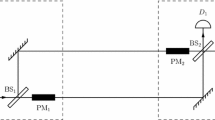
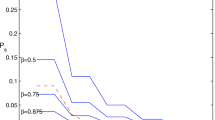
Abstract
Most existing quantum-key-distribution-based quantum private query (QPQ) protocols are designed based on ideal quantum communication devices. However, multiphoton pulses are unavoidable in various light sources due to practical devices. We analyze the security of the QPQ protocol with the user as the light source in the case of non-ideal light sources. The results show that the user’s privacy is seriously threatened when the database utilizes multiphoton pulses to launch attacks. To address this issue, we propose a decoy-state method to resist multiphoton attacks in the QPQ, which is used to verify the honesty of the database. By calculating the ratio of multiphoton pulses, shifting the key, and choosing the suitable light sources, the user can detect and effectively resist the database launching multiphoton attacks. This approach fills the research gap on the user-as-light-source aspect of QPQ protocols, enabling the QPQ to perform better in scenarios involving non-ideal light sources.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
Data underlying the results presented in this paper are not publicly available at this time but may be obtained from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
Wootters, W.K., Zurek, W.H.: A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 299(5886), 802–803 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/299802a0
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum Cryptography: Public Key Distribution and Coin Tossing, pp. 175–179 (1984)
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74(1), 145 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.74.145
Long, G.-L., Liu, X.-S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65(3), 032302 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.65.032302
Lo, H.-K., Ma, X., Chen, K.: Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(23), 230504 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.230504
Wang, X.-B.: Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(23), 230503 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.230503
Ma, X., Qi, B., Zhao, Y., Lo, H.-K.: Practical decoy state for quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 72(1), 012326 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.72.012326
Jackson, D.J., Hockney, G.M.: Securing qkd links in the full hilbert space. Quantum Inf. Process. 4, 35–47 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-005-3194-5
Jackson, D.J., Hockney, G.M.: Securing qkd links in the full hilbert space. Quantum Inf. Process. 4, 35–47 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-005-3194-5
Jin, W., Zheng, L., Wang, F., Liang, R.: The influence of stochastic dispersion on quantum key distribution system. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 56, 1–6 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-012-4586-7
Sasaki, T., Yamamoto, Y., Koashi, M.: Practical quantum key distribution protocol without monitoring signal disturbance. Nature 509(7501), 475–478 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13303
Wang, S., Yin, Z.-Q., He, D.-Y., Chen, W., Wang, R.-Q., Ye, P., Zhou, Y., Fan-Yuan, G.-J., Wang, F.-X., Chen, W., et al.: Twin-field quantum key distribution over 830-km fibre. Nat. Photonics 16(2), 154–161 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00928-2
Huang, W., Wen, Q.-Y., Liu, B., Gao, F., Chen, H.: Deterministic secure quantum communication with collective detection using single photons. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51, 2787–2797 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-012-1154-2
Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.-B.: One-step device-independent quantum secure direct communication. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 65(5), 250311 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-021-1863-9
Qin, L., Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W., Xu, B., Li, Y.: Decoy-state quantum private query protocol with two-way communication. Physica A-Stat. Mech. Appl. 633, 129427 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2023.129427
Lo, H.K., Chau, H.F.: Unconditional security of quantum key distribution over arbitrarily long distances. Science 283(5410), 2050–2056 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.283.5410.2050
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the bb84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(2), 441 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.441
Scarani, V., Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H., Cerf, N.J., Dušek, M., Lütkenhaus, N., Peev, M.: The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81(3), 1301 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.81.1301
Lu, H., Fung, C.-H.F., Cai, Q.-Y.: Two-way deterministic quantum key distribution against detector-side-channel attacks. Phys. Rev. A 88(4), 044302 (2013) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.88.044302
Liu, H., Jiang, C., Zhu, H.-T., Zou, M., Yu, Z.-W., Hu, X.-L., Xu, H., Ma, S., Han, Z., Chen, J.-P., et al.: Field test of twin-field quantum key distribution through sending-or-not-sending over 428 km. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126(25), 250502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.250502
Yin, J., Li, Y.-H., Liao, S.-K., Yang, M., Cao, Y., Zhang, L., Ren, J.-G., Cai, W.-Q., Liu, W.-Y., Li, S.-L., et al.: Entanglement-based secure quantum cryptography over 1120 kilometres. Nature 582(7813), 501–505 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2401-y
Liu, B., Xiao, D., Huang, W., Jia, H.-Y., Song, T.-T.: Quantum private comparison employing single-photon interference. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 1–13 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1630-y
