Abstract
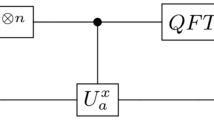
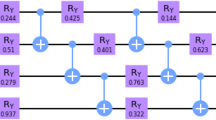
We report a quantum–classical hybrid scheme for factorization of bi-prime numbers (which are odd and square-free) using IBM’s quantum processors. The hybrid scheme proposed here involves both classical optimization techniques and adiabatic quantum optimization techniques, and is build by extending a previous scheme of hybrid factorization [Pal et al., Pramana 92, 26 (2019) and Xu et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130501 (2012)]. The quantum part of the scheme is very general in the sense that it can be implemented using any quantum computing architecture. Here, as an example, we experimentally implement our scheme for prime factorization using IBM’s QX4 quantum processor and have factorized 35.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Rivest, R.L., Shamir, A., Adleman, L.: A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Commun. ACM 21, 120 (1978)
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM review 41, 303 (1999)
Shor, P.W.: Scheme for reducing decoherence in quantum computer memory. Phys. Rev. A 52, R2493 (1995)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441 (2000)
Shor, P. W.: in Proceedings 35th annual symposium on foundations of computer science (Ieee, 1994) pp. 124–134
Vandersypen, L.M.K., Steffen, M., Breyta, G., Yannoni, C.S., Sherwood, M.H., Chuang, I.L.: Experimental realization of Shor’s quantum factoring algorithm using nuclear magnetic resonance. Nature 414, 883 (2001)
Lu, C.-Y., Browne, D.E., Yang, T., Pan, J.-W.: Demonstration of a compiled version of Shor’s quantum factoring algorithm using photonic qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 250504 (2007)
Lanyon, B.P., Weinhold, T.J., Langford, N.K., Barbieri, M., James, D.F., Gilchrist, A., White, A.G.: Experimental demonstration of a compiled version of Shor’s algorithm with quantum entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 250505 (2007)
Politi, A., Matthews, J. C., O’brien, J. L.: Shor’s quantum factoring algorithm on a photonic chip. Science 325, 1221 (2009)
Matthews, J. C., Politi, A., O’Brien, J. L.: A compiled version of Shor’s quantum factoring algorithm on a waveguide chip, in Frontiers in Optics (Optical Society of America, 2009) p. PDPA6
Lucero, E., Barends, R., Chen, Y., Kelly, J., Mariantoni, M., Megrant, A., O’Malley, P., Sank, D., Vainsencher, A., Wenner, J., et al.: Computing prime factors with a Josephson phase qubit quantum processor. Nat. Phys. 8, 719 (2012)
Peng, X., Liao, Z., Xu, N., Qin, G., Zhou, X., Suter, D., Du, J.: Quantum adiabatic algorithm for factorization and its experimental implementation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 220405 (2008)
Pal, S., Moitra, S., Anjusha, V., Kumar, A., Mahesh, T.: Hybrid scheme for factorisation: factoring 551 using a 3-qubit NMR quantum adiabatic processor. Pramana 92, 26 (2019)
Li, Z., Dattani, N. S., Chen, X., Liu, X., Wang, H., Tanburn, R., Chen, H., Peng, X., Du, J.: High-fidelity adiabatic quantum computation using the intrinsic Hamiltonian of a spin system: Application to the experimental factorization of 291311, arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.08061 (2017)
Farhi, E., Goldstone, J., Gutmann, S., Lapan, J., Lundgren, A., Preda, D.: A quantum adiabatic evolution algorithm applied to random instances of an NP-complete problem. Science 292, 472 (2001)
Xu, N., Zhu, J., Lu, D., Zhou, X., Peng, X., Du, J.: Quantum factorization of 143 on a dipolar-coupling nuclear magnetic resonance system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130501 (2012)
Dattani, N. S., Bryans, N.: Quantum factorization of 56153 with only 4 qubits, arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.6758 (2014)
