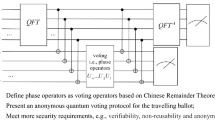
Abstract
Anonymous voting is widely used in economic and social activities, whenever it requires to express opinions privately and fairly. In this paper, we consider the task of anonymous voting using quantum mechanics. Based on quantum Bell states, anonymous entanglement is established between each voter and a tallier; thus, employing the one-time pad technique, each voter can privately cast his/her vote to the tallier. The tallier provides a mechanism of opening and permuting the ordered votes of all voters in an anonymous manner. With the distribution of all counted votes, the voting results can be obtained through a simple calculation. By a private address index, each voter can anonymously trace his/her counted vote, leading to verifiability. Following the practical requirements, the quantum anonymous voting protocol satisfies privacy, non-reusability and verifiability at the same time. Under the ideal conditions, the security concerning some common attacks is given in detail, and the theoretical analysis states that this protocol is secure.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer, Systems Signal Processing, pp. 1–7, Bangalore (1984)
Lo, H., Chau, H., Ardehali, M.: Efficient quantum key distribution scheme and a proof of its unconditional security. J. Cryptol. 18, 133–165 (2005)
Gottesman, D., Hoi-Kwong, L.: Proof of security of quantum key distribution with two-way classical communications. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 49(2), 457–475 (2003)
Horodecki, K., Horodecki, M., Horodecki, P., Leung, D., Oppenheim, J.: Quantum key distribution based on private states: unconditional security over untrusted channels with zero quantum capacity. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 54(6), 2604–2620 (2008)
Xiao, L., Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Pan, J.W.: Efficient multiparty quantum-secret-sharing schemes. Phys. Rev. A 69(5), 052307 (2004)
Zhang, K.J., Zhang, X., Jia, H.Y., Zhang, L.: A new n-party quantum secret sharing model based on multiparty entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 81 (2019)
Yang, Y.G., Gao, S., Li, D., Zhou, Y.H., Shi, W.M.: Three-party quantum secret sharing against collective noise. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 215 (2019)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y.: Multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 1797–1805 (2013)
Wang, P., Sun, Z.W., Sun, X.Q.: Multi-party quantum key agreement protocol secure against collusion attacks. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 170 (2017)
Jiang, D.H., Xu, G.B.: Multiparty quantum key agreement protocol based on locally indistinguishable orthogonal product states. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 180 (2018)
Zeng, G.H., Keitel, C.H.: Arbitrated quantum-signature scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 042312 (2002)
Yang, Y.G., Lei, H., Liu, Z.C., Zhou, Y.H., Shi, W.M.: Arbitrated quantum signature scheme based on cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 2487–2497 (2016)
Xu, G.B., Zhang, K.J.: A novel quantum group signature scheme without using entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 2577–2587 (2015)
Yang, Y.G., Zhang, M.O., Yang, R.: Private database queries using one quantum state. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 1017–1024 (2015)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y.: Quantum private query: a new kind of practical quantum cryptographic protocol. Sci. China Ser. G 62(7), 070301 (2019)
Wei, C.Y., Cai, X.Q., Liu, B., Wang, T.Y., Gao, F.: A generic construction of quantum-oblivious-key-transfer-based private query with ideal database security and zero failure. IEEE Trans. Comput. 67(1), 2–8 (2018)
Shi, R.H., Mu, Y., Zhong, H., Cui, J., Zhang, S.: Secure multiparty quantum computation for summation and multiplication. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 19655 (2016)
Wang, Q.L., Sun, H.X., Huang, W.: Multi-party quantum private comparison protocol with \(n\)-level entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(11), 2375–2389 (2014)
Cao, H., Ma, W.P., Lü, L.D., He, Y.F., Liu, G.: Multi-party quantum privacy comparison of size based on \(d\)-level GHZ states. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 287 (2019)
Fuchs, C.A., Graaf, J.V.D.: Cryptographic distinguishability measures for quantum mechanical states. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 45(4), 1216–1227 (1999)
Ambainis, A.: A new protocol and lower bounds for quantum coin flipping. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 68(2), 398–416 (2004)
Cederlof, J., Larsson, J.: Security aspects of the authentication used in quantum cryptography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 54(4), 1735–1741 (2008)
Dupuis, F., Hayden, P., Li, K.: A father protocol for quantum broadcast channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 56(6), 2946–2956 (2010)
