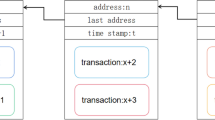
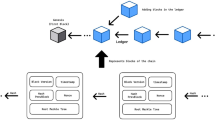
Abstract
The lottery business is a form of gambling activity operated by authority agencies. Due to the substantial economic interests, its security and fairness become the core elements of industry development. To maintain the trust of participants and ensure fair competition, blockchain technology has been widely applied in the lottery field due to the characteristics of decentralization, transparency, and immutability. However, with the rapid advancement of quantum computing, the security of traditional blockchain technology is challenged largely. To tackle this issue, a novel consensus mechanism which can resist quantum attacks is first proposed, based on a self-tallying quantum voting protocol. Then, a quantum circuit is designed, which can encode n-bit binary information into the relative phase of a quantum state and entangle the blocks by means of controlled-Z (CZ) gate, forming a quantum blockchain structure with timestamps. Finally, utilizing the designed quantum blockchain, a new type of lottery protocol is constructed. The proposed protocol meets the requirements of decentralization, unforgeability, verifiability, and quantum attack resistance. Compared to existing lottery protocols, it can support an arbitrary number of players, and only one communication is required for the ticket purchase process of each player, making it suitable for most of lottery game scenarios.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Nakamoto, S.: Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Decentralized Business Review. https://nakamotoinstitute.org/library/bitcoin/ (2024)
King, S., Nadal, S.: PPCoin: peer-to-peer crypto-currency with proof-of-stake. Self-Publ. Paper 19(1), 1–6 (2012)
Larimer, D.: Delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS). Bitshare Whitepaper 81, 85 (2014)
Miller, V.S.: Use of elliptic curves in cryptography. In: Conference on the theory and application of cryptographic techniques, pp. 417–426. Springer, Berlin (1985)
Rivest, R.L.: A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Commun. ACM 26(2), 96–99 (1978)
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 124–134 (1994)
Grover, L.K.: Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79(2), 325–328 (1997)
Sayeed, S., Marco-Gisbert, H.: Assessing blockchain consensus and security mechanisms against the 51% attack. Appl. Sci. 9(9), 1788 (2019)
Jogenfors, J.: Quantum bitcoin: an anonymous and distributed currency secured by the no-cloning theorem of quantum mechanics. In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (ICBC), Seoul, Korea (South), pp 245–252 (2019)
Kiktenko, E.O., Pozhar, N.O., Anufriev, M.N., et al.: Quantum-secured blockchain. Quantum Sci. Technol. 3(3), 035004 (2018)
Rajan, D., Visser, M.: Quantum blockchain using entanglement in time. Quantum Rep. 1(1), 3–11 (2019)
Sun, X., Sopek, M., Wang, Q., Kulicki, P.: Towards quantum-secured permissioned blockchain: signature, consensus, and logic. Entropy 21(9), 1–15 (2019)
Banerjee, S., Mukherjee, A., Panigrahi, P.K.: Quantum blockchain using weighted hypergraph states. Phys. Rev. Res. 2(1), 013322 (2020)
El-Latif, A., Abd-El-Atty, B., Mehmood, I., et al.: Quantum-inspired blockchain-based cybersecurity: securing smart edge utilities in IoT-based smart cities. Inf. Process. Manag. 58(4), 10 (2021)
Wu, F., Zhou, B., Jiang, J., et al.: Blockchain privacy protection based on post-quantum threshold algorithm. Comput. Mater. Contin. 76(1), 1–17 (2023)
Lin, C., He, D., Huang, X., et al.: DCAP: A secure and efficient decentralized conditional anonymous payment system based on blockchain. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 15, 2440–2452 (2020)
Yang, X., Lau, W.F., Ye, Q., et al.: Practical escrow protocol for bitcoin. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 15, 3023–3034 (2020)
Truong, N.B., Sun, K., Lee, G.M., Guo, Y.: GDPR-compliant personal data management: a blockchain-based solution. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 15, 1746–1761 (2020)
Chow, S.S.M., Hui, L.C.K., Yiu, S., and Chow, K.P.: An e-lottery scheme using verifiable random function. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and its Applications, pp 651–660. Singapore, May 9–12, (2005).
