Abstract
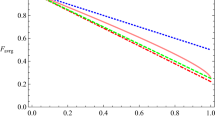
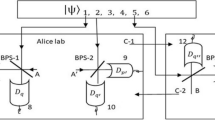
This paper is aimed to design a protocol which enable asymmetric exchange of quantum states between every two adjacent communicating parties under the supervision of a controller in circular quantum communication and analyze how the noise environment affects the process of this protocol. We propose a novel protocol for four-party asymmetric bidirectional cyclic controlled quantum teleportation based on multi-output quantum teleportation, utilizing a seventeen-qubit entangled state as the quantum channel. Moreover, we extended the proposed four-party scheme from three communicators to \(m(m>3)\) communicators, providing flexibility for each communicator to choose one of the two distinct multi-output modes for communication. Additionally, the quantum circuit was designed for experimental implementation of the protocol on the IBM Quantum platform. Lastly, the four-party scheme is analyzed in four noisy environments with bit-flip noise, phase-flip noise, amplitude damping and phase-damping. Furthermore, we give a comparison with previous similar schemes in terms of intrinsic efficiency and achieved method, which illustrates the superiority of our protocol. Regarding experimental implementation, we successfully validated the accuracy and feasibility of the proposed four-party scheme. In the noise analysis, we discovered a correlation between the fidelity of teleported quantum states and both the parameter of the desired quantum state and the decoherence rate. This correlation is attributed to the inherent nature of the four types of noise.








Similar content being viewed by others
Date availability
Codes that support the experimental realization of four-party ABCCQT scheme are available from the author (544,692,060@qq.com) upon reasonable request.
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895–1899 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.1895
Lo, H.-K.: Classical communication cost in distributed quantum information processing: a generalization of quantum communication complexity. Phys. Rev. A. 62, 012313 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.62.012313
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661–663 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.661
Acin, A., Brunner, N., Gisin, N., Massar, S., Pironio, S., Scarani, V.: Device-independent security of quantum cryptography against collective attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 230501 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.230501
Arnon-Friedman, R., Dupuis, F., Fawzi, O., Renner, R., Vidick, T.: Practical device-independent quantum cryptography via entropy accumulation. Nat. Commun. 9, 459 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02307-4
Bera, S., Gupta, S., Majumdar, A.S.: Device-independent quantum key distribution using random quantum states. Quant. Inf. Process. 22, 109 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03852-2
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretical efficient high capacity quantum key distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A. 65, 032302 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.65.032302
Deng, F.-G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.-S.: A two-step quantum direct communication protocol using Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A. 68, 042317 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.68.042317
Sheng, Y.-B., Zhou, L., Long, G.-L.: One-step quantum secure direct communication. Sci. Bull. 67, 367–374 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2021.11.002
Ying, J.-W., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.-B.: Measurement-device-independent one-step quantum secure direct communication. Chin. Phys. B. 31, 120303 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ac8f37
Hong, Y.-P., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.-B.: Measurement-device-independent three-party quantum secure direct communication. Quant. Inf. Process. 22, 111 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03853-1
Yang, C.-W., Lin, J., Wang, K.-L., Tsai, C.-W.: Cryptanalysis and improvement of a controlled quantum secure direct communication with authentication protocol based on five-particle cluster state. Quant. Inf. Process. 22, 196 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03956-9
Shen, S., Yuan, C., Zhang, Z., Yu, H., Zhang, R., Yang, C., Li, H., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Deng, G., Song, H., You, L., Fan, Y., Guo, G., Zhou, Q.: Hertz-rate metropolitan quantum teleportation. Light Sci. Appl. 12, 115 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-023-01158-7
Yan, Z., Jia, X.: Teleportation goes to Hertz rate. Light Sci. Appl. 12, 167 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-023-01216-0
Peng, J.-Y., Tang, L., Yang, Z.: Deterministic hierarchical quantum operation sharing with five-qubit partially entangled states. Quant. Inf. Process. 22, 265 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03963-w
