Abstract
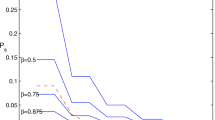
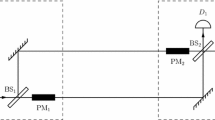
Quantum-key-distribution (QKD)-based quantum private queries (QPQs) are the most practical protocols for the symmetrically private information retrieval problem. But these protocols cannot resist joint-measurement (JM) attack. Recently, Wei et al. proposed a QPQ protocol with good performance in resisting JM attack (RJM-QPQ) (Phys. Rev. A 93, 042318 (2016)). However, due to the imperfections of ideal single-photon source, one has to consider the security of this protocol under weak coherent pulses sources (WCPS). In this paper, after analyzing the security loophole of RJM-QPQ protocol under WCPS, we propose a QPQ protocol with decoy-state method (DS-QPQ). Compared to the RJM-QPQ protocol, DS-QPQ has better performance under WCPS. It can also resist the JM attack. Furthermore, it improves database security, user privacy and efficiency. Moreover, DS-QPQ retains the good characters of QKD-based QPQs, e.g., it is loss tolerant and robust against quantum memory attack.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, pp. 175–179. IEEE, New York (1984)
Kushilevitz, E., Ostrovsky, R.: In: Proceedings of the 38th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, p. 364. IEEE, New York (1997)
Gentner, Y., Ishai, Y., Kushilevitz, E., Malkin, T.: Protecting data privacy in private information retrieval schemes. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 60, 592 (2000)
Chor, B., Goldreich, O., Kushilevitz, E., Sudan, M.: In: Proceedings of the 36th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, p. 41. IEEE, New York (1995)
Shor, P.W.: In: Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on the Foundations of Computer Science, Santa Fe, New Mexico, p. 124. Piscataway, IEEE (1994)
Grover, L.K.: In: Proceedings of the 28th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, p. 212. ACM, New York (1996)
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L.: Quantum private queries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 230502 (2008)
Jakobi, M., Simon, C., Gisin, N., Bancal, J.D., Branciard, C., Walenta, N., Zbinden, H.: Practical private database queries based on a quantum-key-distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. A 83, 022301 (2011)
Lo, H.K., Chau, H.F.: Unconditional security of quantum key distribution over arbitrarily long distances. Science 283, 2050 (1999)
Lo, H.K., Ma, X.F., Chen, K.: Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230504 (2005)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012)
Tang, Z.Y., Liao, Z.F., Xu, F.H., Qi, B., Qian, L., Lo, H.K.: Experimental demonstration of polarization encoding measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 190503 (2014)
Gao, F., Liu, B., Wen, Q.Y., Chen, H.: Flexible quantum private queries based on quantum key distribution. Opt. Express 20, 17411 (2012)
PandurangaRao, M.V., Jakobi, M.: Towards communication-efficient quantum oblivious key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 87, 012331 (2013)
Zhang, J.L., Guo, F.Z., Gao, F., Liu, B., Wen, Q.Y.: Private database queries based on counterfactual quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 88, 022334 (2013)
Yang, Y.G., Sun, S.J., Xu, P., Tiang, J.: Flexible protocol for quantum private query based on b92 protocol. Quant. Info. Proc. 13, 805 (2014)
Wei, C.Y., Gao, F., Wen, Q.Y., Wang, T.Y.: Practical quantum private query of blocks based on unbalanced-state bennett-brassard-1984 quantum-key-distribution protocol. Sci. Rep. 4, 7537 (2014)
Chan, P., Lucio-Martinez, I., Mo, X., Simon, C., Tittel, W.: Performing private database queries in a real-world environment using a quantum protocol. Sci. Rep. 4, 5233 (2014)
Gao, F., Liu, B., Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y.: Postprocessing of the oblivious key in quantum private query. IEEE. J. Sel. Top. Quant. 21, 6600111 (2015)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W.: Qkd-based quantum private query without a failure probability. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 100301 (2015)
Brassard, G., Lutkenhaus, N., Mor, T., Sanders, B.C.: Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1330 (2000)
Niederberger, A., Scarani, V., Gisin, N.: Photon-number-splitting versus cloning attacks in practical implementations of the bennett-brassard 1984 protocol for quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. A 71, 042316 (2005)
Lütkenhaus, N., Jahma, M.: Quantum key distribution with realistic states: photon-number statistics in the photon-number splitting attack. New J. Phys. 4, 44 (2002)
Wei, C.Y., Cai, X.Q., Liu, B., Wang, T., Gao, F.: A generic construction of quantum-oblivious-key-transfer-based private query with ideal database security and zero failure. IEEE Trans. Comput. 67, 2 (2018)
Wei, C.Y., Wang, T.Y., Gao, F.: Practical quantum private query with better performance in resisting joint-measurement attack. Phys. Rev. A 93, 042318 (2016)
Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K., Lutkenhaus, N., Preskill, J.: Security of quantum key distribution with imperfect devices. Quantum Inf. Comput. 4, 325 (2004)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-deviceindependent Quantum key Distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012)
Bergou, J.A.: Discrimination of quantum states. J. Mod. Opt. 57, 160 (2010)
Maitra, A., Paul, G., Roy, S.: Device-independent quantum private query. Phys. Rev. A 95, 042344 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 62171056,61973021), the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (Program No.2021JM-464).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Guo, FZ. & Wen, QY. Practical decoy-state quantum private queries against joint-measurement attack under weak coherent pulse sources. Quantum Inf Process 20, 392 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03329-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03329-0