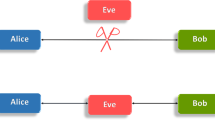
Abstract
Authentication is a security function that ensures the system's proper security by identifying and verifying users. Despite the advantages of quantum computers, it is still difficult to enforce authentication on behalf of multiple quantum channel users without the involvement of a third party because present protocols only consider two parties involved in communication. Scalability becomes an issue as the number of parties engaged in the quantum network increases. In addition, an eavesdropper may disguise herself among numerous participants and take advantage of the circumstances to gather information. The authentication method should be used throughout the quantum data exchange process to ensure that the parties participating in the protocol are who they claim to be. The suggested protocol's implementation has been tested using a simulation written in Python. This research aims to propose a protocol for multiparty authentication procedures without the assistance of a third party. The result of the proposed protocol is expected to be a simple and reliable quantum experiment. Importantly, this protocol can establish an environment that is more secure in terms of authentication and allows numerous parties to communicate freely and openly.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
All data and results are reported in the paper.
References
Wang, M.M., Han, R.F., Gong, L.M.: Multiparty semiquantum key agreement without entanglement. Commun. Theor. Phys. 72(6), 065107 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1572-9494/ab8a10
Dutta, A., and Pathak, A.: “New protocols for quantum key distribution with explicit upper and lower bound on secret-key rate,” Dec. 2022, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2212.13089
Chen, G., Wang, Y., Jian, L., Zhou, Y., Liu, S.: Quantum identity authentication based on the extension of quantum rotation. EPJ Quantum Technol. 10(1), 1–8 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjqt/s40507-023-00170-5
Majumdar, R., and Das, S.: “An evaluation of quantum authentication through systematic literature review,” 2021, https://doi.org/10.14722/usec.2021.23003
Dutta, A., Pathak, A.: Controlled secure direct quantum communication inspired scheme for quantum identity authentication. Quantum Inf. Process. 22(1), 13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03767-4
Dutta, A., Pathak, A.: A short review on quantum identity authentication protocols: how would Bob know that he is talking with Alice? Quantum Inf. Process. 21(11), 369 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03717-0
Harun, N.Z., Ahmad Zukarnain, Z., Hanapi, Z.M., Ahmad, I.: Multi-stage quantum secure direct communication using secure shared authentication key. Symmetry 12(9), 1481 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12091481
Chen, Y.: “Methods and apparatuses for authentication in quantum key distribution and or quantum data communication,” 2018
Rao, B.D., Jayaraman, R.: A novel quantum identity authentication protocol without entanglement and preserving pre-shared key information. Quantum Inform. Process. 22(2), 92 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03832-6
Harun, N.Z., Zukarnain, Z.A., Hanapi, Z.M., Ahmad, I., Khodr, M.F.: Multiphoton quantum communication using multiple-beam concept in free space optical channel. Symmetry 13(1), 1–16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13010066
Kumar, A., Saha, R., Conti, M., Kumar, G., Buchanan, W.J., Kim, T.H.: A comprehensive survey of authentication methods in internet-of-things and its conjunctions. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 204, 103414 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2022.103414
Azahari, N.S.B., Harun, N.Z.B., Zukarnain, Z.B.A.: Quantum identity authentication for non-entanglement multiparty communication: A review, state of art and future directions. ICT Express. Korean Inst. Commun. Sci. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2023.02.010
Wu, Y.T., Chang, H., Guo, G.D., Lin, S.: Multi-party quantum key agreement protocol with authentication. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 60(11), 4066–4077 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04954-2
Zhang, S., Chen, Z.K., Shi, R.H., Liang, F.Y.: A novel quantum identity authentication based on Bell states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59(1), 236–249 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04319-w
Zhou, R.G., Huo, M., Hu, W., Zhao, Y.: Dynamic multiparty quantum secret sharing with a trusted party based on generalized GHZ state. IEEE Access 9, 22986–22995 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3055943
Li, X., Zhang, K., Zhang, L., Zhao, X.: A new quantum multiparty simultaneous identity authentication protocol with the classical third-party. Entropy 24(4), 483 (2022)
Kang, M.S., Heo, J., Hong, C.H., Yang, H.J., Han, S.W., Moon, S.: Controlled mutual quantum entity authentication with an untrusted third party. Quantum Inform. Process. 17, 1–5 (2018)
Yan, L., Zhang, S., Chang, Y., Sun, Z., Sheng, Z.: Quantum secure direct communication protocol with mutual authentication based on single photons and bell states. Comput. Mater. Continua 63(3), 1297–1307 (2020). https://doi.org/10.32604/CMC.2020.09873
Das, N., Paul, G.: Cryptanalysis of quantum secure direct communication protocol with mutual authentication based on single photons and bell states. Europhys. Lett. 138(4), 48001 (2022)
Kang, M.S., Choi, Y.H., Kim, Y.S., Cho, Y.W., Lee, S.Y., Han, S.W., Moon, S.: Quantum message authentication scheme based on remote state preparation. Phys. Scripta. 93(11), 115102 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1681-0
Kak, S.: Authentication using piggy bank approach to secure double-lock cryptography. (2014). https://arxiv.org/abs/1411.3645
Li, H., Li, D., Zhang, X., Shou, G., Hu, Y., Liu, Y.: A security management architecture for time synchronization towards high precision networks. IEEE Access (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3107203
Zhou, N.R., Zhu, K.N., Bi, W., Gong, L.H.: Semi-quantum identification. Quantum Inform. Process. 18, 1–7 (2019)
Jiang, S.Q., Zhou, R.G., Hu, W.W.: Semi-quantum mutual identity authentication using bell states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 60(9), 3353–3362 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04911-z
Zhu, H., Wang, L., Zhang, Y.: An efficient quantum identity authentication key agreement protocol without entanglement. Quantum Inform. Process. 19, 1–4 (2020)
