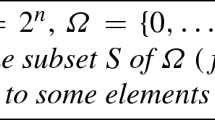Abstract
We introduce the notion of partial orbit for a given set of elementary quantum gates, and we study the action of different sets of gates on an initially three-particle disentangled state. We analyze the entanglement of the resulting quantum states by appealing to the violation of Svetlichny inequality. We find that the violation values are concentrated on specific regions. This constitutes evidence for the existence of a structure, which is quite different from that of a randomly generated (using the Haar measure) set of gates. In turn, this fact highlights the relevance of studying the physical properties of the partial orbits associated with different sets of elementary gates.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Montanaro, A.: Quantum algorithms: an overview. npj Quant. Inf 2(1), 15023 (2016)
Holik, F., Sergioli, G., Freytes, H., Plastino, A.: Logical structures underlying quantum computing. Entropy 21(1), 77 (2019)
Linke, N.M., Maslov, D., Roetteler, M., Debnath, S., Figgatt, C., Landsman, K.A., Wright, K., Monroe, C.: Experimental comparison of two quantum computing architectures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114(13), 3305–3310 (2017)
Preskill, J.: Quantum computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2, 79 (2018)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum computation and quantum information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Svetlichny, G.: Distinguishing three-body from two-body nonseparability by a bell-type inequality. Phys. Rev. D 35, 3066–3069 (1987)
Swain, M., Rai, A., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Experimental demonstration of the violations of mermin’s and svetlichny’s inequalities for w and ghz states. Quant. Inf. Process. 18(7), 218 (2019)
Barenco, A., Bennett, C.H., Cleve, R., DiVincenzo, D.P., Margolus, N., Shor, P., Sleator, T., Smolin, J.A., Weinfurter, H.: Elementary gates for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 52, 3457–3467 (1995)
Kitaev, A.Y.: Quantum computations: algorithms and error correction. Rus. Math. Surv. 52(6), 1191–1249 (1997)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: The Solovay-Kitaev theorem, pp. 617–624. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Vartiainen, J.J., Möttönen, M., Salomaa, M.M.: Efficient decomposition of quantum gates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 177902 (2004)
Möttönen, M., Vartiainen, J.J., Bergholm, V., Salomaa, M.M.: Quantum circuits for general multiqubit gates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 130502 (2004)
Werner, R.F.: Quantum states with einstein-podolsky-rosen correlations admitting a hidden-variable model. Phys. Rev. A 40(8), 4277 (1989)
Bell, J.S.: On the problem of hidden variables in quantum mechanics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 38, 447–452 (1966)
Mermin, N.D.: Extreme quantum entanglement in a superposition of macroscopically distinct states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 1838–1840 (1990)
Huang, W.J., Chien, W.C., Cho, C.H., Huang, C.C., Huang, T.W., Chang, C.R.: Mermin’s inequalities of multiple qubits with orthogonal measurements on ibm q 53-qubit system. Quant. Eng. 2(2), e45 (2020)
Ajoy, A., Rungta, P.: Svetlichny’s inequality and genuine tripartite nonlocality in three-qubit pure states. Phys. Rev. A 81, 052334 (2010)
Wang, K., Zheng, Z.J.: Violation of svetlichny inequality in triple jaynes-cummings models. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 6621 (2020)
Lavoie, J., Kaltenbaek, R., Resch, K.J.: Experimental violation of svetlichny’s inequality. New J. Phys. 11(7), 073051 (2009)
Seevinck, M., Svetlichny, G.: Bell-type inequalities for partial separability in n-particle systems and quantum mechanical violations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 060401 (2002)
Caban, P., Molenda, A., Trzcińska, K.: Activation of the violation of the svetlichny inequality. Phys. Rev. A 92, 032119 (2015)
Funding
This work is supported by 1) MIUR, project PRIN 2017: “Theory and applications of resource sensitive logics” (code: 20173WKCM5). 2) MIUR project PRIN 2017: “Logic and Cognition: theory, experiments, applications” (code: 20173YP4N3). 3) RAS (Regione Autonoma della Sardegna) 2018: “Per un’estensione semantica della Logica Computazionale Quantistica-Impatto teorica e ricadute implementative” (code: RASSR40341).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix
In order to study the violation of the Svetlichny inequality, we consider three particles \(a, \, b, \, c\) and two possible measurements for each particle. For particle a, we consider the measurements \(A = \vec {\alpha }\cdot \vec {\sigma }\) and \(A' = \vec {\alpha '}\cdot \vec {\sigma }\); for particle b, the measurements \(B = \vec {\beta }\cdot \vec {\sigma }\) and \(B'= \vec {\beta '}\cdot \vec {\sigma }\); and for particle c, the measurements \(C = \vec {\gamma }\cdot \vec {\sigma }\) and \(C' = \vec {\gamma '}\cdot \vec {\sigma }\). The Svetlichny inequality of a state \(\rho \) can be expressed in terms of the Svetlichny function \({\mathcal {S}}(\rho ,\vec {\alpha },\vec {\alpha }',\vec {\beta },\vec {\beta }',\vec {\gamma },\vec {\gamma }')\) as follows
where S is the Svetlichny operator defined as follows:
By parameterizing the unit norm vectors \(\vec {\alpha }, \, \vec {\alpha '}, \, \vec {\beta }, \,\vec {\beta '}, \, \vec {\gamma }, \, \vec {\gamma '}\) with spherical coordinates, the dependence of the local observables A, B, and C with respect to the angles is given by:
with similar equations for the primed coordinates. For each state \(\rho \), obtained by applying the elementary gates to the initial sate \(\rho _{0}\), we find the combination of angles that maximizes the Svetlichny function \({\mathcal {S}}(\rho ,\vec {\alpha },\vec {\alpha }',\vec {\beta },\vec {\beta }',\vec {\gamma },\vec {\gamma }')\), i.e., the combination that maximizes the violation of the inequality (6). The maximum value obtained is called Svetlichny maximum value. In this way, we quantify how much entanglement is obtained after the application of a sequence of elementary gates. The Svetlichny maximum values of the states of the partial orbits are used to build the histograms displayed in Section 4.
Appendix
In Fig. 4, we show similar calculations to those of Sect. 4, but starting with a three-qubit GHZ state, i.e., an initially entangled state.
Histograms in logarithmic scale of the maximum values of the Svetlichny function for partial orbits of different degrees, associated with an initial GHZ state. a Clifford set, degree 7; b Clifford set, degree 6 with noise parameter \(=0.2\); c Clifford set, degree 6 with noise parameter \(=0.05\); d Cnot + Toff set, degree 7; e Cnot + Toff set, degree 6 with noise parameter \(=0.2\); f Cnot + Toff set, degree 6 with noise parameter \(=0.05\)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holik, F., Losada, M., Freytes, H. et al. Partial orbits of quantum gates and full three-particle entanglement. Quantum Inf Process 20, 351 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03261-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03261-3