Bentov, I., and Kumaresan, R.: How to use bitcoin to design fair protocols. In Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO 2014—34th Annual Cryptology Conference, pp 421–439. Santa Barbara, CA, USA, August 17–21 (2014)
Grumbach, S., Riemann, R.: Distributed random process for a large-scale peer-to-peer lottery. In: Distributed applications and interoperable systems, pp. 34–48. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2017)
Miller, A., and Bentov, I.: Zero-collateral lotteries in bitcoin and ethereum. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy Workshops, EuroS&P Workshops 2017, pp. 4–13. Paris, France, 26–28 April (2017)
Goldenberg, L., Vaidman, L., Wiesner, S.: Quantum gambling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 3356–3359 (1999)
Spekkens, R.W., Rudolph, T.: Quantum protocol for cheat-sensitive weak coin flipping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 227901 (2002)
Nguyen, A.T., Frison, J., Huy, K.P., Massar, S.: Experimental quantum tossing of a single coin. New J. Phys. 10, 083037 (2008)
Hänggi, E., Wullschleger, J.: Tight bounds for classical and quantum coin flipping. In: Theory of cryptography, pp. 468–485. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany (2011)
Nayak, A., Sikora, J., Tunçel, L.: A search for quantum coin-flipping protocols using optimization techniques. Math. Program. 156, 581–613 (2016)
Sun, X., Sopek, M., Wang, Q., et al.: Towards quantum-secured permissioned blockchain: signature, consensus, and logic. Entropy 21, 887 (2019)
Sun, X., Kulicki, P., Sopek, M.: Lottery and auction on quantum blockchain. Entropy 22(12), 1377 (2020)
Wang, Q., Yu, C., Gao, F., et al.: Self-tallying quantum anonymous voting. Phys. Rev. A 94(2), 022333 (2016)
Nielsen, M.A., and Chuang, I.L.: Quantum computation and quantum information, pp. 203–208 Cambridge University Press, (2000)
Bennett, C.H., and Brassard, G.: An update on quantum cryptography. In Advances in Cryptology–CRYPTO ’84, pp. 475–480. Santa Barbara, California, USA, August 19–22, (1984)
Lo, H.-K., Ma, X., Chen, K.: Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(23), 230504 (2005)
Li, Q., Wu, J., Quan, J., et al.: Efficient quantum blockchain with a consensus mechanism QDPoS. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 17, 3264–3276 (2022)
Weng, C.-X., Gao, R.-Q., Bao, Y., et al.: Beating the fault-tolerance bound and security loopholes for Byzantine agreement with a quantum solution. Research (2022). https://doi.org/10.34133/research.0272
Song, Y.-Q., Wu, Y.-S., Wu, S.-Y., et al.: A quantum federated learning framework for classical clients. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 67, 250311 (2024)
Li, L., Li, J., Song, Y.-Q., et al.: An efficient quantum proactive incremental learning algorithm. Sci. China Phys., Mech. Astron. 68, 210313 (2025)
Song, Y.-Q., Li, J., Wu, Y.-S., et al.: A resource-efficient quantum convolutional neural network. Front. Phys. 12, 1362690 (2024)
Qin, L.-Z., Liu, B., Gao, F., et al.: Decoy-state quantum private query protocol with two-way communication. Phys. A-Stat. Mech. Appl. 633, 129427 (2024)
Li, B.-K., Yang, Y.-G., Wen, Q.-Y.: Threshold quantum secret sharing of secure direct communication. Chin. Phys. Lett. 26(1), 010302 (2009)
Liu, B.-X., Yang, Y.-G., Xu, G.-B., et al.: Heralded quantum network coding of multi-particle states based on quantum time-bin multiplexing. Phys. A. 639, 129683 (2024)
Liu, B.-X., Xu, G.-B., Yang, Y.-G.: Complete security solution for practical quantum network coding. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 43(9), 2692–2704 (2024)
Yang, Y.-G., Teng, Y.-W., Chai, H.-P., Wen, Q.-Y.: Fault-tolerant quantum secret sharing against collective noise. Phys. Scr. 83(2), 025003 (2011)
Yang, Y.-G., Wang, Y., Teng, Y.-W., Chai, H.-P., Wen, Q.-Y.: Scalable arbitrated quantum signature of classical messages with multi-signers. Commun. Theor. Phys. 54(1), 84–88 (2010)
Yang, Y.-G., Chai, H.-P., Teng, Y.-W., Wen, Q.-Y.: Improving the security of controlled quantum secure direct communication by using four particle cluster states against an attack with fake entangled particles. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50(2), 395–400 (2011)
