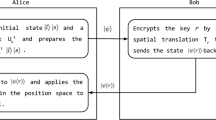
Abstract
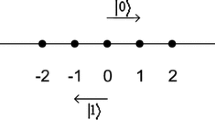
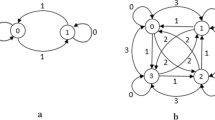
Very recently, many tasks in quantum information processing have been achieved with coined quantum walks. In this paper, an efficient and secure quantum teleportation of shared quantum secret is presented in a quantum-walk architecture. To achieve the transfer of the quantum secret from a group of n senders to another group of m receivers, quantum walk with n walkers on the line is utilized and we adopt two different approaches: the homogeneous coin operator and the position-dependent coin operator. Furthermore, we show that none of the participants can fully access the information. This work not only opens a route to the realization of secure distributed quantum communications and computations in quantum networks, but also opens the wider application purpose of quantum walks.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
Our manuscript has no associated data.
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70(13), 1895 (1993)
Raussendorf, R., Browne, D.E., Briegel, H.J.: Measurement-based quantum computation on cluster states. Phys. Rev. A 68(2), 022312 (2003)
Pirandola, S., Eisert, J., Weedbrook, C., Furusawa, A., Braunstein, S.L.: Advances in quantum teleportation. Nat. Photonics 9(10), 641 (2015)
Lee, S.M., Lee, S.W., Jeong, H., Park, H.S.: Quantum teleportation of shared quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124(6), 060501 (2020)
Kimble, H.J.: The quantum internet. Nature 453(7198), 1023 (2008)
Cacciapuoti, A.S., Caleffi, M., Van Meter, R., Hanzo, L.: When entanglement meets classical communications: quantum teleportation for the quantum internet. IEEE Trans. Commun. 68(6), 3808 (2020)
Wang, X.L., Cai, X.D., Su, Z.E., Chen, M.C., Wu, D., Li, L., Liu, N.L., Lu, C.Y., Pan, J.W.: Quantum teleportation of multiple degrees of freedom of a single photon. Nature 518(7540), 516 (2015)
Sun, Q.C., Mao, Y.L., Chen, S.J., Zhang, W., Jiang, Y.F., Zhang, Y.B., Zhang, W.J., Miki, S., Yamashita, T., Terai, H., et al.: Quantum teleportation with independent sources and prior entanglement distribution over a network. Nat. Photonics 10(10), 671 (2016)
Luo, Y.H., Zhong, H.S., Erhard, M., Wang, X.L., Peng, L.C., Krenn, M., Jiang, X., Li, L., Liu, N.L., Lu, C.Y., et al.: Quantum teleportation in high dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 123(7), 070505 (2019)
Karlsson, A., Bourennane, M.: Quantum teleportation using three-particle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 58(6), 4394 (1998)
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K.: How to share a quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83(3), 648 (1999)
Hillery, M., Bužek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharin. Phys. Rev. A 59(3), 1829 (1999)
Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Quantum information splitting using multipartite cluster states. Phys. Rev. A 78(6), 062333 (2008)
Dou, Z., Xu, G., Chen, X.B., Liu, X., Yang, Y.X.: A secure rational quantum state sharing protocol. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 61(2), 022501 (2018)
Aharonov, Y., Davidovich, L., Zagury, N.: Quantum random walks. Phys. Rev. A 48(2), 1687 (1993)
Farhi, E., Gutmann, S.: Quantum computation and decision trees. Phys. Rev. A 58(2), 915 (1998)
Childs, A.M.: Universal computation by quantum walk. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102(18), 180501 (2009)
Lovett, N.B., Cooper, S., Everitt, M., Trevers, M., Kendon, V.: Universal quantum computation using the discrete-time quantum walk. Phys. Rev. A 81(4), 042330 (2010)
Childs, A.M., Gosset, D., Webb, Z.: Universal computation by multiparticle quantum walk. Science 339(6121), 791 (2013)
Shenvi, N., Kempe, J., Whaley, K.B.: Quantum random-walk search algorithm. Phys. Rev. A 67(5), 052307 (2003)
Ambainis, A., Kempe, J., Rivosh, A.: In coins make quantum walks faster. In: Proceedings of the Sixteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, pp. 1099–1108. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (2005)
Tulsi, A.: Faster quantum-walk algorithm for the two-dimensional spatial search. Phys. Rev. A 78(1), 012310 (2008)
Goyal, S.K., Roux, F.S., Forbes, A., Konrad, T.: Implementing quantum walks using orbital angular momentum of classical light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(26), 263602 (2013)
Xue, P., Zhang, R., Qin, H., Zhan, X., Bian, Z., Li, J., Sanders, B.C.: Experimental quantum-walk revival with a time-dependent coin. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114(14), 140502 (2015)
Kurzyński, P., Wojcik, A.: Discrete-time quantum walk approach to state transfer. Phys. Rev. A 83(6), 062315 (2011)
