Abstract
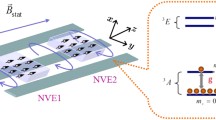
The generation of distributed entangled states among solid-state spins is key to the development of large-scale quantum networks and quantum computation. We propose a dissipative scheme for generating stable entanglement between the electron-spin states of two separated nitrogen-vacancy centers, each coupled to a microtoroidal resonator and separated in space. An optical fiber-taper waveguide links the two microtoroidal resonators. Numerical simulations show that spontaneous emission from the NV centers and the collective decay of delocalized field modes can act as effective resources to generate stationary singlet-like states without the need for initialization and precise control of the evolution of the system over time. Results indicate that the proposed scheme can reach high-fidelity and purity of states, and is resilient against small parameter fluctuations. We also discuss how the pure spin dephasing that arises from longitudinal magnetic-near-field noise affects the fidelity of the target state.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Calderbank, A.R., Shor, P.W.: Good quantum error-correcting codes exist. Phys. Rev. A 54, 1098 (1996)
Bennett, C.H., DiVincenzo, D.P., Smolin, J.A., Wootters, W.K.: Mixed-state entanglement and quantum error correction. Phys. Rev. A 54, 3824 (1996)
Kosut, R.L., Shabani, A., Lidar, D.A.: Robust quantum error correction via convex optimization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 020502 (2008)
Moussa, O., Baugh, J., Ryan, C.A., Laflamme, R.: Demonstration of sufficient control for two rounds of quantum error correction in a solid state ensemble quantum information processor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 160501 (2011)
Reed, M.D., DiCarlo, L., Nigg, S.E., Sun, L., Frunzio, L., Girvin, S.M., Schoelkopf, R.J.: Realization of three-qubit quantum error correction with superconducting circuits. Nature (London) 482, 382 (2012)
Lidar, D.A., Chuang, I.L., Whaley, K.B.: Decoherence-free subspaces for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 2594 (1998)
Beige, A., Braun, D., Tregenna, B., Knight, P.L.: Quantum computing using dissipation to remain in a decoherence-free subspace. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1762 (2000)
Kempe, J., Bacon, D., Lidar, D.A., Whaley, K.B.: Theory of decoherence-free fault-tolerant universal quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 63, 042307 (2001)
Steane, A.M.: Efficient fault-tolerant quantum computing. Nature (London) 399, 124 (1999)
Verstraete, F., Wolf, M.M., Cirac, J.I.: Quantum computation and quantum-state engineering driven by dissipation. Nat. Phys. 5, 633 (2009)
Vollbrecht, K.G.H., Muschik, C.A., Cirac, J.I.: Entanglement distillation by dissipation and continuous quantum repeaters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 120502 (2011)
Pastawski, F., Clemente, L., Cirac, J.I.: Quantum memories based on engineered dissipation. Phys. Rev. A 83, 012304 (2011)
Einstein, A., Podolsky, B., Rosen, N.: Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete? Phys. Rev. 47, 777 (1935)
Schrödinger, E.: Die gegenwärtige situation in der quantenmechanik. Naturwissenschaften 23, 823 (1935)
Lin, J., Shen, L.-T., Wu, H.-Z., Yang, Z.-B.: Stabilizing a Bell state by engineering collective photon decay. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 185 (2015)
Plenio, M.B., Huelga, S.F., Beige, A., Knight, P.L.: Cavity-loss-induced generation of entangled atoms. Phys. Rev. A 59, 2468 (1999)
Clark, S., Peng, A., Gu, M., Parkins, S.: Unconditional preparation of entanglement between atoms in cascaded optical cavities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 177901 (2003)
