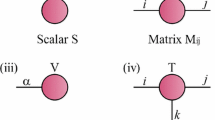
Abstract
During the last three decades, quantum neural computation has received a relatively high amount of attention among researchers and academic communities since the model of quantum neural network has been proposed. Matrix product state is the well-designed class of tensor network states, which plays an important role in processing of quantum information. The area of dynamical systems help us to study the temporal behavior of systems in time. In our previous work, we have shown the relationship between quantum finite state machine and matrix product state. In this paper, we have used the proposed unitary criteria to investigate the dynamics of matrix product state with quantum weightless neural networks, where the output qubit is extracted and fed back (iterated) to input. Further, we have used Von Neumann entropy to measure possible entanglement of output quantum state. Finally, we have plotted the dynamics for each matrix product state against iterations and analyzed their results.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Feynman, R.P.: Simulating physics with computers. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 21(6), 467–488 (1982)
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, 1994 Proceedings, pp. 124–134. IEEE (1994)
Grover, L.K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 212–219. ACM (1996)
Kwiat, P., Mitchell, J., Schwindt, P., White, A.: Grover’s search algorithm: an optical approach. J. Mod. Opt. 47(2–3), 257–266 (2000)
Orús, R.: A practical introduction to tensor networks: matrix product states and projected entangled pair states. Ann. Phys. 349, 117–158 (2014)
White, S.R.: Density-matrix algorithms for quantum renormalization groups. Phys. Rev. B 48(14), 10345 (1993)
Aleksander, I.: Self-adaptive universal logic circuits. Electron. Lett. 2(8), 321–322 (1966)
Kak, S.C.: Quantum neural computing. In: Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics, vol. 94, , pp. 259–313. Elsevier (1995)
Schuld, M., Sinayskiy, I., Petruccione, F.: The quest for a quantum neural network. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(11), 2567–2586 (2014)
Dong, D., Petersen, I.R.: Quantum control theory and applications: a survey. IET Control Theory Appl. 4(12), 2651–2671 (2010)
de Oliveira, W.R., Silva, A.J., Ludermir, T.B., Leonel, A., Galindo, W.R., Pereira, J.C.: Quantum logical neural networks. In: 10th Brazilian Symposium on Neural Networks, SBRN’08, pp. 147–152. IEEE (2008)
Silva, A., de Oliveira, W., Ludermir, T.: A weightless neural node based on a probabilistic quantum memory. In: 2010 Eleventh Brazilian Symposium on Neural Networks (SBRN), pp. 259–264. IEEE (2010)
Da Silva, A.J., De Oliveira, W.R., Ludermir, T.B.: Classical and superposed learning for quantum weightless neural networks. Neurocomputing 75(1), 52–60 (2012)
Panella, M., Martinelli, G.: Neural networks with quantum architecture and quantum learning. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 39(1), 61–77 (2011)
de Paula Neto, F.M., de Oliveira, W.R., da Silva, A.J., Ludermir, T.B.: Chaos in quantum weightless neuron node dynamics. Neurocomputing 183, 23–38 (2016)
de Paula Neto, F.M., Ludermir, T.B., de Oliveira, W.R., da Silva, A.J.: Fitting parameters on quantum weightless neuron dynamics. In: 2015 Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems (BRACIS), pp. 169–174. IEEE (2015)
de Paula Neto, F.M., de Oliveira, W.R., da Silva, A.J., Ludermir, T.B.: On the entanglement dynamics of the quantum weightless neuron. In: 2017 Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems (BRACIS), pp. 175–180. IEEE (2017)
Wang, J.: Handbook of Finite State Based Models and Applications. CRC Press, Cambridge (2012)
Nielsen, M., Chuang, I.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information: 10th Anniversary Edition. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Greenberger, D.M.: GHZ (Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger) theorem and GHZ states. In: Compendium of Quantum Physics, , pp. 258–263. Springer (2009)
Affleck, I., Kennedy, T., Lieb, E.H., Tasaki, H.: Rigorous results on valence-bond ground states in antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 59(7), 799 (1987)
Raussendorf, R.: Measurement-based quantum computation with cluster states. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 7(06), 1053–1203 (2009)
Matrix Product Formalism. http://www2.mpq.mpg.de/Theorygroup/CIRAC/wiki/images/9/9f/Eckholt_Diplom.pdf/. Accessed 15 March 2018
Bhatia, A.S., Kumar, A.: Quantifying matrix product state. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(3), 41 (2018)
Dzelme-Bērziņa, I.: Galīgie kvantu automāti un log̀ika
Petz, D.: Entropy, Von Neumann and the Von Neumann entropy. In: John Von Neumann and the Foundations of Quantum Physics, pp. 83–96. Springer (2001)
Biamonte, J.D., Clark, S.R., Jaksch, D.: Categorical tensor network states. AIP Adv. 1(4), 042172 (2011)
Acknowledgements
Amandeep Singh Bhatia was supported by Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF), funded by Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, A.S., Kumar, A. Neurocomputing approach to matrix product state using quantum dynamics. Quantum Inf Process 17, 278 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-2053-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-2053-0