Abstract
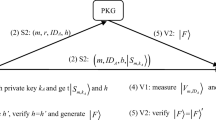
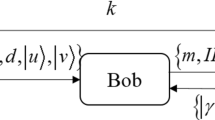
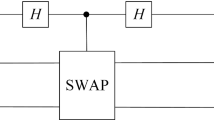
A quantum digital signature scheme is firstly proposed based on public-key quantum cryptosystem. In the scheme, the verification public-key is derived from the signer’s identity information (such as e-mail) on the foundation of identity-based encryption, and the signature private-key is generated by one-time pad (OTP) protocol. The public-key and private-key pair belongs to classical bits, but the signature cipher belongs to quantum qubits. After the signer announces the public-key and generates the final quantum signature, each verifier can verify publicly whether the signature is valid or not with the public-key and quantum digital digest. Analysis results show that the proposed scheme satisfies non-repudiation and unforgeability. Information-theoretic security of the scheme is ensured by quantum indistinguishability mechanics and OTP protocol. Based on the public-key cryptosystem, the proposed scheme is easier to be realized compared with other quantum signature schemes under current technical conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Okamoto, T., Tanaka, K., Uchiyama, S.: Quantum public-key cryptosystems. In: Bellare, M. (ed.) Advances in Cryptology–CRYPTO 2000. LNCS, vol. 1880, pp. 147–165. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Nikolopoulos, G.M.: Applications of single-qubit rotations in quantum public-key cryptography. Phys. Rev. A 77(3), 032348 (2008)
Seyfarth, U., Nikolopoulos, G.M., Alber, G.: Symmetries and security of a quantum-public-key encryption based on single-qubit rotations. Phys. Rev. A 85(2), 022342 (2012)
Yang, L., Liang, M., Li, B., Hu, L., Feng, D. G.: Quantum public-key cryptosystems based on induced trapdoor one-way transformations. arXiv:quant-ph/1012.5249 (2011)
Pan, J., Yang, L.: Quantum public-key encryption with information theoretic security. In: Proceedings of SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, p. 8440 (2012)
Yang, L., Yang, B., Xiang, C.: Quantum public-key encryption schemes based on conjugate coding. arXiv:quant-ph/1112.0421 (2013)
Li, X.Y., Zhang, D.: Quantum public-key cryptosystem based on super dense coding technology. J. Comput. 8(12), 3168 (2013)
Gottesman, D., Chuang, I.: Quantum digital signatures. arXiv:quant-ph/0105032 (2001)
Lamport, L.: Constructing digital signatures from a one-way function. In: Technical Report CSL-98, SRI International (1979)
Zeng, G.H., Keitel, C.H.: Arbitrated quantum-signature scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65(4), 042312 (2002)
Lee, H., Hong, C.H., Kim, H., Lim, J., Yang, H.J.: Arbitrated quantum signature scheme with message recovery. Phys. Lett. A 321(5), 295–300 (2004)
Lu, X., Feng, D.G.: An arbitrated quantum message signature scheme. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 3314, pp. 1054–1060. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Lu, X., Feng, D.G.: Quantum digital signature based on quantum one-way functions. In: The International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology, Vol. 1, pp. 514–517. IEEE (2004)
Yang, Y.G., Wen, Q.Y.: Arbitrated quantum signature of classical messages against collective amplitude damping noise. Opt. Commun. 283(16), 3198–3201 (2010)
Yang, Y.G., Wen, Q.Y.: Erratum: arbitrated quantum signature of classical messages against collective amplitude damping noise. Opt. Commun. 283(19), 3830 (2010)
Luo, Y.P., Hwang, T.: Arbitrated quantum signature of classical messages without using authenticated classical channels. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(1), 113–120 (2013)
Li, Q., Li, C., Wen, Z., Zhao, W., Chan, W.H.: On the security of arbitrated quantum signature schemes. J. Phys. A-Math. Theor. 46(1), 015307 (2012)
Dunjko, V., Wallden, P., Andersson, E.: Quantum digital signatures without quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112(4), 040502 (2014)
Collins, R.J., Donaldson, R.J., Dunjko, V., Wallden, P., Clarke, P.J., Andersson, E., et al.: Realization of quantum digital signatures without the requirement of quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113(4), 040502 (2014)
Amiri, R., Wallden, P., Kent, A., Andersson, E.: Secure quantum signatures using insecure quantum channels. Phys. Rev. A 93(3), 032325 (2016)
Shamir, A.: Identity-Based Cryptosystems and Signature Schemes. In: The Workshop on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic Techniques, Vol. 21, pp. 47–53. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (1984)
Boneh, D., Franklin, M.: Identity based encryption from the weil pairing. SIAM J. Comput. 32(3), 213–229 (2001)
Shannon, C.E.: Communication theory of secrecy systems. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 28, 656–715 (1949)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information, pp. 531–536. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Boykin, P.O., Roychowdhury, V.: Optimal encryption of quantum bits. Phys. Rev. A 67(4), 042317 (2003)
Zhou, N.Y., Liu, Y., Zeng, G.H., Xiong, J., Zhou, F.C.: Novel qubit block encryption algorithm with hybrid keys. Phys. A 375(2), 693–698 (2007)
Buhrman, H., Cleve, R., Watrous, J., de Wolf, R.: Quantum fingerprinting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87(16), 167902 (2001)
Menezes, A.J., Oorschot, P.V., Vanstone, S.A.: Handbook of Applied Cryptography. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1996)
Goldreich, O.: Foundations of Cryptography: Basic Applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Pan, J., Yang, L.: Quantum public-key encryption with information theoretic security. In: Proceedings of SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, p. 8440 (2010)
Yang, L., Xiang, C., Li, B.: Quantum probabilistic encryption scheme based on conjugate coding. China Commun. 10(2), 19–26 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of the Education Department of Anhui Province (Grant Nos. KJ2015A266, KJ2014A144), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61702012) and University Outstanding Young Talent Support Project of Anhui Province of China (Grant No. gxyq2017026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, FL., Liu, WF., Chen, SG. et al. Public-key quantum digital signature scheme with one-time pad private-key. Quantum Inf Process 17, 10 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1778-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1778-5