Zhan, X., Qin, H., Bian, Z.h., Li, J., Xue, P.: Perfect state transfer and efficient quantum routing: a discrete-time quantum-walk approach. Phys. Rev. A 90(1), 012331 (2014)
Wang, Y., Shang, Y., Xue, P.: Generalized teleportation by quantum walks. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(9), 221 (2017)
Li, H.J., Chen, X.B., Wang, Y.L., Hou, Y.Y., Li, J.: A new kind of flexible quantum teleportation of an arbitrary multi-qubit state by multi-walker quantum walks. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(9), 266 (2019)
Li, M., Shang, Y.: Entangled state generation via quantum walks with multiple coins. npj Quantum Inf. 7(1), 1 (2021)
Shang, Y., Li, M.: Experimental realization of state transfer by quantum walks with two coins. Quantum Sci. Technol. 5(1), 015005 (2019)
Chatterjee, Y., Devrari, V., Behera, B.K., Panigrahi, P.K.: Experimental realization of quantum teleportation using coined quantum walks. Quantum Inf. Process. 19(1), 1 (2020)
Pant, M., Krovi, H., Towsley, D., Tassiulas, L., Jiang, L., Basu, P., Englund, D., Guha, S.: Routing entanglement in the quantum internet. npj Quantum Inf. 5(1), 1 (2019)
Brun, T.A., Carteret, H.A., Ambainis, A.: Quantum walks driven by many coins. Phys. Rev. A 67(5), 052317 (2003)
Venegas, Andraca S., Ball, J., Burnett, K., Bose, S.: Quantum walks with entangled coins. New J. Phys. 7(1), 221 (2005)
Liu, C., Petulante, N.: One-dimensional quantum random walks with two entangled coins. Phys. Rev. A 79(3), 032312 (2009)
Liu, C.: Asymptotic distributions of quantum walks on the line with two entangled coins. Quantum Inf. Process. 11(5), 1193 (2012)
Shang, Y., Wang, Y., Li, M., Lu, R.: Quantum communication protocols by quantum walks with two coins. EPL 124(6), 60009 (2019)
Li, H.J., Li, J., Xiang, N., Zheng, Y., Yang, Y.G., Naseri, M.: A new kind of universal and flexible quantum information splitting scheme with multi-coin quantum walks. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(10), 316 (2019)
Chandrashekar, C., Banerjee, S.: Parrondo’s game using a discrete-time quantum walk. Phys. Lett. A 375(14), 1553 (2011)
Rajendran, J., Benjamin, C.: Implementing Parrondo’s paradox with two-coin quantum walks. Open Sci. 5(2), 171599 (2018)
Rajendran, J., Benjamin, C.: Playing a true Parrondo’s game with a three-state coin on a quantum walk. EPL 122(4), 40004 (2018)
Jan, M., Wang, Q.Q., Xu, X.Y., Pan, W.W., Chen, Z., Han, Y.J., Li, C.F., Guo, G.C., Abbott, D.: Experimental realization of Parrondo’s paradox in 1D quantum walks. Adv. Quantum Technol. 66, 1900127 (2020)
Omar, Y., Paunković, N., Sheridan, L., Bose, S.: Quantum walk on a line with two entangled particles. Phys. Rev. A 74(4), 042304 (2006)
Pathak, P., Agarwal, G.: Quantum random walk of two photons in separable and entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 75(3), 032351 (2007)
Štefaňák, M., Barnett, S., Kollár, B., Kiss, T., Jex, I.: Directional correlations in quantum walks with two particles. New J. Phys. 13(3), 033029 (2011)
Rohde, P.P., Schreiber, A., Štefaňák, M., Jex, I., Silberhorn, C.: Multi-walker discrete time quantum walks on arbitrary graphs, their properties and their photonic implementation. New J. Phys. 13(1), 013001 (2011)
Berry, S.D., Wang, J.B.: Two-particle quantum walks: entanglement and graph isomorphism testing. Phys. Rev. A 83(4), 042317 (2011)
Xue, P., Sanders, B.C.: Phys. Rev. A 85(2), 022307 (2012)
Rigovacca, L., Di Franco, C.: Two quantum walkers sharing coins. Sci. Rep. 6, 22052 (2016)
Wang, Q., Li, Z.J.: Repelling, binding, and oscillating of two-particle discrete-time quantum walks. Ann. Phys. 373, 1 (2016)
Rohde, P.P., Schreiber, A., Štefaňák, M., Jex, I., Gilchrist, A., Silberhorn, C.: Increasing the dimensionality of quantum walks using multiple walkers. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 10(7), 1644 (2013)
Li, D., Zhang, J., Guo, F.Z., Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Chen, H.: Discrete-time interacting quantum walks and quantum Hash schemes. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(3), 1501 (2013)
Yang, Y., Yang, J., Zhou, Y., Shi, W., Chen, X., Li, J., Zuo, H.: Quantum network communication: a discrete-time quantum-walk approach. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 61(4), 042501 (2018)
Konno, N., Łuczak, T., Segawa, E.: Limit measures of inhomogeneous discrete-time quantum walks in one dimension. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(1), 33 (2013)
Zhang, R., Xue, P., Twamley, J.: One-dimensional quantum walks with single-point phase defects. Phys. Rev. A 89(4), 042317 (2014)
Suzuki, A.: Asymptotic velocity of a position-dependent quantum walk. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(1), 103 (2016)
