Abstract
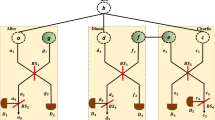
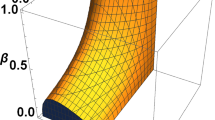
As a new functional network supporting communication, quantum network can provide higher security and lower complexity for quantum information processing. Based on the one-to-one quantum state merging and quantum state redistribution, we first generalize them to the multi-to-one situation and give the optimal cost pair for merging or redistributing quantum states from each sender to the receiver in turn. It is proved that previously received information can reduce the cost of the next transfer. Then, using the method of fusion, we propose a state transfer protocol over the multi-access channel network with one intermediate node and provide its optimal cost pair. Finally, two specific examples are given to demonstrate our results when a GHZ-like state or a Werner-type state is taken as the shared entanglement resource.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Meter, R.V.: Quantum networking and internetworking. IEEE Network 26, 59–64 (2012)
Cacciapuoti, A.S., Caleffi, M., Tafuri, F., Cataliotti, F.S., Gherardini, S., Bianchi, G.: Quantum internet: networking challenges in distributed quantum computing. IEEE Network 34, 137–143 (2020)
Yan, Y.F., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution of multiple degrees of freedom of a single photon. Front. Phys. 16, 11501 (2021)
Liu, B., Xia, S., Xiao, D., Huang, W., Xu, B.J., Li, Y.: Decoy-state method for quantum-key-distribution-based quantum private query. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 65, 240312 (2022)
Li, Z.H., Xue, K.P., Li, J., Yu, N.H., Wei, D.S.L., Li, R.D.: Connection-oriented and connectionless remote entanglement distribution strategies in quantum networks. IEEE Network 36, 150–156 (2022)
Luo, M.X.: Nonsignaling causal hierachy of general multisource networks. Phys. Rev. A 101, 062317 (2020)
Zhou, N.R., Zhang, T.F., Xie, X.W., Wu, J.Y.: Hybrid quantum-classical generative adversarial networks for image generation via learning discrete distribution. Signal Process.: Image Commun. 110, 116891 (2023)
Gong, L., Ma, S.Y., Jiang, J.L.: Controlled cyclic remote preparation. Commun. Theor. Phys. 75, 105103 (2023)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crepeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895–1899 (1993)
Lo, A.K.: Classical-communication cost in distributed quantum-information processing: a generalization of quantum-communication complexity. Phys. Rev. A 62, 012313 (2000)
Pati, A.K.: Minimum classical bit for remote preparation and measurement of a qubit. Phys. Rev. A 63, 014302 (2000)
Ma, S.Y., Jiang, J.L., Yan, X.: Hierarchical quantum information splitting of an arbitrary m-qudit state with multiparty. Quantum Inf. Process. 22, 263 (2023)
Wang, S., Liu, B., Huang, W., Xu, B.J., Li, Y.: Memory-free quantum secret sharing protocol with collective detection. Quantum Inf. Process. 22, 181 (2023)
Rathi, D., Kumar, S.: A \(d\)-level quantum secret sharing scheme with cheat-detection \((t, m)\) threshold. Quantum Inf. Process. 22, 183 (2023)
Lu, Y.J.: A novel practical quantum secure direct communication protocol. Quantum Inf. Process. 60, 1159–1163 (2021)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Long, G.L.: One-step quantum secure direct communication. Sci. Bull. 67, 367–374 (2022)
Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B.: One-step device-independent quantum secure direct communication. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 65, 250311 (2022)
Horodecki, M., Oppenheim, J., Winter, A.: Partial quantum information. Nature 436, 673–676 (2005)
Devetak, I., Yard, J.: Exact cost of redistributing multipartite quantum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 230501 (2008)
Yard, J.T., Devetak, I.: Optimal quantum source coding with quantum side information at the encoder and decoder. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 55, 5339–5351 (2009)
Lee, Y., Lee, S.: State transfer with quantum side information. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 268 (2018)
Wakakuwa, E., Soeda, A., Murao, M.: A coding theorem for bipartite unitaries in distributed quantum computation. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 63, 5372–5403 (2017)
Piparo, N.L., Hanks, M., Gravel, C., Nemoto, K., Munro, W.J.: Resource reduction for distributed quantum information processing using quantum multiplexed photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 210503 (2020)
Avis, D., Hayden, P., Savov, I.: Distributed compression and multiparty squashed entanglement. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 41, 115301 (2008)
Yang, D., Eisert, J.: Entanglement combing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 220501 (2009)
Yang, H.Y., Ye, T.Y.: Secure multi-party quantum summation based on quantum Fourier transform. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 129 (2018)
Streltsov, A., Meignant, C., Eisert, J.: Rates of multipartite entanglement transformations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 080502 (2020)
