Abstract
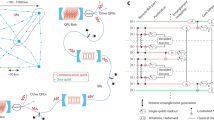
In distributed functional monitoring (DFM), N players located at different sites; each observes a stream of items and communicates with one coordinator, whose goal is to compute a function of the union of the streams. In threshold monitoring, a special case of DFM, the coordinator wants to know whether \(f(v(t)) > T\), where v(t) is a binary vector that represents the state of the stream as an average of local states at the sites. In this paper, we enhance the classical geometric monitoring (GM) method with quantum communication and entanglement. The proposed quantum geometric monitoring (QGM) protocol can be further specialized by defining specific network topologies. In QGM-Flat, the coordinator is connected to all N players. When N becomes too large, the performance of QGM-Flat deteriorates. For a scalable implementation, we propose to organize the players in a tree structure, with the QGM-Tree protocol. We have implemented both QGM-Flat and QGM-Tree with SimulaQron, a novel Python library for the development and simulation of quantum networking applications. We analyze the proposed quantum protocols, showing that they outperform their classical counterparts in terms of reduced communication cost, while showing the same accuracy.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzelius, M., Simon, C., de Riedmatten, H., Gisin, N.: Multimode quantum memory based on atomic frequency combs. Phys. Rev. A 79, 052329 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.79.052329
Amoretti, M.: Entanglement evaluation protocols, Python code. https://github.com/qis-unipr/entanglement-verification. Accessed 25 Jun 2019
Amoretti, M., Pizzoni, M.: QGM source code. https://github.com/qis-unipr/qgm (2019)
Babcock, B., Olston, C.: Distributed top-k monitoring. In: Proceedings of the 2003 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, SIGMOD ’03, pp. 28–39. ACM (2003)
Bahera, B., Seth, S., Das, A., Panigrahi, P.K.: Demonstration of entanglement purification and swapping protocol to design quantum repeater in IBM quantum computer. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 108 (2019)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B., Smolin, J.A., William, K.: Purification of noisy entanglement, and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 722–725 (1996)
Bennett, C.H., Wiesner, S.J.: Communication via one- and two-particle operators on einstein-podolsky-rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 2881–2884 (1992)
Bussieres, F., Sangouard, N., Afzelius, M., de Riedmatten, H., Simon, C., Tittel, W.: Prospective applications of optical quantum memories. J. Mod. Opt. 60(18), 1519–1537 (2013)
Caleffi, M., Cacciapuoti, A.S., Bianchi, G.: Quantum internet: From communication to distributed computing! In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM International Conference on Nanoscale Computing and Communication, NANOCOM ’18, pp. 3:1–3:4. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3233188.3233224
Cormode, G.: The continuous distributed monitoring model. SIGMOD Rec. 42(1), 5–14 (2013)
Cormode, G., Garofalakis, M.: Join sizes, frequency moments, and applications. In: Garofalakis, M., Gehrke, J., Rastogi, R. (eds.) Data Stream Management, pp. 87–102. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Cormode, G., Muthukrishnan, S., Yi, K.: Algorithms for distributed functional monitoring. ACM Trans. Algorithms 7(2), 21 (2011)
Dahlberg, A., Wehner, S.: Simulaqron—A simulator for developing quantum internet software. Quantum Sci. Technol. 4, 015001 (2019)
van Dam, S.B., Humphreys, P.C., Rozpedek, F., Wehner, S., Hanson, R.: Multiplexed entanglement generation over quantum networks using multi-qubit nodes. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2(3), 034002 (2017)
Dilman, M., Raz, D.: Efficient reactive monitoring. In: Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM 2001. Conference on Computer Communications. Twentieth Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Society (Cat. No.01CH37213), vol. 2, pp. 1012–1019 (2001)
Fiorentino, M., Voss, P.L., Sharping, J.E., Kumar, P.: All-fiber photon-pair source for quantum communications. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 14(7), 983–985 (2002)
Giatrakos, N., Deligiannakis, A., Garofalakis, M.: Scalable approximate query tracking over highly distributed data streams. In: ACM SIGMOD ’16. ACM (2016)