Reiter, F., Kastoryano, M.J.S., Sørensen, A.: Driving two atoms in an optical cavity into an steady entangled state using engineered decay. New J. Phys. 14, 053022 (2012)
Kastoryano, M.J., Reiter, F., Sørensen, A.S.: Dissipative preparation of entanglement in optical cavities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 090502 (2011)
Busch, J., De, S., Ivanov, S.S., Torosov, B.T., Spiller, T.P., Beige, A.: Cooling atom-cavity systems into entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 84, 022316 (2011)
Shen, L.T., Chen, X.Y., Yang, Z.B., Wu, H.Z., Zheng, S.B.: Steady-state entanglement for distant atoms by dissipation in coupled cavities. Phys. Rev. A 84, 064302 (2011)
Shen, L.T., Chen, X.Y., Yang, Z.B., Wu, H.Z., Zheng, S.B.: Distributed entanglement induced by dissipative bosonic media. Europhys. Lett. 99, 20003 (2012)
Su, S.L., Shao, X.Q., Wang, H.F., Zhang, S.: Scheme for entanglement generation in an atom-cavity system via dissipation. Phys. Rev. A 90, 054302 (2014)
Li, D.X., Shao, X.Q., Wu, J.H., Yi, X.X.: Noise-induced distributed entanglement in atom-cavity-fiber system. Opt. Express 25, 33359 (2017)
Li, D.X., Shao, X.Q., Wu, J.H., Yi, X.X.: Engineering steady-state entanglement via dissipation and quantum Zeno dynamics, in an optical cavity. Opt. Lett. 42, 3904 (2017)
Wang, Y., Hu, C.S., Shi, Z.C., Huang, B.H., Song, J., Xia, Y.: Accelerated and noise-resistant protocol of dissipation-based Knill–Laflamme–Milburn state generation with Lyapunov control. Ann. Phys. (Berlin) 531, 1900006 (2019)
Borjans, F., Croot, X.G., Mi, X., Gullans, M.J., Petta, J.R.: Resonant microwave-mediated interactions between distant electron spins. Nature 577, 195 (2020)
Bernien, H., Hensen, B., Pfaff, W., Koolstra, G., Blok, M.S., Robledo, L., Taminiau, T.H., Markham, M., Twitchen, D.J., Childress, L., Hanson, R.: Heralded entanglement between solid-state qubits separated by 3 meters. Nature 497, 86 (2013)
Maurer, P.C., Kucsko, G., Latta, C., Jiang, L., Yao, N.Y., Bennett, S.D., Pastawski, F., Hunger, D., Chisholm, N., Markham, M., Twitchen, D.J., Cirac, J.I., Lukin, M.D.: Room-temperature quantum bit memory exceeding one second. Science 336, 1283 (2012)
Togan, E., Chu, Y., Trifonov, A.S., Jiang, L., Maze, J., Childress, L., Dutt, M.V.G., Sørensen, A.S., Hemmer, P.R., Zibrov, A.S., Lukin, M.D.: Quantum entanglement between an optical photon and a solid-state spin qubit. Nature (London) 466, 730 (2010)
Balasubramanian, G., Neumann, P., Twitchen, D., Markham, M., Kolesov, R., Mizuochi, N., Isoya, J., Achard, J., Beck, J., Tissler, J., Jacques, V., Hemmer, P.R., Jelezko, F., Wrachtrup, J.: Ultralong spin coherence time in isotopically engineered diamond Nat. Mater. 8, 383 (2009)
Buckley, B.B., Fuchs, G.D., Bassett, L.C., Awschalom, D.D.: Spin-light coherence for single-spin measurement and control in diamond. Science 330, 1212 (2010)
Fuchs, G.D., Dobrovitski, V.V., Toyli, D.M., Heremans, F.J., Awschalom, D.D.: Gigahertz dynamics of a strongly driven single quantum spin. Science 326, 1520 (2009)
Gaebel, T., Domhan, M., Popa, I., Wittmann, C., Neumann, P., Jelezko, F., Rabeau, J.R., Stavrias, N., Greentree, A.D., Prawer, S., Meijer, J., Twamley, J., Hemmer, P.R., Wrachtrup, J.: Room-temperature coherent coupling of single spins in diamond. Nat. Phys. 2, 408 (2006)
Waldherr, G., Wang, Y., Zaiser, S., Jamali, M., SchulteHerbruggen, T., Abe, H., Ohshima, T., Isoya, J., Du, J.F., Neumann, P., Wrachtrup, J.: Quantum error correction in a solid-state hybrid spin register. Nature (London) 506, 204 (2014)
Robledo, L., Childress, L., Bernien, H., Hensen, B., Alkemade, P.F., Hanson, R.: High-fidelity projective read-out of a solid-state spin quantum register. Nature (London) 477, 574 (2011)
Neumann, P., Beck, J., Steiner, M., Rempp, F., Fedder, H., Hemmer, P.R., Wrachtrup, J., Jelezko, F.: Single-shot readout of a single nuclear spin. Science 329, 542 (2010)