Carleial, A.: Multiple-access channels with different generalized feedback signals. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 28, 841–850 (1982)
Yard, J., Hayden, P., Devetak, I.: Capacity theorems for quantum multiple-access channels: classical-quantum and quantum-quantum capacity regions. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 54, 3091 (2008)
Laurenza, R., Pirandola, S.: General bounds for sender-receiver capacities in multipoint quantum communications. Phys. Rev. A 96, 032318 (2017)
Qi, H., Wang, Q., Wilde, M.M.: Applications of position-based coding to classical communication over quantum channels. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 51, 444002 (2018)
Leditzky, F., Alhejji, M.A., Levin, J., Smith, G.: Playing games with multiple access channels. Nat. Commun. 11, 1497 (2020)
Hao, S.H., Shi, H.W., Li, W., Shapiro, J.H., Zhuang, Q.T., Zhang, Z.S.: Entanglement-assisted communication surpassing the ultimate classical capacity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 250501 (2021)
Traskov, D., Kramer, G.: Reliable communication in networks with multi-access interference. In: IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), pp. 343-348 (2007)
Anathi, M., Vijayakumar, K.: An intelligent approach for dynamic network traffic restriction using MAC address verification. Comput. Commun. 154, 559–564 (2020)
Wu, F., Chen, L., Zhao, N., Chen, Y., Yu, F.R., Wei, G.: Computation over multi-access channels: multi-hop implementation and resource allocation. IEEE Trans. Commun. 69, 1038–1052 (2021)
Shannon, C.E.: A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27, 379–423 (1948)
Khinchin, A.I.: Mathematical foundations of information theory. Dover Publications, New York, USA (1957)
Neumann, J.V.: Mathematical foundations of quantum mechanics. In: Investigations in Physics, pp. 127–136. Princeton University Press, New Jersey (1955)
Bennett, C.H., Shor, P.W.: Quantum information theory. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 44, 2724–2742 (1998)
Bennett, C.H., Shor, P.W., Smolin, J.A., Thapliyal, A.V.: Entanglement-assisted classical capacity of noisy quantum channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 3081–3084 (1999)
Bennett, C.H., Shor, P.W., Smolin, J.A., Thapliyal, A.V.: Entanglement-assisted capacity of a quantum channel and the reverse Shannon theorem. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 48, 2637–2655 (2002)
Mendonca, P.E.M.F., Napolitano, R.D.J., Marchiolli, M.A., Foster, C.J., Liang, Y.C.: Alternative fidelity measure between quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 78, 052330 (2008)
Giovannetti, V., Guha, S., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L., Shapiro, J.H., Yuen, H.P.: Classical capacity of the lossy bosonic channel: the exact solution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 027902 (2004)
Yen, B.J., Shapiro, J.H.: Multiple-access bosonic communications. Phys. Rev. A 72, 062312 (2005)
Shi, H., Hsieh, M.H., Guha, S., Zhang, Z.S., Zhuang, Q.T.: Entanglement-assisted capacity regions and protocol designs for quantum multiple-access channels. npj Quantum Inf. 7, 74 (2021)
Feng, G., Xu, G.F., Long, G.L.: Experimental realization of nonadiabatic holonomic quantum computation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 190501 (2013)
Greenberger, D.M., Horne, M.A., Zeilinger, A.: Going beyond Bell’s theorem: In: Bell’s Theorem, Quantum Theory and Conceptions of the Universe, pp. 69–72. Springer, Dordrecht, Netherlands (1989)
Werner, R.F.: Quantum states with Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen correlations admitting a hidden-variable model. Phys. Rev. A 40, 4277–4281 (1989)
Fortes, R., Rigolin, G.: Fighting noise with noise in realistic quantum teleportation. Phys. Rev. A 92, 012338 (2015)
Wang, M.M., Qu, Z.G., Wang, W., Chen, J.G.: Effect of noise on deterministic joint remote preparation of an arbitrary two-qubit state. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 140 (2017)
Zhang, P., Ma, S.Y., Gong, L.: Deterministic Remote Preparation via the \(\chi \) state in noisy environment. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58, 2795–2809 (2019)
Harraz, S., Cong, S., Nieto, J.J.: Optimal tripartite quantum teleportation protocol through noisy channels. Quantum Inf. Process. 22, 83 (2023)
Yan, P.S., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Advances in quantum entanglement purification. Sci. China Phys. Mech. 66, 250301 (2023)
Qu, C.C., Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B.: Entanglement concentration for concatenated Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 4131–4146 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62172341), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.2682014CX095), Sichuan Natural Science Foundation (No. 2023NSFSC0447) and the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province of China (No. 242300420276).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, X., Luo, M. & Ma, S. State transfer on the multi-access channel network. Quantum Inf Process 23, 171 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04380-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04380-3