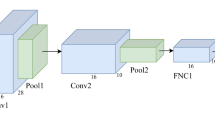
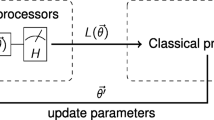
Abstract
A novel quantum neural network(QNN) is proposed, in which quantum probability image encoding(QPIE) and specially designed ansatz are used. QPIE can exponentially reduce qubits for image encoding by using quantum superposition. The parameter gates in ansatz are selected from the universal gate set for quantum computing, which guarantees the expressibility of models. The proposed QNN can be trained by supervised learning. In this article, various experiments are conducted to explore the factors that affect accuracy. The results derive from MNIST show that both the improvement of resolution and the repetition of layers have a positive contribution to accuracy. The enhancement of the expressibility of a single layer by replacing CX gates with \(\hbox {R}_y\) gates also improves the performance of the model.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM Rev. 41(2), 303–332 (1999)
Grover, L.K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of the 28th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 212–219 (1996)
Harrow, A.W., Hassidim, A., Lloyd, S.: Quantum algorithm for linear systems of equations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103(15), 150502 (2009)
Ambainis, A.: Quantum walk algorithm for element distinctness. SIAM J. Comput. 37(1), 210–239 (2007)
Farhi, E., Goldstone, J., Gutmann, S.: A quantum approximate optimization algorithm (2014) arXiv:1411.4028
Lloyd, S., Mohseni, M., Rebentrost, P.: Quantum principal component analysis. Nat. Phys. 10(9), 631–633 (2014)
Rebentrost, P., Mohseni, M., Lloyd, S.: Quantum support vector machine for big data classification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113(13), 130503 (2014)
Peruzzo, A., McClean, J., Shadbolt, P., Yung, M.-H., Zhou, X.-Q., Love, P.J., Aspuru-Guzik, A., O’brien, J.L.: A variational eigenvalue solver on a photonic quantum processor. Nat. Commun. 5(1), 1–7 (2014)
Kandala, A., Mezzacapo, A., Temme, K., Takita, M., Brink, M., Chow, J.M., Gambetta, J.M.: Hardware-efficient variational quantum eigensolver for small molecules and quantum magnets. Nature 549(7671), 242–246 (2017)
Grimsley, H.R., Economou, S.E., Barnes, E., Mayhall, N.J.: An adaptive variational algorithm for exact molecular simulations on a quantum computer. Nat. Commun. 10(1), 1–9 (2019)
Menneer, T., Narayanan, A.: Quantum-inspired neural networks. Technical Report R329, University of Exeter, Exeter (1995).
Shi, J., Li, Z., Lai, W., Li, F., Shi, R., Feng, Y., Zhang, S.: Two End-to-end Quantum-inspired Deep Neural Networks for Text Classification. IEEE, New York (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2021.3130598
Li, Z., Liu, X., Xu, N., Du, J.: Experimental realization of a quantum support vector machine. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114(14), 140504 (2015)
Rosenblatt, F.: The perceptron: a probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain. Psychol. Rev. 65(6), 386 (1958)
Rumelhart, D.E., Hinton, G.E., Williams, R.J.: Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323(6088), 533–536 (1986)
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86(11), 2278–2324 (1998)
Farhi, E., Neven, H.: Classification with quantum neural networks on near term processors (2018) arXiv:1802.06002
LeCun, Y., Cortes, C., Burges, C.: MNIST handwritten digit database. http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/ (2010)
Cong, I., Choi, S., Lukin, M.D.: Quantum convolutional neural networks. Nat. Phys. 15(12), 1273–1278 (2019)
Schuld, M., Bocharov, A., Svore, K.M., Wiebe, N.: Circuit-centric quantum classifiers. Phys. Rev. A 101(3), 032308 (2020)