Yang, Y.-G., Wang, H.-Y., Jia, X., Zhang, H.: A quantum protocol for (t, n)-threshold identity authentication based on Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger States. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52(2), 524–530 (2013)
Yang, Y.-G., Cao, W.-F., Wen, Q.-Y.: Three-party quantum secret sharing of secure direct communication based on χ-type entangled states. Chin. Phys. B 19(5), 050306 (2010)
Yang, Y.-G., Wen, Q.-Y.: Threshold quantum secure direct communication without entanglement. Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. Astron. 51(2), 176–183 (2008)
Yang, Y.-G., Wen, Q.-Y., Zhu, F.-C.: An efficient quantum secret sharing protocol with orthogonal product states. Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. Astron. 50(3), 331–338 (2007)
Yang, Y.-G., Wen, Q.-Y.: Threshold multiparty quantum-information splitting via quantum channel encryption. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 07(06), 1249–1254 (2009)
Yang, Y.-G., Wen, Q.-Y.: Quantum threshold group signature. Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. Astron. 51, 1505–1514 (2008)
Yang, Y.-G., Liu, B.-X., Xu, G.-B., et al.: Flexible quantum network coding by using quantum multiplexing. Adv. Quantum Technol. 7(9), 202400016 (2024)
Yang, Y.-G., Sun, S.-J., Xu, P., et al.: Flexible protocol for quantum private query based on B92 protocol. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 805–813 (2014)
Yang, Y.-G., Liu, B.-X., Xu, G.-B., et al.: Practical quantum anonymous private information retrieval based on quantum key distribution. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forens Secur. 18, 4034–4045 (2023)
Yang, Y.-G., Yang, J.-J., Zhou, Y.-H., et al.: Quantum network communication: A discrete-time quantum-walk approach. Sci. Chin. Inf. Sci. 61, 042501 (2018)
Yang, Y.-G., Wang, Y.-C., Yang, Y.-L., Chen, X.-B., Li, D., Zhou, Y.-H., Shi, W.-M.: Participant attack on the deterministic measurement-device-independent quantum secret sharing protocol. Sci. Chin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 64(6), 121–124 (2021)
Yang, Y.-G., Wen, Q.-Y.: Threshold multiparty quantum-information splitting via quantum channel encryption. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 07(06), 1249–1254 (2009)
Yang, Y.-G., Li, B.-R., Li, D, et al.: New quantum key agreement protocols based on Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(10), 322 (2019)
Yang, Y.-G., Li, B.-R., Kang, S.-Y., et al.: New quantum key agreement protocols based on cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(2), 77 (2019)
Yang, Y.-G., Zhi-Chao Liu, Jian Li, Xiu-Bo Chen, Hui-Juan Zuo, Yi-Hua Zhou, Wei-Min Shi. Theoretically extensible quantum digital signature with starlike cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(1), 2 (2017)
Yang, Y.-G., Gao, S., Li, D., et al.: Three-party quantum secret sharing against collective noise. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(5), 215 (2019)
Yang, Y.-G., Gao, S., Li, D., et al.: New secure quantum dialogue protocols over collective noisy channels. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(9), 2810–2822 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 4252014); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62171264); and Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2023MF080).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yu-Guang Yang (Methodology: Equal; Writing—original draft: Equal) Shi Qiu (Conceptualization: Lead; Investigation: Lead; Validation: Lead; Visualization: Lead; Writing—original draft: Equal) Yue-Chao Wang (Methodology: Equal; Resources: Equal) Guang-Bao Xu (Supervision: Equal; Writing—review and editing: Equal) Donghuan Jiang (Funding acquisition: Lead; Writing–review and editing: Equal).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, YG., Qiu, S., Wang, YC. et al. A novel lottery protocol based on quantum blockchain. Quantum Inf Process 24, 32 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-025-04657-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-025-04657-1