Abstract
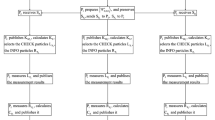
The quantum private comparison aims to make the size comparison of two participants’ private information without leaking the private data of their own with quantum mechanism. In this paper, different from the current method of using single particle or entangled state as the information carrier, a novel two-party quantum private comparison protocol is firstly proposed via quantum walks on circle. In the protocol, a third party is assumed to be semi-honest and allowed to misbehave on his own, but cannot conspire with either of the two dishonest participants and obtain the participants’ private information. The protocol adopts the two-particle quantum walks state on circle rather than entangled state as the initial quantum resource and only needs measurement and quantum walks operator without the unitary operation and quantum entanglement swapping. The two-particle state is transferred as a whole among different parties, which reduces the protocol complexity and avoids the chance of being attacked. It can implement the equality comparison of private information, but also the size comparison. Security analyses show that this protocol is resistant to the external and internal malicious attacks, which can also determine the disputes over the judgment result of the third party. Compared with other quantum private comparison protocols, the proposed protocol has better flexibility and universality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao, A.C.: Protocols for secure computations. In: 23rd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (SFCS 1982), Chicago, IL, USA, 1982, pp. 160–164
Arute, F., Arya, K., Babbush, R., et al.: Quantum supremacy using a programmable superconducting processor. Nature 574, 505–511 (2019)
Qiang, X.G., Zhou, X.Q., Aungskunsiri, K., et al.: Quantum processing by remote quantum control. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2, 045002 (2017)
Long, G.L.: General quantum interference principle and duality computer. Commun. Theor. Phys. 45(5), 825–844 (2006)
Lo, H.K.: Insecurity of quantum secure computations. Phys. Rev. A 56(2), 1154–1162 (1997)
Yang, Y.G., Wen, Q.Y.: An efficient two-party quantum private comparison protocol with decoy photons and two-photon entanglement. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 42(5), 055305 (2009)
Yang, Y.G., Gao, W.F., Wen, Q.Y.: Secure quantum private comparison. Phys. Scr. 80(6), 065002 (2009)
Yang, Y.G., Xia, J., Jia, X., et al.: New quantum private comparison protocol without entanglement. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 10(06), 1250065 (2012)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Lin, B., et al.: Robust and efficient quantum private comparison of equality with collective detection over collective-noise channels. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. 56(9), 1670–1678 (2013)
Yu, C.H., Guo, G.D., Lin, S.: Quantum private comparison with d-level single-particle states. Phys. Scr. 88(6), 065013 (2013)
Liu, B., Xiao, D., Huang, W., et al.: Quantum private comparison employing single-photon interference. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(7), 180 (2017)
Pan, H.M.: Two-party quantum private comparison using single photons. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 3389–3395 (2018)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B., Cui, W.: Quantum private comparison protocol based on Bell entangled states. Commun. Theor. Phys. 57(4), 583–588 (2012)
Tseng, H.Y., Lin, J., Hwang, T.: New quantum private comparison protocol using EPR pairs. Quantum Inf. Process. 11(2), 373–384 (2012)
Wang, C., Xu, G., Yang, Y.X.: Cryptanalysis and improvements for the quantum private comparison protocol using EPR pairs. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 11(04), 1350039 (2013)
Yang, Y.G., Xia, J., Jia, X., Zhang, H.: Comment on quantum private comparison protocols with a semihonest third party. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(2), 877–885 (2013)
Zhang, W.W., Zhang, K.J.: Cryptanalysis and improvement of the quantum private comparison protocol with semi-honest third party. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(5), 1981–1990 (2013)
Lin, S., Sun, Y., Liu, X.F., Yao, Z.Q.: Quantum private comparison protocol with d-dimensional Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(1), 559–568 (2013)
Guo, F.Z., Gao, F., Qin, S.J., et al.: Quantum private comparison protocol based on entanglement swapping of d-level Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(8), 2793–2802 (2013)
Zhang, W.W., Li, D., Zhang, K.J., Zuo, H.J.: A quantum protocol for millionaire problem with Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(6), 2241–2249 (2013)
Liu, W.J., Liu, C., Chen, H.W., et al.: Cryptanalysis and improvement of quantum private comparison protocol based on Bell entangled states. Commun. Theor. Phys. 62(2), 210–214 (2014)
Tan, X.Q., Zhang, X.Q., Li, J.: Big data quantum private comparison with the intelligent third party. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. 6(6), 797–806 (2015)
Wang, F., Luo, M., Li, H., et al.: Quantum private comparison based on quantum dense coding. Sci. China-Inf. Sci. 59(11), 112501 (2016)
Chen, X.B., Xu, G., Niu, X.X., et al.: An efficient protocol for the private comparison of equal information based on the triplet entangled state and single-particle measurement. Opt. Commun. 283(7), 1561–1565 (2010)
Lin, J., Tseng, H.Y., Hwang, T.: Intercept-resend attacks on Chen et al.’s quantum private comparison protocol and the improvements. Opt. Commun. 284(9), 2412–2414 (2011)