Xu, K., Xie, T., Li, Z., Xu, X., Wang, M., Ye, X., Kong, F., Geng, J., Duan, C., Shi, F., et al.: Experimental adiabatic quantum factorization under ambient conditions based on a solid-state single spin system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 130504 (2017)
Dridi, R., Alghassi, H.: Prime factorization using quantum annealing and computational algebraic geometry. Sci. rep. 7, 43048 (2017)
Anschuetz, E., Olson, J., Aspuru-Guzik, A., Cao, Y.: Variational quantum factoring, in International workshop on quantum technology and optimization problems (Springer, 2019) pp. 74-85
“IBM quantum computing platform,” http://research.ibm.com/ibm-q/qx/ (2016)
Devitt, S.J.: Performing quantum computing experiments in the cloud. Phys. Rev. A 94, 032329 (2016)
Steffen, M., DiVincenzo, D.P., Chow, J.M., Theis, T.N., Ketchen, M.B.: Quantum computing: an ibm perspective. IBM J. Res. Develop. 55, 13 (2011)
Wei, S.-J., Xin, T., Long, G.-L.: Efficient universal quantum channel simulation in IBM’s cloud quantum computer. Sci. China Phys Mech. Astronomy 61, 70311 (2018)
Behera, B.K., Banerjee, A., Panigrahi, P.K.: Experimental realization of quantum cheque using a five-qubit quantum computer. Quant. Inform. Process. 16, 312 (2017)
Fedortchenko, S.: A quantum teleportation experiment for undergraduate students, arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.02398 (2016)
Sisodia, M., Shukla, A., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A.: Design and experimental realization of an optimal scheme for teleportation of an n-qubit quantum state. Quant. Inform. Process. 16, 292 (2017)
Alsina, D., Latorre, J.I.: Experimental test of Mermin inequalities on a five-qubit quantum computer. Phys. Rev. A 94, 012314 (2016)
Berta, M., Wehner, S., Wilde, M.M.: Entropic uncertainty and measurement reversibility. New J. Phys. 18, 073004 (2016)
Linke, N.M., Maslov, D., Roetteler, M., Debnath, S., Figgatt, C., Landsman, K.A., Wright, K., Monroe, C.: Experimental comparison of two quantum computing architectures. Proc. Nat. Academy Sci. 114, 3305 (2017)
Yalçınkaya, I., Gedik, Z.: Optimization and experimental realization of the quantum permutation algorithm. Phys. Rev. A 96, 062339 (2017)
Kandala, A., Mezzacapo, A., Temme, K., Takita, M., Brink, M., Chow, J.M., Gambetta, J.M.: Hardware-efficient variational quantum eigensolver for small molecules and quantum magnets. Nature 549, 242 (2017)
Wootton, J.R.: Demonstrating non-Abelian braiding of surface code defects in a five qubit experiment. Quant. Sci. Technol. 2, 015006 (2017)
Hebenstreit, M., Alsina, D., Latorre, J., Kraus, B.: Compressed quantum computation using a remote five-qubit quantum computer. Phys. Rev. A 95, 052339 (2017)
Farhi, E., Goldstone, J., Gutmann, S., Sipser, M.: Quantum computation by adiabatic evolution, arXiv preprint arXiv:quant-ph/0001106 (2000)
Mesiah, A.: Quantum Mechanics: Vol. I, Ii (North-Holla’nd (1961)
Malkoc, O.: Quantum computation with superconducting qubits. Quantum 1, 23 (2013)
Sisodia, M., Shukla, A., Pathak, A.: Experimental realization of nondestructive discrimination of Bell states using a five-qubit quantum computer. Phys. Rev. A 381, 3860 (2017)
Shukla, A., Sisodia, M., Pathak, A.: Complete characterization of the directly implementable quantum gates used in the IBM quantum processors. Phys. Rev. A 384, 126387 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Defense Research & Development Organization (DRDO), India, for the support provided through the project number ERIP/ER/1403163/M/01/1603.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, A., Shukla, A. & Pathak, A. A hybrid scheme for prime factorization and its experimental implementation using IBM quantum processor. Quantum Inf Process 20, 112 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03053-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03053-9