Abstract
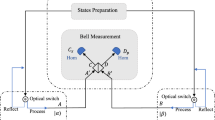
We perform security analysis of a passive measurement-device-independent (MDI) continuous-variable quantum key distribution (CVQKD) protocol with almost no public communication. In the passive MDI-CVQKD protocol, the quantum states are prepared passively by using thermal sources without Gaussian modulations at Alice’s and Bob’s sides. With this technique, Alice and Bob can precisely prepare quantum states to match the high transmission rate in MDI-CVQKD system at the corresponding speed. Here, both asymptotic regime and finite-size regime are considered. In asymptotic case, we derive the security bounds for the protocol against collective attacks, while in finite-size case we show a new conceptual development of passive MDI-CVQKD, namely the final secret key generation can be performed by using almost all raw keys instead of sacrificing part of raw keys for parameter estimation, and thus the improvement performance of passive MDI-CVQKD protocol can be achieved in finite-size scenario.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145 (2002)
Scarani, V., Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H., Cerf, N.J., Dušek, M., Lütkenhaus, N., Peev, M.: The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1301 (2009)
Takeda, S., Fuwa, M., Van Loock, P., Furusawa, A.: Entanglement swapping between discrete and continuous variables. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114(10), 100501 (2014)
Gessner, M., Pezzè, L., Smerzi, A.: Efficient entanglement criteria for discrete, continuous, and hybrid variables. Phys. Rev. A 94(2), 020101 (2016)
Braunstein, S.L., Van Loock, P.: Quantum information with continuous variables. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77(2), 513 (2005)
Weedbrook, C., Pirandola, S., García-Patrón, R., Cerf, N.J., Ralph, T.C., Shapiro, J.H., Lloyd, S.: Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 621 (2012)
Huang, P., Huang, J., Zhang, Z., Zeng, G.: Quantum key distribution using basis encoding of Gaussian-modulated coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 97, 042311 (2018)
Grosshans, F., Van Assche, G., Wenger, J., Brouri, R., Cerf, N.J., Grangier, P.: Quantum key distribution using gaussian-modulated coherent states. Nature 421, 238 (2003)
Grosshans, F., Grangier, P.: Continuous variable quantum cryptography using coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 057902 (2002)
Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Chen, Z., Weedbrook, C., Zhao, Y., Wang, X., Huang, Y., Xu, C., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., Wang, G., Yu, S., Guo, H.: Continuous-variable QKD over 50 km commercial fiber. Quantum Sci. Technol. 4, 035006 (2019)
Brassard, G., Lütkenhaus, N., Mor, T., Sanders, B.C.: Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(6), 1330 (2000)
Yuan, Z.L., Dynes, J.F., Shields, A.J.: Avoiding the blinding attack in QKD. Nat. Photonics 4(12), 800 (2010)
Huang, J.Z., Kunz, J.S., Jouguet, P., Weedbrook, C., Yin, Z.Q., Wang, S., Chen, W., Guo, G.C., Han, Z.F.: Quantum hacking on quantum key distribution using homodyne detection. Phys. Rev. A 89(3), 032304 (2014)
Qin, H.: Saturation attack on continuous-variable quantum key distribution system. Proc. SPIE 8899(2), 88990N (2013)
Qin, H., Kumar, R., Makarov, V., Alléaume, R.: Homodyne detector blinding attack in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 98(1), 012312 (2018)
Filip, R.: Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with noisy coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 77(2), 022310 (2008)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(13), 130503 (2012)
Braunstein, S.L., Pirandola, S.: Side-channel-free quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(13), 130502 (2012)
Da, S., Ferreira, T., Vitoreti, D., Xavier, G.B., Do Amaral, G.C., Temporao, G.P., Von Der Weid, J.P.: Proof-of-principle demonstration of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution using polarization qubits. Phys. Rev. A 88(5), 052303 (2013)
Liu, Y., Chen, T.Y., Wang, L.J., Liang, H., Shentu, G.L., Wang, J., Cui, K., Yin, H.L., Liu, N.L., Li, L.: Experimental measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111(13), 130502 (2013)
Tang, Z., Liao, Z., Xu, F., Qi, B., Qian, L., Lo, H.K.: Experimental demonstration of polarization encoding measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112(19), 190503 (2014)
Curty, M., Xu, F., Cui, W., Lim, C.C.W., Tamaki, K., Lo, H.K.: Finite-key analysis for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. 5, 3732 (2014)
Choi, Y., Kwon, O., Woo, M., Oh, K., Han, S.W., Kim, Y.S., Moon, S.: Plug-and-play measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 93(3), 032319 (2016)
Xu, F., Curty, M., Qi, B., Qian, L., Lo, H.K.: Discrete and continuous variables for measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nat. Photonics 9(12), 772 (2015)
Li, H.W., Yin, Z.Q., Pawłowski, M., Guo, G.C., Han, Z.F.: Detection efficiency and noise in a semi-device-independent randomness-extraction protocol. Phys. Rev. A 91(3), 032305 (2015)