Jia, H.Y., Wen, Q.Y., Song, T.T., Gao, F.: Quantum protocol for millionaire problem. Opt. Commun. 284(1), 545–549 (2011)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B.: Quantum private comparison based on GHZ entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51(11), 3596–3604 (2012)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B., Jiang, Z.T.: An efficient protocol for the quantum private comparison of equality with W state. Opt. Commun. 284, 3160–3163 (2011)
Zhang, W.W., Li, D., Li, Y.B.: Quantum private comparison protocol with W States. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(5), 1723–1729 (2014)
Xu, G.A., Chen, X.B., Wei, Z.H., et al.: An efficient protocol for the quantum private comparison of equality with a four-qubit cluster state. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 10(4), 1250045 (2012)
Sun, Z.W., Long, D.Y.: Quantum private comparison protocol based on cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52(1), 212–218 (2013)
Li, C.Y., Chen, X.B., Li, H., et al.: Efficient quantum private comparison protocol based on the entanglement swapping between four-qubit cluster state and extended Bell state. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(5), 158 (2019)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B., Jiang, Z.T., et al.: A protocol for the quantum private comparison of equality with \(\chi \)-type state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51(1), 69–77 (2012)
Jia, H.Y., Wen, Q.Y., Li, Y.B., Cao, F.: Quantum private comparison using genuine four-particle entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51(4), 1187–1194 (2012)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B., Jiang, Z.T., et al.: New quantum private comparison protocol using \(\chi \)-type state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51(6), 1953–1960 (2012)
Lin, S., Guo, G.D., Liu, X.F.: Quantum private comparison of equality with \(\chi \)-type entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52(11), 4185–4194 (2013)
Pan, H.M.: Quantum private comparison based on \(\chi \)-type entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(10), 3340–3347 (2017)
Li, J., Zhou, H.F., Jia, L., Zhang, T.T.: An efficient protocol for the private comparison of equal information based on four-particle entangled W state and Bell entangled states swapping. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(7), 2167–2176 (2014)
Ji, Z.X., Fan, P.R., Zhang, H.G., Wang, H.Z.: Several two-party protocols for quantum private comparison using entanglement and dense coding. Opt. Commun. 459(15), 124911 (2020)
Ye, T.Y., Ji, Z.X.: Two-party quantum private comparison with five-qubit entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(5), 1517–1529 (2017)
Ji, Z.X., Ye, T.Y.: Quantum private comparison of equal information based on highly entangled six-qubit genuine state. Commun. Theor. Phys. 65(6), 711–715 (2016)
Ji, Z.X., Zhang, H.G., Wang, H.Z.: Quantum private comparison protocols with a number of multi-particle entangled states. IEEE Access 7, 44613–44621 (2019)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B.: Dynamic multi-party quantum private comparison protocol with single photons in both polarization and spatial-mode degrees of freedom. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(12), 5307–5317 (2016)
Ye, C.Q., Ye, T.Y.: Multi-party quantum private comparison of size relation with d-level single-particle states. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(10), 252 (2018)
Du, G., Zhang, F., Ma, C.G.: A new multi-party quantum private comparison protocol based on circle model. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58, 3225–3233 (2019)
Song, X.L., Wen, A.J., Gou, R.: Multiparty quantum private comparison of size relation based on single-particle states. IEEE Access 7, 142507–142514 (2019)
Abulkasim, H., Alsuqaih, H.N., Hamdan, W.F., Hamad, S., et al.: Improved dynamic multi-party quantum private comparison for next-generation mobile network. IEEE Access 7, 17917–17926 (2019)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B., Wang, X.M.: Quantum multi-party private comparison protocol using d-dimensional Bell states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54(6), 1830–1839 (2015)
Ye, T.Y.: Multi-party quantum private comparison protocol based on entanglement swapping of Bell entangled states. Commun. Theor. Phys. 66(3), 280–290 (2016)
Ji, Z.X., Ye, T.Y.: Multi-party quantum private comparison based on the entanglement swapping of d-level Cat states and d-level Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(7), 177 (2017)
Ye, T.Y., Ji, Z.X.: Multi-user quantum private comparison with scattered preparation and one-way convergent transmission of quantum states. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 60(9), 090312 (2017)
Chang, Y.J., Tsai, C.W., Hwang, T.: Multi-user private comparison protocol using GHZ class states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(2), 1077–1088 (2013)
Huang, S.L., Hwang, T., Gope, P.: Multi-party quantum private comparison protocol with an almost-dishonest third party using GHZ states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(6), 2969–2976 (2016)
Huang, S.L., Hwang, T., Gope, P.: Multi-party quantum private comparison with an almost-dishonest third party. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 4225–4235 (2015)
Hung, S.M., Hwang, S.L., Hwang, T., Kao, S.H.: Multiparty quantum private comparison with almost dishonest third parties for strangers. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(2), 36 (2017)
