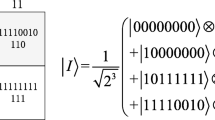Abstract
The initialization of desired quantum states is usually the starting element of quantum algorithms. For quantum image processing, inefficient preparation of quantum images hinders the implement of algorithms on quantum devices. In this study, a ready-to-use quantum circuit simplification method for preparing quantum images is proposed. By encoding the control qubits of the multi-qubit gates as Gray code, an optimized circuit for preparing lossless quantum images is constructed using a technique for simultaneously initializing adjacent pixels. This technique decreases the necessary number of control qubits and the depth of preparation circuits. By validating the proposed algorithm on a medical image dataset, it is demonstrated that a satisfactory depth reduction can be achieved without any quality loss when preparing quantum images.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Availability of data and materials
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper.
References
Kim, Y., Eddins, A., Anand, S., Wei, K., Berg, E., Rosenblatt, S., Nayfeh, H., Wu, Y., Zaletel, M., Temme, K., Kandala, A.: Evidence for the utility of quantum computing before fault tolerance. Nature 618, 500–505 (2023)
Google Quantum Lab AI.: Quantum supremacy using a programmable superconducting processor. Nature 574, 505–510 (2019)
Pino, J.M., Dreiling, J.M., Figgatt, C., Gaebler, J.P., Moses, S.A., Allman, M.S., Baldwin, C.H., Foss-Feig, M., Hayes, D., Mayer, K., Ryan-Anderson, C., Neyenhuis, B.: Demonstration of the trapped-ion quantum CCD computer architecture. Nature 592, 209 (2021)
Preskill, J.: Quantum computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2, 79 (2018)
Bharti, K., Cervera-Lierta, A., Kyaw, T.H., Haug, T., Alperin-Lea, S., Anand, A., Degroote, M., Heimonen, H., Kottmann, J.S., Menke, T., Mok, W.-K., Sim, S., Kwek, L.-C., Aspuru-Guzik, A.: Noisy intermediate-scale quantum algorithms. Rev. Modern Phys. 94, 015004 (2022)
Alok, A., Meizhong, L., Prabh S. B., Vinay P.: Quantum Image Processing. arXiv:2203.01831 [quant-ph].
Schuld, M., Bocharov, A., Svore, K., Wiebe, N.: Circuit centric quantum classifiers. Phys. Rev. A 101, 032308 (2018)
Schuld, M., Fingerhuth, M., Petruccione, F.: Implementing a distance-based classifier with a quantum interference circuit. EPL (Europhysics Letters) 119, 60002 (2017).
Takaki, Y., Mitarai, K., Negoro, M., Fujii, K., Kitagawa, M.: Learning temporal data with a variational quantum recurrent neural network. Phys. Rev. A 103, 052414 (2021)
Havlíček, V., Córcoles, A.D., Temme, K., Harrow, A.W., Kandala, A., Chow, J.M., Gambetta, J.M.: Supervised learning with quantum-enhanced feature spaces. Nature 567, 209 (2019)
Dunjko, V., Briegel, H.J.: Machine learning & artificial intelligence in the quantum domain: a review of recent progress. Reports Progress Phys. 81, 074001 (2018)
Biamonte, J., Wittek, P., Pancotti, N., Rebentrost, P., Wiebe, N., Lloyd, S.: Quantum machine learning. Nature 549, 195 (2017)
Cerezo, M., Arrasmith, A., Babbush, R., Benjamin, S.C., Endo, S., Fujii, K., McClean, J.R., Mitarai, K., Yuan, X., Cincio, L., Coles, P.J.: Variational quantum algorithms. Nat. Rev. Phys. 3, 625 (2021)
Mitarai, K., Negoro, M., Kitagawa, M., Fujii, K.: Quantum circuit learning. Phys. Rev. A 98, 032309 (2018)
Ren, W., Li, W., Xu, S., Wang, K., Jiang, W., Jin, F., Zhu, X., Chen, J., Song, Z., Zhang, P., Dong, H., Zhang, X., Deng, J., Gao, Y., Zhang, C., Wu, Y., Zhang, B., Guo, Q., Li, H., Wang, Z., Biamonte, J., Song, C., Deng, D., Wang, H.: Experimental quantum adversarial learning with programmable superconducting qubits. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2, 711–717 (2022)
Lu, S., Duan, L., Deng, D.: Quantum adversarial machine learning. Phys. Rev. Res. Am. Phys. Soc. 2, 33212 (2020)
Gong, W., Deng, D.-L.: Universal adversarial examples and perturbations for quantum classifiers. National Sci. Rev. 9, nwab130 (2021).
