Abstract
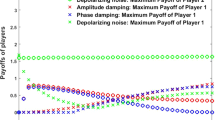
In this paper, an efficient method is proposed to improve the payoffs of cooperators in cooperative three-player quantum game under the action of amplitude damping, bit flip and depolarizing channels using weak measurements. It is shown that the payoffs of cooperators can be enhanced to a great extent in the case of amplitude damping channel, and the payoff sudden death can be avoided in the case of bit flip and depolarizing channels. Moreover, the payoffs of cooperators tend to a constant by changing weak measurement strength in spite of sufficiently strong decoherence.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
von-Neumann, J., Morgenstein, O.: The Theory of Games and Economic Behaviour. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ (1944)
Nash, J.: Equilibrium points in n-person games. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 36, 48 (1950)
Meyer, D.A.: Quantum strategies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 1052 (1999)
Eisert, J., Wilkens, M., Lewenstein, M.: Quantum games and quantum strategies. Phy. Rev. Lett. 83, 3077 (1999)
Marinatto, L., Weber, T.: A quantum approach to static games of complete information. Phys. Lett. A 272, 291 (2000)
Flitney, A.P., Abbott, D.: Quantum games with decoherence. J. Phys. A 38, 449 (2005)
Cheon, T., Iqbal, A.: Bayesian Nash equilibria and Bell inequalities. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 77, 024801 (2008)
Iqbal, A., Abbott, D.: Quantum matching pennies game. J. Phy. Soc. Jpn. 78, 014803 (2009)
Iqbal, A., Cheon, T., Abbott, D.: Probabilistic analysis of three-player symmetric quantum games played using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen–Bohm setting. Phys. Lett. A 372, 6564 (2008)
Iqbal, A., Toor, A.H.: Evolutionarily stable strategies in quantum games. Phys. Lett. A 280, 249 (2001)
Flitney, A.P., Abbott, D.: Quantum version of the Monty Hall problem. Phys. Rev. A 65, 062318 (2002)
Iqbal, A., Toor, A.H.: Quantum mechanics gives stability to Nash equilibrium. Phys. Rev. A 65, 022036 (2002)
Eisert, J., Wilkens, M.: Quantum games. J. Mod. Opt. 47, 2543 (2000)
Ramzan, M., Khan, M.K.: Noise effects in a three-player Prisoner’s dilemma quantum game. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 41, 435302 (2008)
Flitney, A.P., Ng, J., Abbott, D.: Quantum Parrondo’s games. Phys. A 314, 35 (2002)
Iqbal, A., Toor, A.H.: Quantum cooperative games. Phys. Lett. A 293, 103 (2002)
Johnson, N.F.: Playing a quantum game with a corrupted source. Phys. Rev. A 63, 020302(R) (2001)
DAriano, G.M., Gill, R.D., Keyl, M., Kuemmerer, B., Maassen, H., Werner, R.F.: The quantum Monty Hall problem. Quant. Inf. Comp. 2, 355 (2002)
Miszczak, J.A., Gawron, P., Puchala, Z.: Qubit flip game on a Heisenberg spin chain. arXiv:1108.0642 [quant-ph], (2011)
Puya, S., Hoshang, H.: Quantum solution to a three player Kolkata restaurant problem using entangled qutrits. arXiv:1111.1962 [quant-ph], (2011)
Chakrabarti, A.S., Chakrabarti, B.K., Chatterjee, A., Mitra, M.: The Kolkata paise restaurant problem and resource utilization. Phys. A 388, 2420–2426 (2009)
Benjamin, S.C., Hayden, P.M.: Multiplayer quantum games. Phys. Rev. A 64, 030301(R) (2001)
Chen, Q., Wang, Y.: N-player quantum minority game. Phys. Lett. A A 327, 98,102 (2004)
Flitney, A.P., Greentree, A.D.: Coalitions in the quantum Minority game: classical cheats and quantum bullies. Phys. Lett. A 362, 132 (2007)
Schmid, C., Flitney, A.P.: Experimental implementation of a four-player quantum game. arXiv:0901.0063v1 [quant-ph], (2008)
Flitney, A.P., Hollenberg, L.C.L.: Multiplayer quantum minority game with decoherence. Quantum Inf. Comput. 7, 111 (2007)
Flitney, A.P., Abbott, D.: Quantum games with decoherence. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 38, 449 (2005)
Khan, S., Ramzan, M., Khan, M.K.: Quantum Parrondos games under decoherence. Int. J. Theor. Phys 49, 31 (2010)
Khan, S., Ramzan, M., Khan, M.K.: Quantum Monty Hall problem under decoherence. Commun. Theor. Phys. 54, 47 (2010)
Gawron, P., Miszczak, J.A., Sladkowski, J.: Noise effects in quantum magic squares game. Int. J. Quant. Inf. 6, 667 (2008)
Gawron, P.: Noisy quantum Monty Hall game. Fluct. Noise Lett. 9, 9 (2010)
Chen, L.K., Ang, H., Kiang, D., Kwek, L.C., Lo, C.F.: Quantum prisoner dilemma under decoherence. Phys. Lett. A 316, 317 (2003)
Zhu, X., Kuang, L.M.: The influence of entanglement and decoherence on the quantum Stackelberg duopoly game. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 40, 7729 (2007)