Vaccaro, J.A., Spring, J., Chefles, A.: Quantum protocols for anonymous voting and surveying. Phys. Rev. A 75(1), 012333 (2007)
Christandl, M., Wehner, S.: Quantum anonymous transmissions. In Proc. Asiacrypt 05: 11th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, vol. 3788, pp. 217–235. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Hillery, M., Ziman, M., Bužek, V., Bieliková, M.: Towards quantum-based privacy and voting. Phys. Lett. A 349(1–4), 5–81 (2006)
Li, Y., Zeng, G.: Quantum anonymous voting systems based on entangled state. Opt. Rev. 15(5), 219–223 (2008)
Horoshko, D., Kilin, S.: Quantum anonymous voting with anonymity trace. Phys. Lett. A 375(8), 1172–1175 (2009)
Bonanome, M., Bužek, V., Hillery, M., Ziman, M.: Toward protocols for quantum-ensured privacy and secure voting. Phys. Rev. A 84, 022331 (2011)
Jiang, L., He, G., Nie, D., Xiong, J., Zeng, G.H.: Quantum anonymous voting for continuous variables. Phys. Rev. A 85(4), 9335–9340 (2012)
Wang, Q., Yu, C., Gao, F., Qi, H.Y., Wen, Q.Y.: Self-tallying quantum anonymous voting. Phys. Rev. A 94(2), 022333 (2016)
Wang, Y.W.: Quantum voting protocols based on the non-symmetric quantum channel with controlled quantum operation teleportation. Acta Phys. Sin. 62(16), 581–586 (2013)
Guo, Y., Feng, Y.Y., Zeng, G.H.: Quantum anonymous voting with unweighted continuous-variable graph states. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 3327–3345 (2019)
Tian, J.H., Zhang, J.Z., Li, Y.P.: A voting protocol based on the controlled quantum operation teleportation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(5), 2303–2310 (2016)
Xue, P., Zhang, X.: A simple quantum voting scheme with multi-qubit entanglement. Sci. Rep. 7, 7586 (2017)
Arapinis, M., Kashefi, E., Lamprou, N., Pappa, A.: Definitions and analysis of quantum e-voting protocols. arXiv:1810.05083 (2018)
Delaune, S., Kremer, S., M., Ryan, M.: Coercion-resistance and receipt-freeness in electronic voting. In: 19th IEEE Computer Security Foundations Workshop (CSFW’06), Venice, Italy, pp.12-42. https://doi.org/10.1109/CSFW.2006.8. (2006)
Canetti, R.: Universally composable security: a new paradigm for cryptographic protocols. In: Proceedings of the 42nd IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, USA, pp. 136–145 (2001)
Unruh, D.: Universally composable quantum multi-party computation. Lecture Notes Comput Science pp. 486–505 (2010)
Kashefi, E., Music, L., Wallden, P.: The quantum cut-and-choose technique and quantum two-party computation. arXiv:1703.03754 (2017)
Adida, B.: Helios: web-based open-audit voting. In: USENIX Security Symposium, vol. 17 (2008)
Kiayias, A., Zacharias, T., Zhang, B.: End-to-end verifiable elections in the standard model. In: Proceedings of the 34th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Springer, Berlin (2015)
Ryan, P.Y., Bismark, D., Heather, J., Schneider, S., Xia, Z.: Prêt à voter: a voter-verifiable voting system. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensic Security 4(4), 662–673 (2010)
Cortier, V., Galindo, D., Küsters, R., Muller, J., Truderung, T.: Sok: verifiability notions for e-voting protocols. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, USA, pp. 779–798 (2016)
Gritzalis, D.A.: Principles and requirements for a secure e-voting system. Comput. Security 21(6), 539–556 (2002)
Kiayias, A.: Electronic voting (2010)
Zhou, N.R., Wang, L.J., Ding, J., Gong, L.H.: Quantum deterministic key distribution protocols based on the authenticated entanglement channel. Phys. Scr. 81(4), 045009 (2010)
Zawadzki, P.: Quantum identity authentication without entanglement. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(1), 1–12 (2019)
Guo, F.Z., Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Zhang, J., Wen, Q.Y.: Quantum private comparison protocol based on entanglement swapping of \(d\)-level Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 2793–2802 (2013)
Liu, W., Wang, Y., Wang, X.: Quantum multi-party private comparison protocol using d-dimensional Bell states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54, 1830–1839 (2015)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65(3), 032302 (2002)
Rubin, F.: One-time pad cryptography. Cryptologia 20(4), 359–364 (1996)
Ycart, B.: A case of mathematical eponymy: the Vandermonde determinant. arXiv:math.PR:1204.4716
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: A simple participant attack on the brádler-duěk protocol. Quantum Inf. Comput. 7(4), 329 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NSFC (Grant No. 61801126), Open project of CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. KQI201902), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2020MS014) Research and Application of Key Technologies for Open Source Software Security Monitoring (Grant No. SGFJXT00YJJS1800074).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Liu, J., Li, Y. et al. Quantum Bell states-based anonymous voting with anonymity trace. Quantum Inf Process 20, 142 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03081-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03081-5