Fuchs, G.D., Burkard, G., Klimov, P.V., Awschalom, D.D.: A quantum memory intrinsic to single nitrogen-vacancy centres in diamond. Nat. Phys. 7, 789 (2011)
Shim, J.H., Niemeyer, I., Zhang, J., Suter, D.: Room-temperature high-speed nuclear-spin quantum memory in diamond. Phys. Rev. A 87, 012301 (2013)
Chen, Q., Yang, W., Feng, M., Du, J.F.: Entangling separate nitrogen-vacancy centers in a scalable fashion via coupling to microtoroidal resonators. Phys. Rev. A 83, 054305 (2011)
Ren, B.C., Wang, G.Y., Deng, F.G.: Universal hyperparallel hybrid photonic quantum gates with the dipole induced transparency in weak-coupling regime. Phys. Rev. A 91, 032328 (2015)
Zhou, J., Liu, B.J., Hong, Z.P., Xue, Z.Y.: Fast holonomic quantum computation based on solid-state spins with all-optical control. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 61, 010312 (2018)
Doherty, M.W., Manson, N.B., Delaney, P., Hollenberg, L.C.L.: The negatively charged nitrogen-vacancy centre in diamond: the electronic solution. New J. Phys. 13, 025019 (2011)
Hensen, B., Bernien, H., Dréau, A.E., Reiserer, A., Kalb, N., Blok, M.S., Ruitenberg, J., Vermeulen, R.F.L., Schouten, R.N., Abellán, C., Amaya, W., Pruneri, V., Mitchell, M.W., Markham, M., Twitchen, D.J., Elkouss, D., Wehner, S., Taminiau, T.H., Hanson, R.: Loophole-free Bell inequality violation using electron spins separated by 1.3 kilometres. Nature 526, 682 (2015)
Park, Y.S., Cook, A.K., Wang, H.: Cavity QED with diamond nanocrystals and silica microspheres. Nano Lett. 6, 2075 (2006)
Larsson, M., Dinyari, K.N., Wang, H.: Composite optical microcavity of diamond nanopillar and silica microsphere. Nano Lett. 9, 1447 (2009)
Cheng, L.Y., Wang, H.F., Zhang, S., Yeon, K.H.: Quantum state engineering with nitrogen-vacancy centers coupled to low-Q microresonator. Opt. Express 21, 5988 (2013)
Barclay, P.E., Fu, K.M.C., Santori, C., Beausoleil, R.G.: Chip-based microcavities coupled to nitrogenvacancy centers in single crystal diamond. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 191115 (2009)
McCutcheon, M.W., Lončar, M.: Design of a silicon nitride photonic crystal nanocavity with a Quality factor of one million for coupling to a diamond nanocrystal. Opt. Express 16, 19136 (2008)
Acharyya, N., Kozyreff, G.: Large Q factor with very small whispering-gallery-mode resonators. Phys. Rev. Appl. 12, 014060 (2019)
Armani, D.K., Kippenberg, T.J., Spillane, S.M., Vahala, K.J.: Ultra-high-Q toroid microcavity on a chip. Nature 421, 925 (2003)
Kippenberg, T.J., Spillane, S.M., Vahala, K.J.: Demonstration of ultra-high-Q small mode volume toroid microcavities on a chip. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 61115 (2004)
Gramotnev, D.K., Bozhevolnyi, S.I.: Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit. Nat. Photon. 4, 91 (2010)
Shen, Z., Zhou, Z.H., Zou, C.L., Sun, F.W., Guo, G.P., Dong, C.H., Guo, G.C.: Observation of high-Q optomechanical modes in the mounted silica microspheres. Photon. Res. 3, 243 (2015)
Jiang, X.F., Shao, L.B., Zhang, S.X., Yi, X., Wiersig, J., Wang, L., Gong, Q.H., Lončar, M., Yang, L., Xiao, Y.F.: Chaos-assisted broadband momentum transformation in optical microresonators. Science 358, 344 (2017)
Suh, M.G., Yang, Q.F., Yang, K.Y., Yi, X., Vahala, K.J.: Microresonator soliton dual-comb spectroscopy. Science 354, 600 (2016)
Tian, Z., Li, S.L., Kiravittaya, S., Xu, B.R., Tang, S.W., Zhen, H.L., Lu, W., Mei, Y.F.: Selected and enhanced single whispering-gallery mode emission from a mesostructured nanomembrane microcavity. Nano Lett. 18, 8035 (2018)
Li, P.B., Gao, S.Y., Li, H.R., Ma, S.L., Li, F.L.: Dissipative preparation of entangled states between two spatially separated. nitrogen-vacancy centers. Phys. Rev. A 85, 042306 (2012)