Greve, K.D., Yu, L., McMahon, P.L., Pelc, J.S., Natarajan, C.M., Kim, N.Y., Abe, E., Maier, S., Schneider, C., Kamp, M., Höfling, S., Hadfield, R.H., Forchel, A., Fejer, M.M., Yamamoto, Y.: Quantum-dot spin-photon entanglement via frequency downconversion to telecom wavelength. Nature 491, 421–425 (2012)
Gundogan, M., Ledingham, P.M., Kutluer, K., Mazzera, M., de Riedmatten, H.: Solid state spin-wave quantum memory for time-bin qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 230501 (2015)
Hammerer, K., Sørensen, A.S., Polzik, E.S.: Quantum interface between light and atomic ensembles. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 1041–1093 (2010)
Holevo, A.S.: Bounds for the quantity of information transmitted by a quantum communication channel. Probl. Inform. Transm. 9(3), 177–183 (1973)
Huang, L., Nguyen, X., Garofalakis, M., Hellerstein, J.M., Jordan, M.I., Joseph, A.D., Taft, N.: Communication-efficient online detection of network-wide anomalies. In: IEEE INFOCOM 2007 - 26th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, pp. 134–142 (2007)
Huffman, W.C., Pless, V.: Fundamentals of Error-Correcting Codes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Humphreys, P.: Deterministic delivery of remote entanglement on a quantum network. Nature 558, (2018)
Hushilevitz, E., Nisan, N.: Communication Complexity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1997)
Jobez, P., Usmani, I., Timoney, N., Laplane, C., Gisin, N., Afzelius, M.: Cavity-enhanced storage in an optical spin-wave memory. New J. Phys. 16(8), 083005 (2014)
Keralapura, R., Cormode, G., Ramamirtham, J.: Communication-efficient distributed monitoring of thresholded counts. In: Proceedings of the 2006 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, SIGMOD ’06, pp. 289–300. ACM (2006)
Kompella, K., Aelmans, M., Wehner, S., Sirbu, C.: Advertising entanglement capabilities in quantum networks. Internet-Draft draft-kaws-qirg-advent-00, IETF Secretariat (2018). http://www.ietf.org/internet-drafts/draft-kaws-qirg-advent-00.txt
Krastanov, S., Albert, V.V., Jiang, L.: Optimized entanglement purification. Quantum J. 3, 123–141 (2019)
Kurtsiefer, C., Oberparleiter, M., Weinfurter, H.: Generation of correlated photon pairs in type-ii parametric down conversion-revisited. J. Mod. Opt. 48(13), 1997–2007 (2001)
Li, M., Liu, Y.: Underground coal mine monitoring with wireless sensor networks. ACM Trans. Sen. Netw. 5(2), 10:1–10:29 (2009)
Montanaro, A.: The quantum complexity of approximating the frequency moments. Quantum Inf. Comput. 16, 13–14 (2016)
Nagy, M., Akl, S.G.: Entanglement verification with application to key distribution protocols. Par. Proc. Lett. 20(3), 227–237 (2010)
Pan, J.W., Simon, C., Brukner, C., Zeilinger, A.: Entanglement purification for quantum communication. Nature 410, 1067–1070 (2001)
Panigrahi, P.K., Gupta, M., Pathak, A., Srikanth, R.: Circuits for distributing quantum measurement. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 864 (2006)
Rozpedek, F., Schiet, T., Thinh, L., Elkouss, D., Doherty, A., Wehner, S.: Optimizing practical entanglement distillation. Phys. Rev. A 97, 062333 (2018)
Sharfman, I., Schuster, A., Keren, D.: A geometric approach to monitoring threshold functions over distributed data streams. In: ACM SIGMOD ’06. ACM (2006)
Steiger, D., Häner, T., Troyer, M.: Projectq: an open source software framework for quantum computing. Quantum 2(49), 10 (2018)
van Enk, S.J., Lütkenhaus, N., Kimble, H.J.: Experimental procedures for entanglement verification. Phys. Rev. A 75(5), 052318 (2007)
Van Meter, Rodney: Quantum Networking. Wiley, London (2014)
Wehner, S., Elkouss, D., Hanson, R.: Quantum internet: A vision for the road ahead. Science 362(6412), 1–9 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aam9288
Zhong, M., Hedges, M., Ahlefeldt, R., Bartholomew, J., Beavan, S., Wittig, S., Longdell, J., Sellars, M.: Optically addressable nuclear spins in a solid with a six-hour coherence time. Nature 517(8), 177–180 (2015)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Axel Dahlberg and Stephanie Wehner for their support during our software development and debugging activities, and for adding features to SimulaQron that allowed us to implement fully working QGM protocols.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amoretti, M., Pizzoni, M. & Carretta, S. Enhancing distributed functional monitoring with quantum protocols. Quantum Inf Process 18, 371 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2484-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2484-2