Abstract
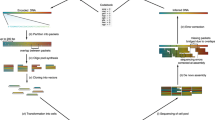
This research explores the application of quantum computing to DNA analysis, focusing on transitioning classical data to quantum information formats. We developed the Quantum Cache Memory (QCM) framework, which utilizes superposition and hybrid encoding via entanglement. The QCM framework is designed to preserve the integrity of genetic sequences throughout the quantum computing process. The effectiveness of this approach is demonstrated through implementations of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) detection and pattern search algorithms using a perfect quantum simulator. The results demonstrate the potential for leveraging quantum phenomena to process classical data in parallel on quantum hardware. However, the limitations of current quantum hardware and data encoding efficiency are acknowledged. This study shows the groundwork for future improvements in quantum computing ecosystems, such as the need for persistent quantum states and more effective handling of large-scale data. Our research has been conducted solely through simulations and mathematical modeling, indicating the necessity for future work on actual quantum servers.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM J. Comput. 26, 1484–1509 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1137/S0097539795293172
Grover LK (1996) A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of the twenty-eighth annual ACM symposium on Theory of computing - STOC ’96. ACM Press, Philadelphia, pp 212–219
Blekos, K., Brand, D., Ceschini, A., et al.: A review on quantum approximate optimization algorithm and its variants. Phys. Rep. 1068, 1–66 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2024.03.002
Tilly, J., Chen, H., Cao, S., et al.: The variational quantum eigensolver: a review of methods and best practices. Phys. Rep. 986, 1–128 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2022.08.003
Jäger, J., Krems, R.V.: Universal expressiveness of variational quantum classifiers and quantum kernels for support vector machines. Nat. Commun. 14, 576 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36144-5
Clark, D.P., Pazdernik, N.J.: DNA, RNA, and protein. In: Biotechnology, pp. 33–61. Elsevier, New York (2016)
Pearson, W.R.: Rapid and sensitive sequence comparison with FASTP and FASTA. In: Methods in Enzymology, pp. 63–98. Elsevier, New York (1990)
Shastry, B.S.: SNPs in disease gene mapping, medicinal drug development and evolution. J. Hum. Genet. 52, 871–880 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-007-0200-z
Innan, N., Khan, M.A.-Z.: Classical-to-quantum sequence encoding in genomics. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2304.10786 (2023)
Kösoglu-Kind, B., Loredo, R., Grossi, M., et al.: A biological sequence comparison algorithm using quantum computers. Sci. Rep. 13, 14552 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-41086-5
Chang, Y.-F.: Extensive quantum theory of DNA and biological string. Neuroquantology 12, 738 (2014). https://doi.org/10.14704/nq.2014.12.3.738
Bhabhatsatam, B., Smanchat, S.: Hybrid quantum encoding: combining amplitude and basis encoding for enhanced data storage and processing in quantum computing. In: 2023 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE), pp. 512–516. IEEE, Phitsanulok (2023)
Weigold, M., Barzen, J., Leymann, F., Salm, M.: Encoding patterns for quantum algorithms. IET Quantum Commun. 2, 141–152 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1049/qtc2.12032
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L.: Quantum random access memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 160501 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.160501
Shepherd, D., Bremner, M.J.: Temporally unstructured quantum computation. Proc. R. Soc. A 465, 1413–1439 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.2008.0443
Khan, M.A., Aman, M.N., Sikdar, B.: Beyond bits: a review of quantum embedding techniques for efficient information processing. IEEE Access 12, 46118–46137 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3382150
Phalak, K., Chatterjee, A., Ghosh, S.: Quantum random access memory for dummies. Sensors 23, 7462 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23177462
Park, D.K., Petruccione, F., Rhee, J.-K.K.: Circuit-based quantum random access memory for classical data. Sci. Rep. 9, 3949 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40439-3
Djordjevic, I.: Quantum algorithms. In: Quantum information processing and quantum error correction, pp. 145–173. Elsevier, New York (2012)
Sang, J., Yu, C.: Understanding quantum parallelism through programming. In: 2023 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), pp. 1072–1078. IEEE, Las Vegas (2023)
Niroula, P., Nam, Y.: A quantum algorithm for string matching. npj Quantum Inf. 7, 37 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-021-00369-3
Soni, K.K., Rasool, A.: Quantum-effective exact multiple patterns matching algorithms for biological sequences. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 8, e957 (2022). https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.957
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.B. conceptualized the study, developed the architecture, wrote the code, set up the environment, conducted testing, analyzed and validated the results, and wrote and edited the main manuscript text. S.S. supervised the research, analyzed and validated the results, and contributed to writing and editing the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhabhatsatam, B., Smanchat, S. Quantum cache memory: a framework for enhancing DNA analysis through quantum computing. Quantum Inf Process 23, 390 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04595-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04595-4