglement purification for quantum communication. Nature 410(6832), 1067–1070 (2001)
Simon, C., Pan, J.W.: Polarization entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89(25), 257901 (2002)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Efficient polarization-entanglement purification based on parametric down-conversion sources with cross-kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. A 77(4), 042308 (2008)
Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Özdemir, Ş.K., Imoto, N.: Experimental extraction of an entangled photon pair from two identically decohered pairs. Nature 421(6921), 343–346 (2003)
Ren, B.C., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement purification and concentration assisted by diamond nv centers inside photonic crystal cavities. Laser Phys. Lett. 10(11), 115201 (2013)
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement concentration for two-photon four-qubit systems with linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 88(1), 012302 (2013)
Wang, T.J., Cao, C., Wang, C.: Linear-optical implementation of hyperdistillation from photon loss. Phys. Rev. A 89, 052303 (2014)
Rohde, P.P., Ralph, T.C., Munro, W.J.: Practical limitations in optical entanglement purification. Phys. Rev. A 73(3), 030301 (2006)
Briegel, H.J., Dür, W., Cirac, J.I., Zoller, P.: Quantum repeaters: the role of imperfect local operations in quantum communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81(26), 5932–5935 (1998)
Wang, H.F., Zhang, S.: Linear optical generation of multipartite entanglement with conventional photon detectors. Phys. Rev. A 79(4), 042336 (2009)
Wang, H.F., Zhang, S., Zhu, A.D., Yi, X.X., Yeon, K.H.: Local conversion of four einstein-podolsky-rosen photon pairs into four-photon polarization-entangled decoherence-free states with non-photon-number-resolving detectors. Opt. Express 19(25), 25433–25440 (2011)
Zou, X., Pahlke, K., Mathis, W.: Generation of an entangled four-photon w state. Phys. Rev. A 66(4), 044302 (2002)
Tashima, T., Özdemir, Ş.K., Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Elementary optical gate for expanding an entanglement web. Phys. Rev. A 77(3), 030302 (2008)
Bugu, S., Yesilyurt, C., Ozaydin, F.: Enhancing the w-state quantum-network-fusion process with a single fredkin gate. Phys. Rev. A 87(3), 032331 (2013)
Tashima, T., Wakatsuki, T., Özdemir, Ş.K., Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Local transformation of two einstein-podolsky-rosen photon pairs into a three-photon w state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102(13), 130502 (2009)
Yesilyurt, C., Bugu, S., Ozaydin, F.: An optical gate for simultaneous fusion of four photonic w or bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(9), 2965–2975 (2013)
Ozaydin, F., Bugu, S., Yesilyurt, C., Altintas, A.A., Tame, M., Özdemir, Ş.K.: Fusing multiple w states simultaneously with a fredkin gate. Phys. Rev. A 89, 042311 (2014)
Kok, P., Munro, W.J., Nemoto, K., Ralph, T.C., Dowling, J.P., Milburn, G.: Linear optical quantum computing with photonic qubits. Rev. Mod. Phys. 79(1), 135 (2007)
Calkins, B., Mennea, P.L., Lita, A.E., Metcalf, B.J., Kolthammer, W.S., Lamas-Linares, A., Spring, J.B., Humphreys, P.C., Mirin, R.P., Gates, J.C., Smith, P.G.R., Walmsley, I.A., Gerrits, T., Nam, S.W.: High quantum-efficiency photon-number-resolving detector for photonic on-chip information processing. Opt. Express 21(19), 22657–22670 (2013)
E, K.B., L, Y.Z., J, S.A.: An avalanche-photodiode-based photon-number-resolving detector. Nat. Photon. 2(7), 425–428 (2008)
Bimbard, E., Boddeda, R., Vitrant, N., Grankin, A., Parigi, V., Stanojevic, J., Ourjoumtsev, A., Grangier, P.: Homodyne tomography of a single photon retrieved on demand from a cavity-enhanced cold atom memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 033601 (2014)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by China National Natural Science Foundation Grant Nos. 11347211, 61471050 and 11404031. Beijing Higher Education Young Elite Teacher Project No. YETP0456, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities No. 2014RC0903.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mi, S., Wang, C. & Wang, TJ. Hyperentanglement purification with linear optics assisted by W-states. Quantum Inf Process 14, 623–634 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0878-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0878-8