Zhang, Z., Sang, Y.: Bidirectional quantum teleportation in multi-hop communication network. Quant. Inf. Process. 22, 201 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03950-1
Harraz, S., Cong, S., Nieto, J.J.: Optimal tripartite quantum teleportation protocol through noisy channels. Quant. Inf. Process. 22, 83 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03830-8
Hassanpour, S., Houshmand, M.: Bidirectional quantum teleportation via entanglement swapping. In: 2015 23rd Iranian conference on electrical engineering, IEEE, pp. 501–503, Tehran, Iran (2015) doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IranianCEE.2015.7146267
Li, Y., Nie, L., Li, X., Sang, M.: Asymmetric bidirectional controlled teleportation by using six-qubit cluster state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55, 3008–3016 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-016-2933-y
Yu, Y., Zha, X.W., Li, W.: Quantum broadcast scheme and multi-output quantum teleportation via four-qubit cluster state. Quant. Inf. Process. 16, 41 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1500-z
Kalra, A.R., Gupta, N., Behera, B.K., Prakash, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Demonstration of the No-Hiding theorem on the 5 Qubit IBM quantum computer in a category theoretic framework. Quant. Inf. Process. 18, 170 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2288-4
Roffe, J., Headley, D., Chancellor, N., Horsman, D., Kendon, V.: Protecting quantum memories using coherent parity check codes. Quant. Sci. Technol. 3, 035010 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-9565/aac64e
Alvarez-Rodriguez, U., Sanz, M., Lamata, L., Solano, E.: Quantum artificial Life in an IBM quantum computer. Sci Rep. 8, 14793 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-33125-3
Chen, Y.-X., Du, J., Liu, S.-Y., Wang, X.-H.: Cyclic quantum teleportation. Quant. Inf. Process. 16, 201 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1648-1
Li, Y., Qiao, Y., Sang, M., Nie, Y.: Controlled cyclic quantum teleportation of an arbitrary two-qubit entangled state by using a Ten-Qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58, 1541–1545 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04041-7
Zhao, N., Wu, T., Yu, Y., Pei, C.: A scheme for controlled cyclic asymmetric remote state preparation in noisy environment. Appl. Sci. 11, 1405 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041405
Zhou, R.-G., Ling, C.: Asymmetric cyclic controlled quantum teleportation by using Nine-Qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 60, 3435–3459 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04825-w
Zhou, R.-G., Qian, C., Ian, H.: Cyclic and bidirectional quantum teleportation via pseudo multi-qubit states. IEEE Access. 7, 42445–42449 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2907963
Jiang, S.-X., Zhou, R.-G., Xu, R., Luo, G.: Cyclic hybrid double-channel quantum communication via bell-state and GHZ-state in noisy environments. IEEE Access. 7, 80530–80541 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2923322
Sun, S., Zhang, H.: Quantum double-direction cyclic controlled communication via a thirteen-qubit entangled state. Quant. Inf Process. 19, 120 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-2619-5
Gong, L., Chen, X.-B., Xu, G., Chang, Y., Yang, Y.-X.: Multi-party controlled cyclic hybrid quantum communication protocol in noisy environment. Quant. Inf Process. 21, 375 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03725-0
Sun, S., Zhang, H.: Double-direction quantum cyclic controlled remote state preparation of two-qubit states. Quant. Inf Process. 20, 211 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03149-2
Zarmehi, F., Kochakzadeh, M.H., Abbasi-Moghadam, D., Talebi, S.: Efficient circular controlled quantum teleportation and broadcast schemes in the presence of quantum noises. Quant. Inf Process. 20, 175 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03088-y
Ikram, M., Zhu, S.-Y., Zubairy, M.S.: Quantum teleportation of an entangled state. Phys. Rev. A. 62, 022307 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.62.022307
Riebe, M., Häffner, H., Roos, C.F., Hänsel, W., Benhelm, J., Lancaster, G.P.T., Körber, T.W., Becher, C., Schmidt-Kaler, F., James, D.F.V., Blatt, R.: Deterministic quantum teleportation with atoms. Nature 429, 734–737 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02570
Boschi, D., Branca, S., De Martini, F., Hardy, L., Popescu, S.: Experimental realization of teleporting an unknown pure quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolski-Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 1121–1125 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.1121
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 62172268 and Shanghai Science and Technology Project under Grant Nos. 21JC1402800 and 20040501500.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Zhou, RG. Asymmetric bidirectional cyclic controlled quantum teleportation in noisy environment. Quantum Inf Process 22, 376 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-04116-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-04116-9