Ramzan, M., Nawaz, A., Toor, A.H., Khan, M.K.: The effect of quantum memory on quantum games. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 41, 055307 (2008)
Ramzan, M.: Three-player quantum Kolkata restaurant problem under decoherence. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(1), 577–586 (2013)
Khan, S., Ramzan, M., Khan, M.K.: Decoherence effects on multiplayer cooperative quantum games. Commun. Theor. Phys. 56, 228–234 (2011)
Gawron, P., Kurzyk, D., Pawela, L.: Decoherence effects in the quantum qubit flip game using Markovian approximation. Quantum. Inf. Process. 13, 665–682 (2014)
Aharonov, Y., Albert, D.Z., Vaidman, L.: How the result of a measurement of a component of the spin of a spin-1/2 particle can turn out to be 100. Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 1351 (1988)
Aharonov, Y., Botero, A., Pospescu, S., Reznik, B., Tollaksen, J.: Revisiting Hardy’s paradox: counterfactual statements, real measurements, entanglement and weak values. Phys. Lett. A 301, 130 (2002)
Lundeen, J.S., Steinberg, A.M.: Experimental joint weak measurement on a photon pair as a probe of Hardys paradox. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 020404 (2009)
Yokota, K., Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Direct observation of Hardy’s paradox by joint weak measurement with an entangled photon pair. N. J. Phys. 11, 033011 (2009)
Korotkov, A.N., Jordan, A.N.: Undoing a weak quantum measurement of a solid-state qubit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 166805 (2006)
Kim, Y.S., Cho, Y.W., Ra, Y.S., Kim, Y.H.: Reversing the weak quantum measurement for a photonic qubit. Opt. Express 17, 11978 (2009)
Lee, J.C., Jeong, Y.C., Kim, Y.S., Kim, Y.H.: Experimental demonstration of decoherence suppression via quantum measurement reversal. Opt. Express 19, 16309 (2011)
Kim, Y.S., Lee, J.C., Kwon, O., Kim, Y.H.: Protecting entanglement from decoherence using weak measurement and quantum measurement reversal. Nat. Phys. 8, 117 (2012)
Man, Z.X., Xia, Y.J., An, N.B.: Enhancing entanglement of two qubits undergoing independent decoherences by local pre- and postmeasurements. Phys. Rev. A 86, 052322 (2012)
Burger, E., Freund, J.E.: Introduction to the Theory of Games. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1963)
Wang, S.C., Yu, Z.W., Zou, W.J., Wang, X.B.: Protecting quantum states from decoherence of finite temperature using weak measurement. Phys. Rev. A 89, 022318 (2014)
Du, J., Li, H., Xu, X., Shi, M., Wu, J., Zhou, X., Han, R.: Experimental realization of quantum games on a quantum computer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 137902 (2002)
Prevedel, R., Stefanov, A., Walther, P., Zeilinger, A.: Experimental realization of a quantum game on a one-way quantum computer. N. J. Phys. 9, 205 (2007)
Kolenderski, P., Sinha, U., Youning, L., Zhao, T., Volpini, M., Cabello, A., Laflamme, R., Jennewein, T.: Aharon–Vaidman quantum game with a Young-type photonic qutrit. Phys. Rev. A 86, 012321 (2012)
Korotkov, A.N., Jordan, A.N.: Undoing a weak quantum measurement of a solid-state qubit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 166805 (2006)
Katz, N., Neeley, M., Ansmann, M., Bialczak, R.C., Hofheinz, M., Lucero, E., OConnell, A., Wang, H., Cleland, A.N., Martinis, J.M., Korotkov, A.N.: Reversal of the weak measurement of a quantum state in a superconducting phase qubit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 200401 (2008)
Kim, Y.S., Cho, Y.W., Ra, Y.S., Kim, Y.H.: Reversing the weak quantum measurement for a photonic qubit. Opt. Express 17, 11978 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.11374096) and the Major Program for the Research Foundation of Education Bureau of Hunan Province of China (Grant No. 10A026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1
In this Appendix, we present the payoff function of cooperators A and B by using Eq. (5) for the amplitude damping channel using weak measurements as follows:
When the initial state is maximally entangled, i.e., \(Q=\pi /2\), we obtain the payoff function Eq. (10).
Appendix 2
In this Appendix, we present the payoff function of cooperators A and B by using Eq. (5) for the bit flip channel using weak measurements as follows:
When the initial state is maximally entangled, i.e., \(Q=\pi /2\), we obtain the payoff function Eq. (16).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, XP., Ding, XZ. & Fang, MF. Improving the payoffs of cooperators in three-player cooperative game using weak measurements. Quantum Inf Process 14, 4395–4412 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-015-1144-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-015-1144-4