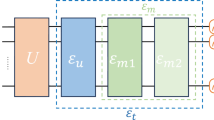
Abstract
Quantum feedback control (QFBC) and quantum feedforward control (QFFC) are two major techniques for protecting quantum states against decoherence. Based on this, Guo et al. proposed a scheme by combining the QFFC and the minimum-error discrimination (MED) to realize a better effect of discriminating two non-orthogonal states after passing a noisy channel (Phys Rev A 91:022321, 2015) than the scheme without the QFFC. Recently, Cao et al. proposed a novel composite control scheme for protecting such states (Phys Rev A 95:032313, 2017), where QFBC and QFFC are combined. They showed that the performance of the composite control scheme is better than that of the previous control schemes in terms of the success probability and the fidelity. In this paper, we examine the discrimination scheme by combining the composite control and the MED and observe an interesting phenomenon, i.e., better quantum control does not imply better discrimination effect. Finally, we explain this phenomenon.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, and Signal Processing. IEEE, New York, p. 175 (1984)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Mermin, N.D.: Quantum cryptography without Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 557–559 (1992)
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3121–3124 (1992)
Helstrom, C.W.: Quantum Detection and Estimation Theory, Mathematics in Science and Engineering, vol. 123. Academic, New York (1976)
Holevo, A.S.: Statistical decision theory for quantum systems. J. Multivar Anal. 3, 337–394 (1973)
Yuen, H.P., Kenndey, R.S., Lax, M.: Optimum testing of multiple hypotheses in quantum detection theory. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 21, 125–134 (1975)
Bergou, J.A.: Discrimination of quantum states. J. Mod. Opt. 57, 160–180 (2010)
Barnett, S.M.: Minimum-error discrimination between multiply symmetric states. Phys. Rev. A 64, 030303 (2001)
Andersson, E., Barnett, S.M., Gilson, C.R., Hunter, K.: Minimum-error discrimination between three mirror-symmetric states. Phys. Rev. A 65, 052308 (2002)
Chou, C.L., Hsu, L.Y.: Minimum-error discrimination between symmetric mixed quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042305 (2003)
Herzog, U., Bergou, J.A.: Minimum-error discrimination between subsets of linearly dependent quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 65, 050305 (2002)
Ivanovic, I.D.: How to differentiate between non-orthogonal states. Phys. Lett. A 123, 257–259 (1987)
Dieks, D.: Overlap and distinguishability of quantum states. Phys. Lett. A 126, 303–306 (1988)
Peres, A.: How to differentiate between non-orthogonal states. Phys. Lett. A 128, 19 (1988)
Jaeger, G., Shimony, A.: Optimal distinction between two non-orthogonal quantum states. Phys. Lett. A 197, 83–87 (1995)
Peres, A., Terno, D.R.: Optimal distinction between two non-orthogonal quantum states. J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 31, 7105–7111 (1998)
Zhang, C.W., Li, C.F., Guo, G.C.: General strategies for discrimination of quantum states. Phys. Lett. A 261, 25–29 (1999)
Chefles, A., Barnett, S.M.: Optimum unambiguous discrimination between linearly independent symmetric states. Phys. Lett. A 250, 223–229 (1998)
Sun, Y., Bergou, J.A., Hillery, M.: Optimum unambiguous discrimination between subsets of nonorthogonal quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 66, 032315 (2002)
Eldar, Y.C.: A semidefinite programming approach to optimal unambiguous discrimination of quantum states. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 49, 446–456 (2003)
Qiu, D.: Optimum unambiguous discrimination between subsets of quantum states. Phys. Lett. A 309, 189–197 (2003)
Rudolph, T., Spekkens, R.W., Turner, P.S.: Unambiguous discrimination of mixed states. Phys. Rev. A 68, 010301 (2003)
Feng, Y., Duan, R., Ying, M.: Unambiguous discrimination between mixed quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 70, 012308 (2004)
Raynal, P., Lütkenhaus, N., van Enk, S.J.: Reduction theorems for optimal unambiguous state discrimination of density matrices. Phys. Rev. A 68, 022308 (2003)
Herzog, U., Bergou, J.A.: Optimum unambiguous discrimination of two mixed quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 71, 050301 (2005)
Raynal, P., Lütkenhaus, N.: Optimal unambiguous state discrimination of two density matrices: lower bound and class of exact solutions. Phys. Rev. A 72, 022342 (2005)
Bergou, J.A., Feldman, E., Hillery, M.: Optimal unambiguous discrimination of two subspaces as a case in mixed-state discrimination. Phys. Rev. A 73, 032107 (2006)
