Abstract
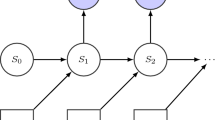
We investigate the possibility of optimizing genuine tripartite quantum steering inequalities via machine learning. In particular, we consider two types of hybrid scenarios: one-sided device-independent scenario (where one party is considered to be untrusted) and two-sided device-independent scenario (where two parties are considered to be untrusted). In both scenarios, we apply a method of machine learning, known as artificial neuron networks, to optimize the quantum steering inequalities for the family of noisy Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger states and noisy W states. The results show that the optimized steering classifiers can verify quantum steering well with only a small number of Pauli measurements, which can be easily realized in experiment. The method can be generalized to other multipartite or high-dimensional quantum systems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Einstein, A., Podolsky, B., Rosen, N.: Can it quantum mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete? Phys. Rev. 47(10), 777 (1935)
Schrödinger, E.: Probability relations between separated systems. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 32(3), 446 (1936)
Jones, S.J., Wiseman, H.M., Doherty, A.C.: Entanglement, Einstein–Podolsky-Rosen correlations, Bell nonlocality, and steering. Phys. Rev. A 76(5), 052116 (2007)
Bowles, J., Vértesi, T., Quintino, M.T., Brunner, N.: One-way Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen steering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112(20), 200402 (2014)
Händchen, V., Eberle, T., Steinlechner, S., Samblowski, A., Franz, T., Werner, R.F., Schnabel, R.: Observation of one-way Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen steering. Nat. Photonics 6, 596 (2012)
Wollmann, S., Walk, N., Bennet, A.J., Wiseman, H.M., Pryde, G.J.: Observation of genuine one-way Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen steering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116(16), 160403 (2016)
Piani, M., Watrous, J.: Necessary and sufficient quantum information characterization of Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen steering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114(6), 060404 (2015)
Sun, K., Ye, X.J., Xiao, Y., Xu, X.Y., Wu, Y.C., Xu, J.S., Chen, J.L., Li, C.F., Guo, G.C.: Demonstration of Einstein CPodolsky CRosen steering with enhanced subchannel discrimination. NPJ Quantum Inf. 4, 12 (2018)
Reid, M.D.: Signifying quantum benchmarks for qubit teleportation and secure quantum communication using Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen steering inequalities. Phys. Rev. A 88(6), 062338 (2013)
He, Q., Rosales-Zárate, L., Adesso, G., Reid, M.D.: Secure continuous variable teleportation and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen steering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115(18), 180502 (2015)
Walk, N., Hosseini, S., Geng, J., Thearle, O., Haw, J.Y., Armstrong, S., Assad, S.M., Janousek, J., Ralph, T.C., Symul, T., Wiseman, H.M., Lam, P.K.: Experimental demonstration of Gaussian protocols for one-sided device-independent quantum key distribution. Optica 3(6), 634 (2016)
Kogias, I., Xiang, Y., He, Q., Adesso, G.: Unconditional security of entanglement-based continuous-variable quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 95(1), 012315 (2017)
Branciard, C., Cavalcanti, E.G., Walborn, S.P., Scarani, V., Wiseman, H.M.: One-sided device-independent quantum key distribution: security, feasibility, and the connection with steering. Phys. Rev. A 85(1), 010301(R) (2012)
Jebaratnam, C.: Detecting genuine multipartite entanglement in steering scenarios. Phys. Rev. A 93(5), 052311 (2016)
Cavalcanti, E.G., Jones, S.J., Wiseman, H.M., Reid, M.D.: Experimental criteria for steering and the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen paradox. Phys. Rev. A 80(3), 032112 (2009)
Zheng, Y.L., Zhen, Y.Z., Chen, Z.B., Liu, N.L., Chen, K., Pan, J.W.: Efficient linear criterion for witnessing Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen nonlocality under many-setting local measurements. Phys. Rev. A 95(1), 012142 (2017)
Zheng, Y.L., Zhen, Y.Z., Cao, W.F., Li, L., Chen, Z.B., Liu, N.L., Chen, K.: Optimized detection of steering via linear criteria for arbitrary-dimensional states. Phys. Rev. A 95(3), 032128 (2017)
Schneeloch, J., Broadbent, C.J., Walborn, S.P., Cavalcanti, E.G., Howell, J.C.: Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen steering inequalities from entropic uncertainty relations. Phys. Rev. A 87(6), 062103 (2013)
Zhen, Y.Z., Zheng, Y.L., Cao, W.F., Li, L., Chen, Z.B., Liu, N.L., Chen, K.: Certifying Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen steering via the local uncertainty principle. Phys. Rev. A 93(1), 012108 (2016)
Ji, S.W., Lee, J., Park, J., Nha, H.: Steering criteria via covariance matrices of local observables in arbitrary-dimensional quantum systems. Phys. Rev. A 92(6), 062130 (2015)
Cavalcanti, D., Skrzypczyk, P., Aguilar, G.H., Nery, R.V., Ribeiro, P.S., Walborn, S.P.: Detection of entanglement in asymmetric quantum networks and multipartite quantum steering. Nat. Commun. 6, 7941 (2015)
Wiebe, N., Granade, C., Ferrie, C., Cory, D.G.: Hamiltonian learning and certification using quantum resources. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112(19), 190501 (2014)
Krenn, M., Malik, M., Fickler, R., Lapkiewicz, R., Zeilinger, A.: Automated search for new quantum experiments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116(9), 090405 (2016)
van Nieuwenburg, E.P.L., Liu, Y.-H., Huber, S.D.: Learning phase transitions by confusion. Nat. Phys. 13, 435 (2017)
Deng, D.L.: Machine learning detection of bell nonlocality in quantum many-body systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120(24), 240402 (2018)
Ma, Y.C., Yung, M.H.: Transforming Bell’s inequalities into state classifiers with machine learning. NPJ Quantum Inf. 4, 34 (2018)
Yang, M., Ren, C.L., Ma, Y.C., Xiao, Y., Ye, X.J., Song, L.L., Xu, J.S., Yung, M.H., Li, C.F., Guo, G.C.: Experimental simultaneous learning of multiple nonclassical correlations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 123(19), 190401 (2019)
Canabarro, A., Brito, S., Chaves, R.: Machine learning nonlocal correlations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122(20), 200401 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province under Grant Nos. 2008085MA16 and 2008085MA20, the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province under Grant Nos. GXXT-2022-039 and GXXT-2021-026, the Excellent Talents Support Program of Anhui Province under Grant No. gxyq2021208, the Natural Science Research Key Project of Education Department of Anhui Province under Grant Nos. 2022AH051681, KJ2020A0760 and KJ2021A0943, the Research Foundation for Advanced Talents of West Anhui University under Grant Nos. WGKQ202001004 and WGKQ2021004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, GZ., Yang, M., Zhou, J. et al. Optimization of tripartite quantum steering inequalities via machine learning. Quantum Inf Process 22, 162 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03873-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03873-x