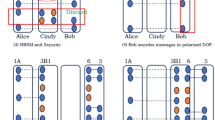
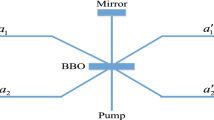
Abstract
Quantum secure direct communication (QSDC) can directly transmit secure messages through quantum channel without sharing keys. Three-party (3P) QSDC enables two communication parties synchronously transmit secret messages to a third party through the quantum channels. Previous 3P-QSDC protocols all require ideal and trusted measurement devices, which are hard to realize under current experimental condition. Practical imperfect measurement devices would bring security loophole in the 3P-QSDC. In the paper, we propose a measurement-device-independent (MDI) 3P-QSDC protocol based on the polarization-spatial-mode hyperentanglement, which can resist all possible attacks from practical imperfect measurement devices. Our protocol is unconditionally secure in theory and can enhance 3P-QSDC’s security under practical experimental condition. In one round of communication, two parties can each send 2 bits of secure messages to the third party. Our MDI-3P-QSDC protocol has application potential in future multipartite quantum communication field.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that all data and models generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895–1899 (1993)
Bouwmeester, D., Pan, J.W., Mattle, K., Eibl, M., Weinfurter, H., Zeilinger, A.: Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature 390, 575–579 (1997)
Yan, Z.H., Qin, J.L., Qin, Z.Z., Su, X.L., Jia, X.J., Xie, C.D., Peng, K.C.: Generation of non-classical states of light and their application in deterministic quantum teleportation. Fund. Res. 1, 43–49 (2021)
Pandey, R.K., Prakash, R., Prakash, H.: High success standard quantum teleportation using entangled coherent state and two-level atoms in cavities. Quant. Inform. Process. 20, 322 (2021)
Quan, Q., Zhao, M.J., Fei, S.M., Fan, H., Yang, W.L., Wang, T.J., Long, G.L.: Two-copy quantum teleportation based on GHZ measurement. Quant. Inform. Process. 19, 205 (2020)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computers, systems, and signal processing, pp.175. IEEE, New York (1984)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum crytography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661 (1991)
Acín, A., Brunner, N., Gisin, N., et al.: Device-independent security of quantum cryptography against collective attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 230501 (2007)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012)
Wang, S., Yin, Z.Q., Chen, W., et al.: Experimental demonstration of quantum key distribution without monitoring of the signal disturbance. Nat. Photon. 9, 832–836 (2015)
Xu, F.H., Ma, X.F., Zhang, Q., et al.: Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices. Rev. Mod. Phys. 92, 025002 (2020)
Zhao, S., Zeng, P., Cao, W.F., et al.: Phase-matching quantum cryptographic conferencing. Phys. Rev. Appl. 14, 024010 (2020)
Jin, A.R., Zeng, P., Penty, R.V., et al.: Reference-frame-independent design of phase-matching quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Appl. 16, 034017 (2021)
Chen, Y.A., Zhang, Q., Chen, T.Y., et al.: An integrated space-to-ground quantum communication network over 4600 kilometres. Nature 589, 214–219 (2021)
Kwek, L.C., Cao, L., Luo, W., et al.: Chip-based quantum key distribution. AAPPS Bull. 31, 15 (2021)
Yin, Z.Q., Lu, F.Y., Teng, J., et al.: Twin-field protocols: towards intercity quantum key distribution without quantum repeaters. Fund. Res. 1, 93–95 (2021)
Guo, H., Li, Z.Y., Yu, S.: Toward practical quantum key distribution using telecom components. Fund. Res. 1, 96–98 (2021)
Tang, G.Z., Li, C.Y., Wang, M.: Polarization discriminated time-bin phase-encoding measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Quant. Eng. 3, e79 (2021)
Wang, X.F., Sun, X.J., Liu, Y.X.: Transmission of photonic polarization states from geosynchronous earth orbit satellite to the ground. Quant. Eng. 3, e73 (2021)
Liu, W.B., Li, C.L., Xie, Y.M., et al.: Homodyne detection quadrature phase shift keying continuous-variable quantum key distribution with high excess noise tolerance. PRX Quant. 2, 040334 (2021)
Hajji, H., El-Baz, M.: Qutrit-based semi-quantum key distribution protocol. Quant. Inform. Process. 20, 4 (2021)