Ahmad, R., Sajjad, U., Sajid, M.: One-dimensional quantum walks with a position-dependent coin. Commun. Theor. Phys. 72(6), 065101 (2020)
Montero, M.: Invariance in quantum walks with time-dependent coin operators. Phys. Rev. A 90(6), 062312 (2014)
Panahiyan, S., Fritzsche, S.: Controlling quantum random walk with a step-dependent coin. New J. Phys. 20(8), 083028 (2018)
Yalçınkaya, İ, Gedik, Z.: Qubit state transfer via discrete-time quantum walks. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 48(22), 225302 (2015)
Montero, M.: Quantum and random walks as universal generators of probability distributions. Phys. Rev. A 95(6), 062326 (2017)
Štefaňák, M., Skoupỳ, S.: Perfect state transfer by means of discrete-time quantum walk on complete bipartite graphs. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(3), 72 (2017)
Kurzyński, P., Wójcik, A.: Quantum walk as a generalized measuring device. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(20), 200404 (2013)
Li, Z., Zhang, H., Zhu, H.: Implementation of generalized measurements on a qudit via quantum walks. Phys. Rev. A 99(6), 062342 (2019)
Schreiber, A., Cassemiro, K.N., Potoček, V., Gábris, A., Mosley, P.J., Andersson, E., Jex, I., Silberhorn, C.: Photons walking the line: a quantum walk with adjustable coin operations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104(5), 050502 (2010)
Ambainis, A., Bach, E., Nayak, A., Vishwanath, A., Watrous, J.: One-dimensional quantum walks. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-Third Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 37–49 (2001)
Aharonov, D., Ambainis, A., Kempe, J., Vazirani, U.: Quantum walks on graphs. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-Third Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 50–59 (2001)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Open Fund of Advanced Cryptography and System Security Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Grant No. SKLACSS-202108), the Open Research Fund of Key Laboratory of Cryptography of Zhejiang Province, the BUPT Excellent Ph.D. Students Foundation (No. CX2020310), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2019XD-A02), the Open Foundation of Guizhou Provincial Key Laboratory of Public Big Data (Grant Nos. 2018BDKFJJ016, 2018BDKFJJ018, 2019BDKFJJ010, 2019BDKFJJ014), and Huawei Technologies Co.Ltd (No. YBN2020085019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendices
1.1 Appendix A: The derivation process of the formula (18)
Firstly, we give the quantum state
according to the parity of k, which can be written as: \(\left| \varPhi ^{\prime }\right\rangle = \left| \varPhi ^{\prime }\right\rangle _{\text {even}} +\left| \varPhi ^{\prime }\right\rangle _{\text {odd}}\) defined by
where \(m^{\prime }=[\frac{m}{2}]\), \(m^{\prime \prime }=[\frac{m-1}{2}]\). Next, by utilizing the following equations:
the initial state \(\left| \varPhi ^{\prime }\right\rangle \) can be expressed as:
Then, by adjusting the order of the terms, it will become the same as the formula (18).
1.2 Appendix B
Next, we prove that any two quantum states at the receivers \(\{{\varvec{{r}}}_{1}, {\varvec{{r}}}_{2},\ldots ,{\varvec{{r}}}_{m}\}\) are symmetric, that is
First of all, it can be derived that
with the equation
which implies that the quantum states of \(\{{\varvec{{r}}}_{m-1},{\varvec{{r}}}_{m}\}\) are symmetric. It is obvious that the quantum states of any two receivers of \(\{{\varvec{{r}}}_{1},\ldots ,{\varvec{{r}}}_{m-1}\}\) are symmetric. Therefore, it can be concluded that any two quantum states at the receivers \(\{{\varvec{{r}}}_{1}, {\varvec{{r}}}_{2},\ldots ,{\varvec{{r}}}_{m}\}\) are symmetric.
Next, after any receiver \({\varvec{{r}}}_{j}\) and the other \(m\!-\!1\) receivers, respectively, performing the Pauli operator \(\sigma _{z}^{\omega _{h,m}}\sigma _{x}\) and \(\sigma _{z}^{\omega _{h,m}}\), it will yield
which is equal to \(|1\rangle ^{\otimes ^{m\!-\!1}}_{\text {odd}}|\phi \rangle +(-1)^{w_{h}+s}|1\rangle ^{\otimes ^{m\!-\!1}}_{\text {even}}\sigma _{x}R_{z}(\theta _{s})|\phi \rangle \), that can be proved by the following equation
As a result, the state \(|\varPhi _{h,s}\rangle _{r}^{m}\) will become \(|\varPhi _{h,s}^{\prime }\rangle _{r}^{m}\), after the proper unitary operators. Similarly, while the result on \(s_{p_{1}}\) is 0s, the receivers can do the same as the result is 1t, however, which will yield
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, HJ., Li, J. & Chen, X. Generalized quantum teleportation of shared quantum secret: a coined quantum-walk approach. Quantum Inf Process 21, 387 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03741-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03741-0