Abstract
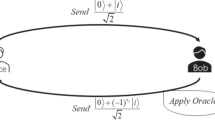
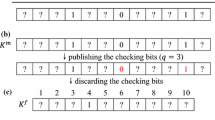
The point-inclusion problem is an important secure multi-party computation that it involves two parties, where one has a private point and the other has a private area, and they want to determine whether the point is inside the area without revealing their respective private information. All previously proposed point-inclusion protocols are only suitable for a specific area, such as circle, rectangle and convex polygon. In this paper, we present a novel privacy-preserving point-inclusion quantum protocol for an arbitrary area, which is surrounded by any plane geometric figure. Compared to the classical related protocols, our protocol has the advantages of the higher security and the lower communication complexity.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Yao, A.: Protocols for secure computations. In: Proceedings of 23rd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS ’82), Chicago, USA, pp. 160–164. IEEE Computer Society Press, New York (1982)
Atallah, M.J., Du, W.: Secure multi-party computational geometry. In: Proceedings of 7th International Workshop on Algorithms and Data Structures, pp. 165–179. Springer, Providence (2001)
Luo, Y., Huang, L., Zhong, H., et al.: A secure protocol for determining whether a point is inside a convex polygon. Chin. J. Electron. 15(4), 578–582 (2006)
Troncoso-Pastoriza, J.R., Katzenbeisser, S., Celik, M., et al.: A secure multidimensional point inclusion protocol. In: Proceedings of 9th ACM Multimedia and Security Workshop (MM&SEC’07), Dallas, TX, Assoc Computing Machinery, pp. 109–119 (2007)
Ye, Y., Huang, L., Yang, W., et al.: Efficient secure protocols to determine whether a point is inside a convex hull. In: Proceedings of 1st International Symposium on Information Engineering and Electronic Commerce (IEEC 2009), Ternopil, Ukraine, IEEE Computer Soc., pp. 100–105 (2009)
Li, S., Wang, D., Dai, Y.: Efficient secure multiparty computational geometry. Chin. J. Electron. 19(2), 324–328 (2010)
Shor, P. W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete log and factoring. In: Proceedings of 35th Annual Symposium on the Foundations of Computer Science, Santa Fe, New Mexico, pp. 124–134. IEEE, New York (1994)
Grover, L. K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of 28th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Coimbra, Portugal, pp. 212–219. ACM, New York (1996)
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L.: Quantum private queries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 230502 (2008)
Olejnik, L.: Secure quantum private information retrieval using phase-encoded queries. Phys. Rev. A 84, 022313 (2011)
Shi, R.-H., Mu, Y., Zhong, H., Zhang, S.: Quantum oblivious set-member decision protocol. Phys. Rev. A 92, 022309 (2015)
Shi, R.-H., Mu, Y., Zhong, H., Cui, J., Zhang, S.: An efficient quantum scheme for Private Set Intersection. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(1), 363–371 (2016)
Weimann, S., Perez-Leija, A., Lebugle, M., et al.: Implementation of quantum and classical discrete fractional fourier transforms. Nat. Commun. 7, 11027 (2016)
Dogra, S., Dorai, A., Dorai, K.: Implementation of the quantum Fourier transform on a hybrid qubit-qutrit NMR quantum emulator. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 13(7), 1550059 (2015)
Li, Y.L., Huang, J.S., Xu, Z.H.: Implementation of a remote three-qubit controlled-Z gate via quantum zeno dynamics. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54(5), 1680–1688 (2015)
Li, W.A., Wei, L.F.: One-step implementation of quantum controlled-phase gate via quantum zeno dynamics. Quantum Inf. Compt. 14(1–2), 137–143 (2014)
Dong, D., Zhang, Y.L., Zou, C.L., et al.: Scheme for purifying a general mixed entangled state and its linear optical implementation. Chin. Phys. B 24(10), 100306 (2015)
Smania, M., Elhassan, A.M., Tavakoli, A., Bourennane, M.: Experimental quantum multiparty communication protocols. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2, 16010 (2016)
Chen, Y.H., Xia, Y., Chen, Q.Q., et al.: Fast and noise-resistant implementation of quantum phase gates and creation of quantum entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 91(1), 012325 (2015)
Liu, H.W., Wang, F., Li, H.R., et al.: Optimal bipartite entanglement transfer and photonic implementations. Opt. Commun. 334(1), 273–279 (2015)
Meng, F., Zhu, A., Yeon, K.H., et al.: Preparation of multipartite entangled states and one-step implementation of 1 \(\rightarrow \) M economical phase-covariant quantum anti-cloning in cavity QED. Phys. Scr. 81(1), 015009 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61173187, 61572001), Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (20133401110004), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1408085QF107), Talents Youth Fund of Anhui Province Universities (2013SQRL006ZD), 211 Project of Anhui University (17110099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Rh., Mu, Y., Zhong, H. et al. Privacy-preserving point-inclusion protocol for an arbitrary area based on phase-encoded quantum private query. Quantum Inf Process 16, 8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1476-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1476-8