Zhang, C.Y., Zheng, Z.J.: Entanglement-based quantum key distribution with untrusted third party. Quant. Inform. Process. 20, 146 (2021)
Xie, Y.M., Lu, Y.S., Weng, C.X., et al.: Breaking the rate-loss bound of quantum key distribution with asynchronous two-photon interference. PRX Quant. 3, 020315 (2022)
Wang, S., Yin, Z.Q., He, D.Y., et al.: Twin-field quantum key distribution over 830 km fibre. Nat. Photon. 16, 154 (2022)
Gu, J., Cao, X.Y., Fu, Y., He, Z.W., Yin, Z.J., Yin, H.L., Chen, Z.B.: Experimental measurement-device-independent type quantum key distribution with flawed and correlated sources. Sci. Bull. 67, 2167 (2022)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretical efficient high capacity quantum key distribution Scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042317 (2003)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad. Phys. Rev. A 69, 052319 (2004)
Wang, C., Deng, F.G., Li, Y.S.: Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum hyperdense coding. Phys. Rev. A 71, 044305 (2005)
Jin, X.R., Ji, X., et al.: Three-party quantum secure direct communication based on GHZ states. Phys. Lett. A 354, 67 (2006)
Wang, M.Y., Yan, F.L.: Three-party simultaneous quantum secure direct communication scheme with EPR pairs. Phys. Lett. A 24, 2486 (2007)
Chong, S.K., Hwang, T.: The enhancement of three-party simultaneous quantum secure direct communication scheme with EPR pairs. Opt. Commun. 284, 515 (2011)
Hu, J.Y., Yu, B., Jing, M.Y., et al.: Experimental quantum secure direct communication with single photons. Light Sci. Appl. 5, e16144 (2016)
Zhang, W., Ding, D.S., Sheng, Y.B., et al.: Quantum secure direct communication with quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 220501 (2017)
Zhu, F., Zhang, W., Sheng, Y.B., et al.: Experimental long-distance quantum secure direct communication. Sci. Bull. 62, 1519–1524 (2017)
Qi, R.Y., Sun, Z., Lin, Z.S., et al.: Implementation and security analysis of practical quantum secure direct communication. Light Sci. Appl. 8, 22 (2019)
Pan, D., Lin, Z.S., Wu, J.W., et al.: Experimental free-space quantum secure direct communication and its security analysis. Photon. Res. 8, 1522–1531 (2020)
Qi, Z.T., Li, Y.H., Huang, Y.W., et al.: A 15-user quantum secure direct communication network. Light Sci. Appl. 10, 183 (2021)
Sun, Z., Song, L., Huang, Q., et al.: Toward practical quantum secure direct communication: a quantum-memory-free protocol and code design. IEEE Trans. Commun. 68, 5778–5792 (2020)
Zhang, H.R., Sun, Z., Qi, R.Y., et al.: Realization of quantum secure direct communication over 100 km fiber with time-bin and phase quantum states. Light Sci. Appl. 11, 83 (2022)
Long, G.L., Pan, D., Sheng, Y.B., Xue, Q.K., Lu, J.H., Hanzo, L.: An evolutionary pathway for the quantum internet relying on secure classical repeaters. IEEE Netw. 36, 82–88 (2022)
Chen, S.S., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., et al.: Three-step three-party quantum secure direct communication. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 61, 090312 (2018)
Niu, P.H., Zhou, Z.R., Lin, Z.S., et al.: Measurement-device-independent quantum communication without encryption. Sci. Bull. 63, 1345–1350 (2018)
Zhou, Z.R., Sheng, Y.B., Niu, P.H., et al.: Measurement-device-independent quantum secure direct communication. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 63, 230362 (2020)
Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B., Long, G.L.: Device-independent quantum secure direct communication against collective attacks. Sci. Bull. 65, 12–20 (2020)
Wu, X.D., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: High-capacity measurement-device-independent quantum secure direct communication. Quant. Inf. Process. 19, 354 (2020)
Liu, L., Niu, J.L., Fan, C.R., Feng, X.T., Wang, C.: High-dimensional measurement-device-independent quantum secure direct communication. Quant. Inf. Process. 19, 404 (2020)
Wu, J.W., Lin, Z.S., Yin, L.G., Long, G.L.: Security of quantum secure direct communication based on Wyner’s wiretap channel theory. Quant. Engin. 1, e26 (2019)
Niu, P.H., Wu, J.W., Yin, L.G., Long, G.L.: Security analysis of measurement-device-independent quantum secure direct communication. Quant. Inf. Process. 19, 356 (2020)
Yang, L., Wu, J.W., Lin, Z.S., et al.: Quantum secure direct communication with entanglement source and single-photon measurement. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 63, 110311 (2020)
