Abstract
Heisenberg model allows a more compact representation of certain quantum states and enables efficient modelling of stabilizer gates operation and single-qubit measurement in computational basis on classical computers. Since generic quantum circuit modelling appears intractable on classical computers, the Heisenberg representation that makes the modelling process at least practical for certain circuits is crucial. This paper proposes efficient algorithms to facilitate accurate global phase maintenance for both stabilizer and non-stabilizer gates application that play a vital role in the stabilizer frames data structure, which is based on the Heisenberg representation. The proposed algorithms are critical as maintaining global phase involves compute-intensive operations that are necessary for the modelling of each quantum gate. In addition, the proposed work overcomes the limitations of prior work where the phase factors due to non-stabilizer gates application was not taken into consideration. The verification of the proposed algorithms is made against the golden reference model that is constructed based on the conventional state vector approach.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
The terms Heisenberg model and stabilizer formalism are used interchangeably in this paper.
Global phase is important in quantum mechanics when the differences in phase factors between two interacting quantum states are measurable [21].
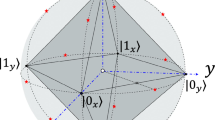
A three-dimensional sphere of radius 1 that provides a way of visualizing a single-qubit state.
Recall that the eigenvalue \(\lambda \) and eigenvector v of an n-by-n square matrix A are defined as \(Av = \lambda v\).
The complexities stated in the caption of Algorithms 2–4 are for the computation of a complete set of N basis amplitudes. In the case of global phase maintenance, it only requires to obtain the amplitude of one or more basis indexes depending on the quantum gate type, regardless of the qubit size of the quantum circuit.
References
Aaronson, S., Gottesman, D.: Improved simulation of stabilizer circuits. Phys. Rev. A 70(5), 052,328 (2004)
Abubakar, M.Y., Jung, L.T., Zakaria, M.N., Younesy, A., Abdel-Atyz, A.H.: New universal gate library for synthesizing reversible logic circuit using genetic programming. In: International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCOINS), pp. 316–321. IEEE (2016)
Abubakar, M.Y., Jung, L.T., Zakaria, N., Younes, A., Abdel-Aty, A.H.: Reversible circuit synthesis by genetic programming using dynamic gate libraries. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(6), 160 (2017)
Barenco, A., Deutsch, D., Ekert, A., Jozsa, R.: Conditional quantum dynamics and logic gates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74(20), 4083 (1995)
Bennink, R.S., Ferragut, E.M., Humble, T.S., Laska, J.A., Nutaro, J.J., Pleszkoch, M.G., Pooser, R.C.: Unbiased simulation of near-Clifford quantum circuits. Phys. Rev. A 95(6), 062,337 (2017)
Bravyi, S., Gosset, D.: Improved classical simulation of quantum circuits dominated by Clifford gates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116(25), 250,501 (2016)
García, H.J., Markov, I.L.: Simulation of quantum circuits via stabilizer frames. IEEE Trans. Comput. 64(8), 2323–2336 (2015)
García-Ramírez, H.J.: Hybrid techniques for simulating quantum circuits using the Heisenberg representation. Ph.D. thesis, The University of Michigan (2014)
Gershenfeld, N.A., Chuang, I.L.: Bulk spin-resonance quantum computation. Science 275(5298), 350–356 (1997)
Gottesman, D.: Stabilizer codes and quantum error correction. Ph.D. thesis, California Institute of Technology (1997)
Gottesman, D.: The Heisenberg representation of quantum computers. arXiv:quant-ph/9807006 (1998)
Homid, A., Abdel-Aty, A., Abdel-Aty, M., Badawi, A., Obada, A.S.: Efficient realization of quantum search algorithm using quantum annealing processor with dissipation. JOSA B 32(9), 2025–2033 (2015)
Johansson, N., Larsson, J.Å.: Efficient classical simulation of the Deutsch–Jozsa and Simons algorithms. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(9), 233 (2017)
Khalid, A.U., Zilic, Z., Radecka, K.: FPGA emulation of quantum circuits. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Design: VLSI in Computers and Processors. ICCD 2004, pp. 310–315. IEEE (2004)
Khalil-Hani, M., Lee, Y.H., Marsono, M.N.: An accurate FPGA-based hardware emulation on quantum fourier transform. In: Australasian Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Computing (AusPDC), vol. 1, p. a1b3 (2015)
Kliuchnikov, V., Maslov, D.: Optimization of Clifford circuits. Phys. Rev. A 88(5), 052,307 (2013)
Kliuchnikov, V., Maslov, D., Mosca, M.: Asymptotically optimal approximation of single qubit unitaries by Clifford and T circuits using a constant number of ancillary qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(19), 190,502 (2013)
Knill, E., Leibfried, D., Reichle, R., Britton, J., Blakestad, R., Jost, J., Langer, C., Ozeri, R., Seidelin, S., Wineland, D.: Randomized benchmarking of quantum gates. Phys. Rev. A 77(1), 012,307 (2008)
Lee, Y.H.: QCM: Quantum circuit modelling using state vector and Heisenberg representations. https://github.com/yeehui1988/QCM (2017)
Lee, Y.H., Khalil-Hani, M., Marsono, M.N.: An FPGA-based quantum computing emulation framework based on serial-parallel architecture. Int. J. Reconfigurable Comput. 2016, 1–18 (2016)
Messiah, A.: Quantum Mechanics. Dover Publications, New York (1999)
Miller, D.M., Thornton, M.A.: QMDD: a decision diagram structure for reversible and quantum circuits. In: 36th International Symposium on Multiple-Valued Logic, pp. 30–30. IEEE (2006)
Monroe, C., Meekhof, D., King, B., Itano, W., Wineland, D.: Demonstration of a fundamental quantum logic gate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75(25), 4714 (1995)
Mooij, J., Orlando, T., Levitov, L., Tian, L., Van der Wal, C.H., Lloyd, S.: Josephson persistent-current qubit. Science 285(5430), 1036–1039 (1999)
Muñoz-Coreas, E., Thapliyal, H.: Design of quantum circuits for galois field squaring and exponentiation. In: IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI), pp. 68–73. IEEE (2017)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Shiou-An, W., Chin-Yung, L., Sy-Yen, K., et al.: An XQDD-based verification method for quantum circuits. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 91(2), 584–594 (2008)
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, 1994 Proceedings, pp. 124–134. IEEE (1994)
Simon, D.R.: On the power of quantum computation. SIAM J. Comput. 26(5), 1474–1483 (1997)
Smelyanskiy, M., Sawaya, N.P., Aspuru-Guzik, A.: qHiPSTER: the quantum high performance software testing environment. arXiv:1601.07195 (2016)
Viamontes, G.F., Markov, I.L., Hayes, J.P.: Improving QuIDD-based simulation. In: Quantum Circuit Simulation, pp. 133–152. Springer, Dordrecht (2009)
Yanofsky, N.S., Mannucci, M.A.: Quantum Computing for Computer Scientists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work is supported by the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) and Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) under Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) Vote No. 4F422.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.H., Khalil-Hani, M. & Marsono, M.N. Improved quantum circuit modelling based on Heisenberg representation. Quantum Inf Process 17, 36 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1806-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1806-5