Gertner, Y., Ishai, Y., Kushilevitz, E., Malkin, T.: Protecting data privacy in private information retrieval schemes. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 60(3), 592–629 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcss.1999.1689
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring, 124–134 (1994) https://doi.org/10.1109/SFCS.1994.365700. IEEE
Zhou, X., Qiu, D., Luo, L.: Distributed exact Grover’s algorithm. Front. Phys. 18, 51305 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-023-1327-x
Liu, B., Gao, F., Qin, S.-J., Huang, W., Liu, F., Wen, Q.-Y.: Choice of measurement as the secret. Phys. Rev. A 89(4), 042318 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.89.042318
Wang, J., Cui, K., Luo, C., Zhang, H., Zhou, L., Chen, T., Liang, H., Jin, G.: Design of a high-repetition rate photon source in a quantum key distribution system. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 56, 1–7 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-012-4671-y
Yan, P.-S., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.-B.: Advances in quantum entanglement purification. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 66(5), 250301 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-022-2065-x
Sheng, Y.-B., Zhou, L.: A step toward fault-tolerant distributed quantum computing: entangling nonlocal logical-qubit with optical quantum multiplexing. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 67(2), 220331 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-023-2258-x
Liu, W., Peng, J., Wang, C., Cao, Z., Huang, D., Lin, D., Huang, P., Zeng, G.: Hybrid quantum private communication with continuous-variable and discrete-variable signals. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 1–7 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5632-9
Tang, Z., Liao, Z., Xu, F., Qi, B., Qian, L., Lo, H.-K.: Experimental demonstration of polarization encoding measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112(19), 190503 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.190503
Lo, H.-K.: Insecurity of quantum secure computations. Phys. Rev. A 56(2), 1154 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.56.1154
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L.: Quantum private queries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100(23), 230502 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.230502
Jakobi, M., Simon, C., Gisin, N., Bancal, J.-D., Branciard, C., Walenta, N., Zbinden, H.: Practical private database queries based on a quantum-key-distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. A 83(2), 022301 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.83.022301
Gao, F., Liu, B., Wen, Q.-Y., Chen, H.: Flexible quantum private queries based on quantum key distribution. Opt. Express 20(16), 17411–17420 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.20.017411
Yang, Y.-G., Zhang, M.-O., Yang, R.: Private database queries using one quantum state. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 1017–1024 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0902-z
Wei, C.-Y., Wang, T.-Y., Gao, F.: Practical quantum private query with better performance in resisting joint-measurement attack. Phys. Rev. A 93(4), 042318 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.93.042318
Huttner, B., Imoto, N., Gisin, N., Mor, T.: Quantum cryptography with coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 51(3), 1863 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.51.1863
Hwang, W.-Y.: Quantum key distribution with high loss: toward global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91(5), 057901 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.057901
Liu, B., Xia, S., Xiao, D., Huang, W., Xu, B., Li, Y.: Decoy-state method for quantum-key-distribution-based quantum private query. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 65(4), 240312 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-021-1843-7
Scarani, V., Acin, A., Ribordy, G., Gisin, N.: Quantum cryptography protocols robust against photon number splitting attacks for weak laser pulse implementations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(5), 057901 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.057901
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68(21), 3121 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.3121
Gao, F., Liu, B., Huang, W., Wen, Q.-Y.: Postprocessing of the oblivious key in quantum private query. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 21(3), 98–108 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2014.2358192
Dušek, M., Jahma, M., Lütkenhaus, N.: Unambiguous state discrimination in quantum cryptography with weak coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 62(2), 022306 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.62.022306
Wei, C.-Y., Cai, X.-Q., Wang, T.-Y., Qin, S.-J., Gao, F., Wen, Q.-Y.: Error tolerance bound in qkd-based quantum private query. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 38(3), 517–527 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2020.2968998
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R &D Program of China (Grant Nos. 2022YFC3801700), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 62171418), and Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant No. 2023JDRC0017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, YF., Huang, W., Liu, B. et al. Analysis and protection to user privacy in quantum private query with non-ideal light source. Quantum Inf Process 23, 133 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04346-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04346-5