Li, T., Long, G.L.: Quantum secure direct communication based on single-photon Bell-state measurement. New J. Phys. 22, 063017 (2020)
Wang, C.: Quantum secure direct communication: intersection of communication and cryptography. Fund. Res. 1, 91 (2021)
Long, G.L., Zhang, H.R.: Drastic increase of channel capacity in quantum secure direct communication using masking. Sci. Bull. 66, 1267–1269 (2021)
Cao, Z.W., Wang, L., Liang, K.X., et al.: Continuous-variable quantum secure direct communication based on Gaussian mapping. Phys. Rev. Appl. 16, 024012 (2021)
Liu, X., Li, Z.J., Luo, D., Huang, C.F., Ma, D., Geng, M.M., Wang, J.W., Zhang, Z.R., Wei, K.J.: Practical decoy-state quantum secure direct communication. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 64, 120311 (2021)
Rong, Z.B., Qiu, D.W., Mateus, P., Zou, X.F.: Mediated semi-quantum secure direct communication. Quant. Inform. Process. 20, 58 (2021)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Long, G.L.: One-step quantum secure direct communication. Sci. Bull. 67, 367–374 (2022)
Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B.: One-step device-independent quantum secure direct communication. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 65, 250311 (2022)
Ying, J.W., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Measurement-device-independent one-step quantum secure direct communication. Chin. Phys. B 31, 120303 (2022)
Wang, P., Chen, X.H., Sun, Z.W.: Semi-quantum secure direct communication against collective-dephasing noise. Quant. Inform. Process. 21, 352 (2022)
Huang, Z.M., Rong, Z.B., Zou, X.F., He, Z.M.: Semi-quantum secure direct communication in the curved spacetime. Quant. Inform. Process. 20, 375 (2022)
Liu, X., Luo, Di., Lin, G.S., et al.: Fiber-based quantum secure direct communication without active polarization compensation. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron 65, 120311 (2022)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Complete hyper-entangled-Bell-state analysis for quantum communication. Phys. Rev. A 82, 032318 (2010)
Wyner, A.D.: The wire-tap channel. Bell System Tech. J. 54, 1355–1387 (1975)
Hu, X.M., Huang, C.X., Sheng, Y.B., et al.: Long-distance entanglement purification for quantum communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 010503 (2021)
Ma, X.F., Fung, C.H.F., Lo, H.K.: Quantum key distribution with entangled photon sources. Phys. Rev. A 76, 012307 (2007)
Takesue, H., Harada, K., Tamaki, K., Fukuda, H., Tsuchizawa, T., Watanabe, T., Yamada, K., Itabashi, S.: Long-distance entanglement-based quantum key distribution experiment using practical detectors. Opt. Exp. 18, 16777–16787 (2010)
Ren, B.C., Wei, H.R., Hua, M., et al.: Complete hyperentangled-Bell-state analysis for photon systems assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Opt. Exp. 20, 24664–24677 (2012)
Wang, T.J., Lu, Y., Long, G.L.: Generation and complete analysis of the hyperentangled Bell state for photons assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. A 86, 042337 (2012)
Wang, G.Y., Ai, Q., Ren, B.C., et al.: Error-detected generation and complete analysis of hyperentangled Bell states for photons assisted by quantum-dot spins in double-sided optical microcavities. Opt. Exp. 24, 28444–28458 (2016)
Liu, Q., Zhang, M.: Generation and complete nondestructive analysis of hyperentanglement assisted by nitrogen-vacancy centers in resonators. Phys. Rev. A 91, 062321 (2015)
Wang, T.J., Wang, C.: Nonlocal hyperconcentration on entangled photons using photonic module system. Sci. Rep. 6, 19497 (2016)
Gao, C.Y., Ren, B.C., Zhang, Y.X.: Universal linear-optical hyper-entangled Bell-state measurement. Appl. Phys. Exp. 13, 027004 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 11974189 and 12175106, the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China under Grant No. 20KJB140001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are not any possible conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, YP., Zhou, L., Zhong, W. et al. Measurement-device-independent three-party quantum secure direct communication. Quantum Inf Process 22, 111 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03853-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03853-1