Brańczyk, A.M., Mendonça, P.E.M.F., Gilchrist, A., Doherty, A.C., Bartlett, S.D.: Quantum control of a single qubit. Phys. Rev. A 75, 012329 (2007)
Xiao, X., Feng, M.: Reexamination of the feedback control on quantum states via weak measurements. Phys. Rev. A 83, 054301 (2011)
Yang, Y., Zhang, X.Y., Ma, J., Yi, X.X.: Extended techniques for feedback control of a single qubit. Phys. Rev. A 87, 012333 (2013)
Jacobs, K.: Feedback control for communication with non-orthogonal states. Quantum Inf. Comput. 7, 127–138 (2007)
Wang, C.-Q., Xu, B.M., Zou, J., He, Z., Yan, Y., Li, J.-G., Shao, B.: Feed-forward control for quantum state protection against decoherence. Phys. Rev. A 89, 032303 (2014)
Harraz, S., Cong, S., Li, K.: Two-qubit state recovery from amplitude damping based on weak measurement. eprint arXiv:1808.03094 (2018)
Cao, Y., Tian, G., Zhang, Z.C., Yang, Y.H., Wen, Q.Y., Gao, F.: Composite control for protecting two nonorthogonal qubit states against decoherence. Phys. Rev. A 95, 032313 (2017)
Carvalho, A.R.R., Reid, A.J.S., Hope, J.J.: Controlling entanglement by direct quantum feedback. Phys. Rev. A 78, 012334 (2008)
Guo, L.S., Xu, B.M., Zou, J., Wang, C., Li, H., Li, J., Shao, B.: Discriminating two nonorthogonal states against a noise channel by feed-forward control. Phys. Rev. A 91, 022321 (2015)
Gillett, G.G., Dalton, R.B., Lanyon, B.P., Almeida, M.P., Barbieri, M., Pryde, G.J., O’Brien, J.L., Resch, K.J., Bartlett, S.D., White, A.G.: Experimental feedback control of quantum systems using weak measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 080503 (2010)
Kim, Y.S., Lee, J.C., Kwon, O., Kim, Y.H.: Protecting entanglement from decoherence using weak measurement and quantum measurement reversal. Nat. Phys. 8, 117–120 (2012)
Solis-Prosser, M.A., Fernandes, M.F., Jimenez, O., Delgado, A., Neves, L.: Experimental minimum-error quantum-state discrimination in high dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 100501 (2017)
Li, J.Y., Ma, C.C., Zhang, K.J.: A novel lattice-based CP-ABPRE scheme for cloud sharing. Symmetry 11(10), 1262 (2019)
Zhang, K.J., Zhang, X., Jia, H.Y., Zhang, L.: A new n-party quantum secret sharing model based on multiparty entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(3), 21 (2019)
Zhang, K.J., Zhang, L., Song, T.T., Yang, Y.H.: A potential application in quantum networks—deterministic quantum operation sharing schemes with Bell states. Sci. Chin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 59(6), 660302 (2016)
Zhang, L., Sun, H.W., Zhang, K.J., Jia, H.Y.: An improved arbitrated quantum signature protocol based on the key-controlled chained CNOT encryption. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(3), 70 (2017)
Zhang, K.J., Kwek, L., Ma, C.G., Zhang, L., Sun, H.-W.: Security analysis with improved design of post-confirmation mechanism for quantum sealed-bid auction with single photons. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(2), 38 (2018)
Zhang, L., Dong, S., Zhang, K.J.: A controller-independent quantum dialogue protocol with four-particle states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(6), 1972–1936 (2019)
Zhang, L., Li, S., Zhang, K.J., Sun, H.-W.: Cryptanalysis and improvement of some quantum proxy blind signature schemes. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(4), 1047–1059 (2019)
Zhang, H.Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, K.J.: A new quantum proxy signature model based on a series of genuine entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(2), 591–604 (2019)
Zhang, L., Sun, H.-W., Zhang, K.J., Wang, Q.L., Cai, X.Q.: The security problems in some novel arbitrated quantum signature protocols. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(8), 2433–2444 (2017)
Zhang, L., Zhang, H.Y., Zhang, K.J., Wang, Q.L.: The security analysis and improvement of some novel quantum proxy signature schemes. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(6), 1983–1994 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61572053); Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 4182006); and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Cryptography and Information Security (Grant No. GCIS201810).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, YG., Chen, N., Yang, YL. et al. Better quantum control does not imply better discrimination effect. Quantum Inf Process 19, 168 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-02667-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-02667-9