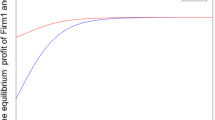
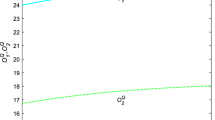
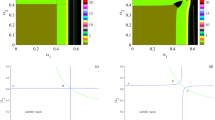
Abstract
This paper establishes a dynamic quantum Cournot game model incorporating an externality cost function, where participants aim to maximize relative profits and possess bounded rationality, updating their output for the next period using a gradient adjustment mechanism. Based on the established model, we analyze the existence and stability of quantum Nash equilibria and investigate the complex behavior of the system. The research results indicate that as the adjustment speed increases, the system’s stability decreases due to the emergence of Flip and Neimark–Sacker bifurcations. However, increasing the degree of quantum entanglement can delay the occurrence of bifurcation behavior. Furthermore, we find that when enterprises cannot control chaotic states by adjusting external cost parameters, they can transition the system from a chaotic to a stable state by altering product differentiation and quantum entanglement. Finally, numerical simulations validate the theoretical analysis and visually demonstrate complex dynamic characteristics, such as bifurcation diagrams, the maximum Lyapunov exponent, strange attractors, sensitivity to initial conditions, and chaos.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Meyer, D.A.: Quantum strategies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82(5), 1052–1055 (1999)
Eisert, J., Wilkens, M., Lewenstein, M.: Quantum games and quantum strategies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83(15), 3077–3080 (1999)
Marinatto, L., Weber, T.: A quantum approach to static games of complete information. Phys. Lett. A 272(5–6), 291–303 (2000)
Du, J., Ju, C., Li, H.: Quantum entanglement helps in improving economic efficiency. J. Phys. A 38(7), 1559–1565 (2005)
Busemeyer, J.R., Bruza, P.D.: Quantum Models of Cognition and Decision. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2012)
Piotrowski, E.W., Sladkowski, J.: An invitation to quantum game theory. Int. Theor. Phys. 42(5), 1089–1099 (2003)
Guo, H., Zhang, J., Koehler, G.J.: A survey of quantum games. Decis. Support. Syst. 46(1), 318–332 (2008)
Li, H., Du, J., Massar, S.: Continuous-variable quantum games. Phys. Lett. A 306(2–3), 73–78 (2002)
Frąckiewicz, P.: Quantum approach to Cournot-type competition. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(2), 353–362 (2018)
Alonso-Sanz, R.: Simulation of the quantum Cournot duopoly game. Phys. A 534, 122116 (2019)
Khan, S.M., Ramzan, M., Khan, M.K.: Quantum model of Bertrand duopoly. Chin. Phys. Lett. 27(8), 11–14 (2010)
Sekiguchi, Y., Sakahara, K., Sato, T.: Existence of equilibria in quantum Bertrand–Edgeworth duopoly game. Quantum Inf. Process. 11(6), 1371–1379 (2012)
Yu, R., Xiao, R.: Quantum Stackelberg duopoly with isoelastic demand function. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 8(9), 3643–3650 (2012)
Grau-Climent, J., Garcia-Perez, L., Alonso-Sanz, R., Losada, C.: Effect of players’ expectations and memory in a quantum Cournot game. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 175, 113950 (2023)
Rand, D.: Exotic phenomena in games and duopoly models. J. Math. Econ. 5(2), 173–184 (1978)
Agiza, H.N., Elsadany, A.A.: Nonlinear dynamics in the Cournot duopoly game with heterogeneous players. Phys. A 320(8), 512–524 (2003)
Agiza, H.N., Elsadany, A.A.: Chaotic dynamics in nonlinear duopoly game with heterogeneous players. Appl. Math. Comput. 149(3), 843–860 (2004)
Elsadany, A.A.: A dynamic Cournot duopoly model with different strategies. J. Egypt. Math. Soc. 23(1), 56–61 (2015)
Ding, Z., Li, Q., Jiang, S., Wang, X.: Dynamics in a Cournot investment game with heterogeneous players. Appl. Math. Comput. 256, 939–950 (2015)
Pecora, N., Sodini, M.: A heterogenous Cournot duopoly with delay dynamics: Hopf bifurcations and stability switching curves. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Simul. 58, 36–46 (2018)
Askar, S.S.: Nonlinear dynamic investigations and global analysis of a Cournot duopoly game with two different objectives. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 155, 111711 (2022)
Wang, C., Pi, J., Zhou, D., Tang, W., Yang, G.: Dynamics of n-person Cournot games with asymmetric information and heterogeneous expectations. Phys. A 618, 128691 (2023)