Yan, F., Venegas-Andraca, S.E. (2020). Quantum Image Representations. In: Quantum Image Processing. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9331-1_2.
Liu, Y., Qi, Z., Liu, Q.: Comparison of the similarity between two quantum images. Sci. Rep. 12, 7776 (2022)
Liu, X., Zhou, R., El-Rafei, A., Li, F., Xu, R.: Similarity assessment of quantum images. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(8), 244 (2019)
Jiang, N., Wang, J., Mu, Y.: Quantum image scaling up based on nearest-neighbor interpolation with integer scaling ratio. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 4001–4026 (2015)
Zhou, R., Hu, W., Fan, P., Hou, I.: Quantum realization of the bilinear interpolation method for NEQR. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–17 (2017)
Yao, X., Wang, H., Liao, Z., Chen, M., Pan, J., Li, J., Zhang, K., Lin, X., Wang, Z., Luo, Z., Zheng, W., Li, J., Zhao, M., Peng, X., Suter, D.: Quantum image processing and its application to edge detection: Theory and experiment. Phys. Rev. x. 7(3), 031041 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Lu, K., Gao, Y.: QSobel: A novel quantum image edge extraction algorithm. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 58, 1–13 (2015)
He, Y., Luo, M.X., Zhang, E., Wang, H.K., Wang, X.F.: Decompositions of n-qubit toffoli gates with linear circuit complexity. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56, 2350–2361 (2017)
Gidney, C.: https://algassert.com/circuits/2015/06/05/Constructing-Large-Controlled-Nots.html
Sleeman, J., Dorband, J., Halem, M. A.: A hybrid approach: Convolutional autoencoders for quantum image compression and RBMs for generative learning (Conference Presentation). In: Quantum Information Science, Sensing, and Computation XII. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2558832.
Jiang, N., Lu, X., Hu, H., Dang, Y., Cai, Y.: A novel quantum image compression method based on JPEG. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 1 (2017).
Amankwah, M.G., Camps, D., Bethel, E.W., Beeumen, R.V., Perciano, T.: Quantum pixel representations and compression for N-dimensional images. Sci. Rep. 12, 7712 (2022)
Zhang, Y., Lu, K., Gao, Y.H., Wang, M.: NEQR: A novel enhanced quantum representation of digital images. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(12), 2833–2860 (2013)
Press, W. H., Flannery, B. P., Teukolsky, S. A., Vetterling, W. T.: ” Gray Codes.” In: Numerical Recipes in FORTRAN: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd ed.. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 886-888 (1992).
Vartiainen, J.J., Mottonen, M., Salomaa, M.M.: Efficient decomposition of quantum gates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 177902 (2004)
Hayit, G., Ginneken, B.V., Summers, R.M.: Guest editorial deep learning in medical imaging: overview and future promise of an exciting new technique. IEEE T. Med. Imaging 35, 1153 (2016)
Polanco, A.: Medical MNIST classification (2017). https://github.com/apolanco3225/Medical-MNIST-Classification
Sang, J., Wang, S., Li, Q.: A novel quantum representation of color digital images. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 42–56 (2017)
Wakerly, J. F.: Digital design : principles and practices. Prentice Hall, New Jersey (1989).
Rosenbaum, D., Perkowski, M.: Extended superposed quantum-state initialization using disjoint prime implicants. Phys. Rev. A 79(5), 52310 (2009)
Jumade, R., Sawaya, N. P. D.: Data is often loadable in short depth: Quantum circuits from tensor networks for finance, images, fluids, and proteins. arXiv:2309.13108 [quant-ph].
Acknowledgments
This work is funded by Qilu Normal University with Grant No. JG202235.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
You-hang Liu is responsible for designing the algorithms, programming software, writing the original draft and preparing all figures and tables. Xiao-shuang Cheng and You-hang Liu are responsible for validating the effectiveness of the algorithms. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to this work. We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Yh., Cheng, Xs., Loh, Cw. et al. Efficient preparation of lossless quantum images based on Gray code. Quantum Inf Process 23, 161 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04369-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04369-y