Wang, Q.L., Sun, H.X., Huang, W.: Multi-party quantum private comparison protocol with n-level entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(11), 2375–2389 (2014)
Luo, Q.B., Yang, G.W., She, K., et al.: Multi-party quantum private comparison protocol based on d-dimensional entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(10), 2343–2352 (2014)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B., Wang, X.M.: Multi-party quantum private comparison protocol using d-dimensional basis states without entanglement swapping. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(4), 1085–1091 (2014)
Aharonov, Y., Davidovich, L., Zagury, N.: Quantum random walks. Phys. Rev. A 48(2), 1687–1690 (1993)
Farhi, E., Gutmann, S.: Quantum computation and decision trees. Phys. Rev. A 58(2), 915–928 (1998)
Ambainis, A.: Quantum walk algorithm for element distinctness. In: 45th Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Rome, Italy, pp. 22–31 (2004)
Magniez, F., Santha, M., Szegedy, M.: Quantum algorithms for the triangle problem. SIAM J. Comput. 37(2), 413–424 (2007)
Tamascelli, D., Zanetti, L.: A quantum-walk-inspired adiabatic algorithm for solving graph isomorphism problems. J. Phys. A-Math. Theor. 47(32), 3025302 (2014)
Chakraborty, S., Novo, L., Giorgio, S.D., Omar, Y.: Optimal quantum spatial search on random temporal networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119(22), 220503 (2017)
Yang, Y.G., Yang, J.J., Zhou, Y.H., et al.: Quantum network communication: a discrete-time quantum-walk approach. Sci. China-Inf. Sci. 61(4), 042501 (2018)
Kurzyński, P., Wójcik, A.: Quantum walk as a generalized measuring device. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(20), 200404 (2013)
Zhan, X., Qin, H., Bian, Z.H., et al.: Perfect state transfer and efficient quantum routing: a discrete-time quantum-walk approach. Phys. Rev. A 90(1), 012331 (2014)
Yalccinkaya, I., Gedik, Z.: Qubit state transfer via discrete-time quantum walks. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 48(22), 225302 (2015)
Babatunde, A.M., Cresser, J., Twamley, J.: Using a biased quantum random walk as a quantum lumped element router. Phys. Rev. A 90(1), 124–129 (2014)
Vlachou, C., Rodrigues, J., Mateus, P., et al.: Quantum walk public-key cryptographic system. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 13(07), 1550050 (2015)
Vlachou, C., Krawec, W., Mateus, P., et al.: Quantum key distribution with quantum walks. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(11), 288 (2018)
Li, H.J., Jian, J., Xiang, N., et al.: A new kind of universal and flexible quantum information splitting scheme with multi-coin quantum walks. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(10), 316 (2019)
Wang, Y., Shang, Y., Xue, P.: Generalized teleportation by quantum walks. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(9), 221 (2017)
Yang, Y.G., Cao, S.N., Chao, W.F., et al.: Generalized teleportation by means of discrete-time quantum walks on N-lines and N-cycles. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 33(06), 1950070 (2019)
Gnutzmann, S., Smilansky, U.: Quantum graphs: applications to quantum chaos and universal spectral statistics. Adv. Phys. 55(5–6), 527–625 (2006)
Gao, F., Gao, F.Z., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Comment on “experimental demonstration of a quantum protocol for byzantine agreement and liar detection’’. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101(20), 208901 (2008)
Gao, F., Lin, S., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: A special eavesdropping on one-sender versus n-receiver QSDC protocol. Chin. Phys. Lett. 25(5), 1561–1563 (2008)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: A simple participant attack on the brádler-dušek protocol. Quantum Inf. Comput. 7(4), 329–334 (2007)
Li, C.Y., Zhou, H.Y., Wang, Y., Deng, F.G.: Secure quantum key distribution network with Bell states and local unitary operations. Chin. Phys. Lett. 22(5), 1049–1052 (2005)
Li, C.Y., Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., et al.: Efficient quantum cryptography network without entanglement and quantum memory. Chin. Phys. Lett. 23(11), 2896–2899 (2006)
Chen, Y., Man, Z.X., Xia, Y.J.: Quantum bidirectional secure direct communication via entanglement swapping. Chin. Phys. Lett. 24(1), 19 (2007)
Ye, T.Y., Jiang, L.Z.: Improvement of controlled bidirectional quantum direct communication using a GHZ state. Chin. Phys. Lett. 30(04), 040305 (2013)
Gao, G., Wang, L.P.: A protocol for bidirectional quantum secure communication based on genuine four-particle entangled states. Commun. Theor. Phys. 54(3), 447–451 (2010)
Xiu, X.M., Dong, H.K., Dong, L., et al.: Deterministic secure quantum communication using four-particle genuine entangled state and entanglement swapping. Opt. Commun. 282(12), 2457–2459 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by University Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Province of China (Grant Nos. KJ2019A0580, KJ2019A0562), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11975025, 11701009) and Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province of China (Grant No. 1708085MA10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, FL., Zhang, H., Chen, SG. et al. Novel two-party quantum private comparison via quantum walks on circle. Quantum Inf Process 20, 178 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03084-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03084-2