Zeng, Y., Wang, H., He, J., Huang, Q., Chang, S.: A multi-classification hybrid quantum neural network using an all-qubit multi-observable measurement strategy. Entropy 24(3), 394 (2022)
Zhao, W., Wang, Y., Qu, Y., Ma, H., Wang, S.: Binary classification quantum neural network model based on optimized grover algorithm. Entropy 24(12), 1783 (2022)
Grant, E., Benedetti, M., Cao, S., Hallam, A., Lockhart, J., Stojevic, V., Green, A.G., Severini, S.: Hierarchical quantum classifiers. NPJ Quant. Inf. 4(1), 1–8 (2018)
Oh, S., Choi, J., Kim, J.: A tutorial on quantum convolutional neural networks (qcnn). In: 2020 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), pp. 236–239 (2020)
Li, W., Chu, P.-C., Liu, G.-Z., Tian, Y.-B., Qiu, T.-H., Wang, S.-M.: An image classification algorithm based on hybrid quantum classical convolutional neural network. Quantum Eng. 2022 (2022)
Venegas-Andraca, S.E., Bose, S.: Storing, processing and retrieving an image using quantum mechanics. In: Proceedings of the SPIE Conference Quantum Information and Computation, pp. 137–147 (2003)
Latorre, J.I.: Image compression and entanglement (2005) arXiv:quant-ph/0510031
Le, P.Q., Dong, F., Hirota, K.: A flexible representation of quantum images for polynomial preparation, image compression, and processing operations. Quant. Inf. Process. 10(1), 63–84 (2011)
Zhang, Y., Lu, K., Gao, Y., Wang, M.: Neqr: a novel enhanced quantum representation of digital images. Quant. Inf. Process. 12(8), 2833–2860 (2013)
Yao, X.-W., Wang, H., Liao, Z., Chen, M.-C., Pan, J., Li, J., Zhang, K., Lin, X., Wang, Z., Luo, Z.: Quantum image processing and its application to edge detection: theory and experiment. Phys. Rev. X 7(3), 031041 (2017)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. American Association of Physics Teachers, College Park (2002)
Kitaev, A.Y., Shen, A., Vyalyi, M.N., Vyalyi, M.N.: Classical and Quantum Computation, vol. 47. American Mathematical Society, Providence (2002)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Benedetti, M., Lloyd, E., Sack, S., Fiorentini, M.: Parameterized quantum circuits as machine learning models. Quantum Sci. Technol. 4(4), 043001 (2019)
Shi, J., Wang, W., Lou, X., Zhang, S., Li, X.: IEEE Transaction Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. Parameterized Hamiltonian learning with quantum circuit, IEEE, New York (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3203157
Shi, J., Tang, Y., Lu, Y., Feng, Y., Shi, R., Zhang, S.: IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. Quantum circuit learning with parameterized boson sampling, IEEE, Data Eng (2021)
Sim, S., Johnson, P.D., Aspuru-Guzik, A.: Expressibility and entangling capability of parameterized quantum circuits for hybrid quantum-classical algorithms. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2(12), 1900070 (2019)
Mitarai, K., Negoro, M., Kitagawa, M., Fujii, K.: Quantum circuit learning. Phys. Rev. A 98(3), 032309 (2018)
Schuld, M., Bergholm, V., Gogolin, C., Izaac, J., Killoran, N.: Evaluating analytic gradients on quantum hardware. Phys. Rev. A 99(3), 032331 (2019)
Broughton, M., Verdon, G., McCourt, T., Martinez, A.J., Yoo, J.H., Isakov, S.V., Massey, P., Halavati, R., Niu, M.Y., Zlokapa, A., et al.: Tensorflow quantum: A software framework for quantum machine learning (2020) arXiv:2003.02989
Funding
This work was supported by the fundamental research funds for the central universities [Project No.K20210337]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Q., Hu, X. Quantity study on a novel quantum neural network with alternately controlled gates for binary image classification. Quantum Inf Process 22, 184 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03929-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03929-y