Yang, W.L., Yin, Z.Q., Xu, Z.Y., Feng, M., Oh, C.H.: Quantum dynamics and quantum state transfer between separated nitrogen-vacancy centers embedded in photonic crystal cavities. Phys. Rev. A 84, 043849 (2011)
Jin, Z., Su, S.L., Zhang, S.: Preparation of a steady entangled state of two nitrogen-vacancy centers by simultaneously utilizing two dissipative factors. Phys. Rev. A 100, 052332 (2019)
Li, P.B., Gao, S.Y., Li, F.L.: Quantum information transfer with nitrogen-vacancy centers coupled to a whispering-gallery microresonator. Phys. Rev. A 83, 054306 (2011)
Yi, X., Xiao, Y.F., Liu, Y.C., Li, B.B., Chen, Y.L., Li, Y., Gong, Q.: Multiple-Rayleigh–Scatterer-induced mode splitting in a high-Q whispering-gallery-mode microresonator. Phys. Rev. A 83, 023803 (2011)
Yale, C.G., Buckley, B.B., Christle, D.J., Burkard, G., Heremans, F.J., Bassett, L.C., Awschalom, D.D.: All-optical control of a solid-state spin using coherent dark states. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 7595 (2013)
Santori, C., Tamarat, P., Neumann, P., Wrachtrup, J., Fattal, D., Beausoleil, J.R., Olivero, P., Greentree, A., Prawer, S., Jelezko, F., Hemmer, P.: Coherent population trapping of single spins in diamond under optical excitation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 247401 (2006)
Manson, N.B., Harrison, J.P., Sellars, M.J.: Nitrogen-vacancy center in diamond: model of the electronic structure and associated dynamics. Phys. Rev. B 74, 104303 (2006)
Serafini, A., Mancini, S., Bose, S.: Distributed quantum computation via optical fibers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 010503 (2006)
Reiter, F., Sørensen, A.S.: Effective operator formalism for open quantum systems. Phys. Rev. A 85, 032111 (2012)
Knill, E., Laflamme, R., Milburn, G.J.: A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46 (2001)
Shen, C.P., Gao, Y., Su, S.L., Liang, E., Mao, Y., Chen, S.: Mutual conversions between Knill–Laflamme–Milburn and W states. Ann. Phys. (Berlin) 530, 1800114 (2018)
Shen, C.P., Xiu, X.-M., Dong, L., Zhu, X.-Y., Chen, L., Liang, E., Yan, L.-L., Su, S.L.: Conversion of Knill–Laflamme–Milburn entanglement to Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger entanglement. Ann. Phys. (Berlin) 531, 1900160 (2019)
Park, Y.S., Cook, A.K., Wang, H.: Cavity QED with diamond nanocrystals and silica microspheres. Nano Lett. 6, 2075 (2006)
Dayan, B., Parkins, A.S., Aoki, T., Ostby, E.P., Vahala, K.I., Kimble, H.J.: A photon turnstile dynamically regulated by one atom. Science 319, 1062 (2008)
Yin, Z.Q., Xu, Z.Y., Feng, M., Du, J.F.: One-step implementation of multiqubit conditional phase gating with nitrogen-vacancy centers coupled to a high-Q silica microsphere cavity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 241113 (2010)
Spillane, S.M., Kippenberg, T.J., Painter, O.J., Vahala, K.J.: Ideality in a fiber-taper-coupled microresonator system for application to cavity quantum electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 043902 (2003)
Spillane, S.M., Kippenberg, T.J., Vahala, K.J., Goh, K.W., Wilcut, E., Kimble, H.J.: Ultrahigh-Q toroidal microresonators for cavity quantum electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. A 71, 013817 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China under Grants Nos. 11804308, 11747096, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant No. 2018T110735, and Basal Research Fund under Grant No. 02060022120009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Z., Zhu, AD., Zhang, S. et al. Generation of distributed steady entangled state between two solid-state spins. Quantum Inf Process 19, 318 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-02812-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-02812-4