Li, H.W., Yin, Z.Q., Chen, W., Wang, S., Guo, G.C., Han, Z.F.: Quantum key distribution based on quantum dimension and independent devices. Phys. Rev. A 89(3), 032302 (2014)
Liao, Q., Wang, Y., Huang, D., Guo, Y.: Dual-phase-modulated plug-and-play measurement-device-independent continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Opt. Express 26(16), 19907 (2018)
Pirandola, S., Ottaviani, C., Spedalieri, G., Weedbrook, C., Braunstein, S.L., Lloyd, S., Gehring, T., Jacobsen, C.S., Andersen, U.L.: High-rate measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nat. Photonics 9(6), 397 (2015)
Ma, X.C., Sun, S.H., Jiang, M.S., Gui, M., Liang, L.M.: Gaussian-modulated coherent-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 89(4), 042335 (2014)
Guo, Y., Liao, Q., Huang, D., Zeng, G.: Quantum relay schemes for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 95(4), 042326 (2017)
Li, Z., Zhang, Y.C., Xu, F., Peng, X., Guo, H.: Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 89(5), 052301 (2014)
Zhang, Y.C., Li, Z., Yu, S., Gu, W., Peng, X., Guo, H.: Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution using squeezed states. Phys. Rev. A 90(5), 052325 (2014)
Chen, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, G., Li, Z., Guo, H.: Composable security analysis of continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with squeezed states for coherent attacks. Phys. Rev. A 98(1), 012314 (2018)
Qi, B., Evans, P.G., Grice, W.P.: Passive state preparation in the Gaussian-modulated coherent-states quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 97(1), 012317 (2018)
Bai, D., Huang, P., Ma, H., Wang, T., Zeng, G.: Passive state preparation in continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. J. Phys. B 52(13), 135502 (2019)
Renner, R., Cirac, J.I.: de Finetti representation theorem for infinite-dimensional quantum systems and applications to quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102(11), 110504 (2009)
Furrer, F., Franz, T., Berta, M., Leverrier, A., Scholz, V.B., Tomamichel, M., Werner, R.F.: Continuous variable quantum key distribution: finite-key analysis of composable security against coherent attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109(10), 100502 (2012)
Leverrier, A., García-Patrón, R., Renner, R., Cerf, N.J.: Security of continuous-variable quantum key distribution against general attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(3), 030502 (2013)
Leverrier, A., Grosshans, F., Grangier, P.: Finite-size analysis of a continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 81(6), 062343 (2010)
Papanastasiou, P., Ottaviani, C., Pirandola, S.: Finite-size analysis of measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography with continuous variables. Phys. Rev. A 96(4), 042332 (2017)
Kumar, R., Qin, H., Alléaume, R.: Coexistence of continuous variable QKD with intense DWDM classical channels. New J. Phys. 17(4), 043027 (2015)
Huang, D., Huang, P., Lin, D., Zeng, G.: Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution by controlling excess noise. Sci. Rep. 6, 19201 (2016)
Huang, D., Huang, P., Wang, T., Li, H., Zhou, Y., Zeng, G.: Continuous-variable quantum key distribution based on a plug-and-play dual-phase-modulated coherent-states protocol. Phys. Rev. A 94(3), 032305 (2016)
Qi, B., Huang, L.L., Qian, L., Lo, H.K.: Experimental study on the Gaussian-modulated coherent-state quantum key distribution over standard telecommunication fibers. Phys. Rev. A 76(5), 052323 (2007)
Lodewyck, J., Bloch, M., García-Patrón, R., Fossier, S., Karpov, E., Diamanti, E., Debuisschert, T., Cerf, N.J., Tualle-Brouri, R., McLaughlin, S.W.: Quantum key distribution over 25 km with an all-fiber continuous-variable system. Phys. Rev. A 76(4), 042305 (2007)
García-Patrón, R.: Quantum Information with Optical Continuous Variables: From Bell Tests to Key Distribution. Universite Libre De Bruxelles, Brussels (2007)
Pirandola, S., Laurenza, R., Ottaviani, C., Banchi, L.: Fundamental limits of repeaterless quantum communications. Nat. Commun. 8, 15043 (2017)
Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Zhao, Y., Wang, X., Guo, H.: Finite-size analysis of continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 96(4), 042334 (2017)
Lupo, C., Ottaviani, C., Papanastasiou, P., Pirandola, S.: Parameter estimation with almost no public communication for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120(22), 220505 (2018)
Lupo, C., Ottaviani, C., Papanastasiou, P., Pirandola, S.: CV MDI QKD: composable security against coherent attacks. Phys. Rev. A 97(5), 052327 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61801522) and National Nature Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (Grant No. 2019JJ40352).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Wang, Y., Li, S. et al. Security analysis of passive measurement-device-independent continuous-variable quantum key distribution with almost no public communication. Quantum Inf Process 18, 372 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2486-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2486-0