Neill, C., Roushan, P., Fang, M., et al.: Ergodic dynamics and thermalization in an isolated quantum system. Nat. Phys. 12(11), 1037–1041 (2016)
Anand, A., Srivastava, S., Gangopadhyay, S., et al.: Simulating quantum chaos on a quantum computer. Sci. Rep. 14(1), 26890 (2024)
Kumari, M., Ghose, S.: Untangling entanglement and chaos. Phys. Rev. A 99(4), 042311 (2019)
Ghose, S., Stock, R., Jessen, P., et al.: Chaos, entanglement, and decoherence in the quantum kicked top. Phys. Rev. A: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 78(4), 042318 (2008)
Yang, Z., Gong, Q.: Nonlinear dynamics of continuous-variable quantum games with bounded rationality. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(11), 1–15 (2018)
Shi, L., Xu, F.: Nonlinear dynamics of a quantum Cournot duopoly game with heterogeneous players. Quantum Inf. Process 18(7), 1–15 (2019)
Zhang, X., Sun, D., Jiang, W.: Dynamics of a heterogeneous quantum Cournot duopoly with adjusting players and quadratic costs. Quantum Inf. Process. 19(11), 1–15 (2020)
Zhou, D., Yang, H., Pi, J., Yang, G.: The dynamics of a quantum Cournot duopoly with asymmetric information and heterogeneous players. Phys. Lett. A 483, 129033 (2023)
Schaffer, M.E.: Are profit-maximisers the best survivors?: A Darwinian model of economic natural selection. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 12(1), 29–45 (1989)
Lu, J.: Study of informative advertising competition model in duopolistic market with relative profit object. J. Serv. Sci. Manag. 10(2), 105–111 (2017)
Elsadany, A.A.: Dynamics of a Cournot duopoly game with bounded rationality based on relative profit maximization. Appl. Math. Comput. 294, 253–263 (2017)
Jansen, T., van Lier, A., Van Witteloostuijn, A.: On the impact of managerial bonus systems on firm profit and market competition: the cases of pure profit, sales, market share and relative profits compared. Manag. Decis. Econ. 30(3), 141–153 (2009)
Lu, Y.: The relative-profit-maximization objective of private firms and endogenous timing in a mixed oligopoly. Singapore Econ. Rev. 56(02), 203–213 (2011)
Satoh, A., Tanaka, Y.: Relative profit maximization and Bertrand equilibrium with quadratic cost functions. Econ. Bus. Lett. 2(3), 134–139 (2013)
Satoh, A., Tanaka, Y.: Choice of strategic variables under relative profit maximization in asymmetric oligopoly: non-equivalence of price strategy and quantity strategy. Econ. Bus. Lett. 3(2), 115–126 (2014)
Peng, Y., Xiao, Y., Lu, Q., Wu, X., Zhao, Y.: Chaotic dynamics in Cournot duopoly model with bounded rationality based on relative profit delegation maximization. Phys. A 560, 125174 (2020)
Li, H., Zhou, W., Elsadany, A.A., Chu, T.: Stability, multi-stability and instability in Cournot duopoly game with knowledge spillover effects and relative profit maximization. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 146, 110936 (2021)
Askar, S.: On dynamic investigations of Cournot Duopoly Game: when firms want to maximize their relative profits. Symmetry 13(12), 2235 (2021)
Askar, S.S., Al-Khedhairi, A.: Dynamic investigations in a duopoly game with price competition based on relative profit and profit maximization. J. Comput. Appl. Math 367, 112464 (2020)
Wei, Z., Tan, W., Elsadany, A.A., Moroz, I.: Complexity and chaos control in a Cournot duopoly model based on bounded rationality and relative profit maximization. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(18), 17561–17589 (2023)
Askar, S., Foul, A., Mahrous, T., Djemele, S., Ibrahim, E.: Global and local analysis for a Cournot duopoly game with two different objective functions. Mathematics 9(23), 3119 (2021)
Gandolfo, G.: Economic Dynamics: Methods and Models. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1971)
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 11271098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dandan Guo contributed to software, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing. Die Zhou was involved in the conceptualization and writing—review and editing. Chun Wang and Guanghui Yang assisted in writing–review and editing. Hui Yang contributed to the supervision and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, D., Zhou, D., Wang, C. et al. Dynamic quantum Cournot duopoly with externality cost functions and relative profit maximization. Quantum Inf Process 24, 43 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-025-04662-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-025-04662-4