Tao, Z., Chang, Y., Zhang, S., Dai, J., Li, X.: Two semi-quantum direct communication protocols with mutual authentication based on bell states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(9), 2986–2993 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04178-5
Rodzi, N.S., Azahari, N.S., Harun, N.Z.: Protocol efficiency using multiple level encoding in quantum secure direct communication protocol. Int. J. Softw. Eng. Comput. Syst. 9(2), 105–118 (2023)
Azahari, N. S., and Harun, N. Z.: “Quantum cryptography experiment using optical devices,” 2023. [Online]. Available: www.ijacsa.thesai.org
Narula, L., Humphreys, T.E.: Requirements for secure clock synchronization. IEEE J. Select. Topics Signal Process. 12(4), 749–762 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2835772
Kong, X., et al.: Demonstration of multiparty quantum clock synchronization. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(11), 1–17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-2057-9
Nande, S.S., Paul, M., Senk, S., Ulbricht, M., Bassoli, R., Fitzek, F.H., Boche, H.: Quantum enhanced time synchronisation for communication network. Comput. Netw. 1(229), 109772 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2023.109772
Agnesi, C., et al.: Simple quantum key distribution with qubit-based synchronization and a self-compensating polarization encoder. Optica 7(4), 284 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1364/optica.381013
Abushgra, A.A., Elleithy, K.M.: A shared secret key initiated by EPR authentication and Qubit transmission channels. IEEE Access 5, 17753–17763 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2741899
Babar, Z., et al.: Duality of quantum and classical error correction codes: Design principles and examples. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 21(1), 970–1010 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2018.2861361
Chang, Y., Zhang, S., Yan, L., Li, J.: Deterministic secure quantum communication and authentication protocol based on three-particle W state and quantum one-time pad. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59(23), 2835–2840 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0333-3
Azahari, N.S.B., Harun, N.Z.B., Zukarnain, Z.B.A.: Quantum identity authentication for non-entanglement multiparty communication: A review, state of art and future directions. ICT Express (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2023.02.010
Azahari, N.S.B., Harun, N.Z.B., Zulkarnain, Z.B.A.: Quantum identity authentication for non-entanglement multiparty communication: a review, state of art and future directions. ICT Express (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2023.02.010
Verma, P.K., El Rifai, M., Chan, K.W.: Multi-photon Quantum Secure Communication. Springer, Singapore (2019)
Cleve, R., Buhrman, H.: Substituting quantum entanglement for communication. Phys. Rev. A 56(2), 1201 (1997)
Ghilen, A., Bekmabrouk, H., and Bouallegue, R.: Classification of quantum authentication protocols and calculation of their complexity. IEEE, 2014
Guedes, E. B., and de Assis, F. M.: “Quantum communication complexity of quantum authentication protocols,” May 2011, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1105.5370
Yao and Andrew, C. C.: “Quantum circuit complexity,” in Proceedings of the 1993 IEEE 34th Annual Foundations of Computer Science, IEEE Computer Society, 1998, pp. 352–361
Roell, J.: “Demystifying quantum gates — one Qubit at a time.” Accessed: Jan. 18, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://towardsdatascience.com/demystifying-quantum-gates-one-qubit-at-a-time-54404ed80640
El-Latif, A.A.A., Abd-El-Atty, B., Hossain, M.S., Elmougy, S., Ghoneim, A.: Secure quantum steganography protocol for fog cloud internet of things. IEEE Access 6, 10332–10340 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2799879
Rifai, El. et al., “Quantum secure communication using polarization hopping multistage protocols,” Ph.D. dissertation, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Oklahoma (2016)
Jian, L., et al.: A survey on quantum cryptography. Chin. J. Electron. 27(2), 223–228 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/cje.2018.01.017
Dutta, A., and Pathak, A.: “Collective attack free controlled quantum key agreement without quantum memory,” Aug. 2023, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2308.05470
Boyer, M., Liss, R., Mor, T.: Composable security against collective attacks of a modified BB84 QKD protocol with information only in one basis. Theor. Comput. Sci. 801, 96–109 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2019.08.014
Mafu, M., Sekga, C., Senekane, M.: Security of bennett-brassard 1984 quantum-key distribution under a collective-rotation noise channel. Photonics (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9120941
Wu, L., Chen, Y.: Three-stage quantum cryptography protocol under collective-rotation noise. Entropy 17(5), 2919–2931 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/e17052919
Li, L., Li, H., Li, C., Chen, X., Chang, Y., Yang, Y., Li, J.: The security analysis of E91 protocol in collective-rotation noise channel. Int. J. Distribut. Sensor Netw. 14(5), 1550147718778192 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1550147718778192
Li, J., Pan, Z., Zheng, J., Sun, F., Ye, X., Yuan, K.: The security analysis of quantum SAGR04 protocol in collective-rotation noise channel. Chin. J. Electron. 24, 689–693 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1049/cje.2015.10.005
Harun, N.Z., Zukarnain, Z.A., Hanapi, Z.M., Ahmad, I.: Evaluation of parameters effect in multiphoton quantum key distribution over fiber optic. IEEE Access 6, 47699–47706 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2866554
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) through the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS/1/2021/ICT11/UTHM/03/1). We also want to thank the Government of Malaysia, which provided the MyBrain15 program, for sponsoring this work under the self-funded research grant and L00022 from the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation (MOSTI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest among authors.
Ethical approval
The submitted work is original and has not been published elsewhere in any form or language.
Information consent
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Azahari, N.S., Harun, N.Z., Ramli, S.N. et al. Secured shared authentication key with two-way clock synchronization over multiparty quantum communication. Quantum Inf Process 22, 410 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-04158-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-04158-z