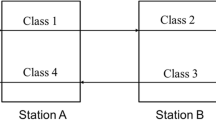
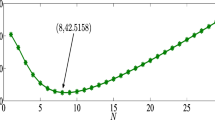
Abstract
This paper is concerned with the dynamic assignment of servers to tasks in queueing networks where demand may exceed the capacity for service. The objective is to maximize the system throughput. We use fluid limit analysis to show that several quantities of interest, namely the maximum possible throughput, the maximum throughput for a given arrival rate, the minimum arrival rate that will yield a desired feasible throughput, and the optimal allocations of servers to classes for a given arrival rate and desired throughput, can be computed by solving linear programming problems. We develop generalized round-robin policies for assigning servers to classes for a given arrival rate and desired throughput, and show that our policies achieve the desired throughput as long as this throughput is feasible for the arrival rate. We conclude with numerical examples that illustrate the points discussed and provide insights into the system behavior when the arrival rate deviates from the one the system is designed for.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, H.-S., Duenyas, I., Zhang, R.: Optimal stochastic scheduling of a two-stage tandem queue with parallel servers. Adv. Appl. Probab. 16, 453–469 (1999)
Ahn, H.-S., Duenyas, I., Lewis, M.E.: The optimal control of a two-stage tandem queueing system with flexible servers. Probab. Eng. Inf. Sci. 16, 453–469 (2002)
Ahn, H.-S., Duenyas, I., Zhang, R.: Optimal control of a flexible server. Adv. Appl. Probab. 36, 139–170 (2004)
Andradóttir, S., Ayhan, H.: Throughput maximization for tandem lines with two stations and flexible servers. Oper. Res. 53, 516–531 (2005)
Andradóttir, S., Ayhan, H., Down, D.G.: Server assignment policies for maximizing the steady-state throughput of finite queueing systems. Manag. Sci. 47, 1421–1439 (2001)
Andradóttir, S., Ayhan, H., Down, D.G.: Dynamic server allocation for queueing network with flexible servers. Oper. Res. 51, 952–968 (2003)
Andradóttir, S., Ayhan, H., Down, D.G.: Compensating for failures with flexible servers. Oper. Res. 55, 753–768 (2007)
Andradóttir, S., Ayhan, H., Down, D.G.: Dynamic assignment of dedicated and flexible servers in tandem lines. Probab. Eng. Inf. Sci. 21, 497–538 (2007)
Bell, S.L., Williams, R.J.: Dynamic scheduling of a system with two parallel servers in heavy traffic with complete resource pooling: Asymptotic optimality of a continuous review threshold policy. Ann. Appl. Probab. 11, 608–649 (2001)
Bell, S.L., Williams, R.J.: Dynamic scheduling of a parallel server system in heavy traffic with complete resource pooling: Asymptotic optimality of a threshold policy. Electron. J. Probab. 10, 1044–1115 (2005)
Bertsimas, D., Tsitsiklis, J.N.: Introduction to Linear Optimization, 2nd edn. Athena Scientific, Belmont (1997)
Bramson, M., Williams, R.J.: On dynamic scheduling of stochastic networks in heavy traffic and some new results for the workload process. In: Proceedings of the 39th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 516–521 (2000)
Chen, H., Mandelbaum, A.: Discrete flow networks: Bottleneck analysis and fluid limit approximations. Math. Oper. Res. 16, 408–445 (1991)
Chen, H., Mandelbaum, A.: Stochastic discrete flow networks: Diffusion approximations and bottlenecks. Ann. Probab. 19(4), 1463–1519 (1991)
Dai, J.G.: On positive Harris recurrence of multiclass queueing networks: A unified approach via fluid limit models. Ann. Appl. Probab. 5, 49–77 (1995)
Dai, J.G.: A fluid limit model criterion for instability of multiclass queueing networks. Ann. Appl. Probab. 6, 751–757 (1996)
Dai, J.G.: Stability of Fluid and Stochastic Processing Networks. MaPhySto Miscellanea Publications, vol. 9. Centre for Mathematical Physics and Stochastics, Ny Munkegade (1999)
Dai, J.G., Lin, W.: Maximum pressure policies in stochastic processing networks. Oper. Res. 53, 197–218 (2005)
Davis, M.H.A.: Piecewise deterministic Markov processes: A general class of diffusion stochastic models. J. R. Stat. Soc., Ser. B, Stat. Methodol. 46, 353–388 (1984)
Egorova, R., Borst, S., Zwart, B.: Bandwidth-sharing networks in overload. Perform. Eval. 64(9–12), 978–993 (2007)
Farrar, T.M.: Optimal use of an extra server in a two station tandem queueing network. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 38, 1296–1299 (1993)
Georgiadis, L., Tassiulas, L.: Optimal overload response in sensor networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 14, 2684–2696 (2006)
Goodman, J.B., Massey, W.A.: The non-ergodic Jackson network. J. Appl. Probab. 21, 860–869 (1984)
Hajek, B.: Optimal control of interacting service stations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 29, 491–499 (1984)
Harrison, J.M.: Brownian models of open processing networks: Canonical representation of workload. Ann. Appl. Probab. 10, 75–103 (2000)
Harrison, J.M.: A broader view of Brownian networks. Ann. Appl. Probab. 13, 1119–1150 (2001)
Harrison, J.M.: Stochastic networks and activity analysis. In: Suhov, Yu.M. (ed.) Analytic Methods in Applied Probability: In Memory of Fridrikh Karpelevich. American Mathematical Society, Providence (2002)
Harrison, J.M., López, M.J.: Heavy traffic resource pooling in parallel-server systems. Queueing Syst. 33, 339–368 (1999)
Jonckheere, M., van der Mei, R.D., van der Weij, W.: Rate stability and output rates in queueing networks with shared resources. Perform. Eval. 67(1), 28–42 (2010)
Kelly, F., Laws, C.: Dynamic routing in open queueing networks. Queueing Syst. 13, 47–86 (1993)
Kopzon, A., Nazarathy, Y., Weiss, G.: A push–pull network with infinite supply of work. Queueing Syst. 62(1–2), 75–111 (2009)
Lawler, G.F.: Introduction to Stochastic Processes, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2006)
Nazarathy, Y., Weiss, G.: Near-optimal control of queueing networks over a finite time horizon. Ann. Oper. Res. 170, 233–249 (2009)
Nazarathy, Y., Weiss, G.: Positive Harris recurrence and diffusion scale analysis of a push-pull queueing network. Perform. Eval. 67(4), 201–217 (2010)
Pandelis, D.G., Teneketzis, D.: Optimal multiserver stochastic scheduling of two interconnected priority queues. Adv. Appl. Probab. 26, 258–279 (1994)
Rosberg, Z., Varaiya, P.P., Walrand, J.C.: Optimal control of service in tandem queues. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 27(3), 600–609 (1982)
Shah, D., Wischik, D.: Fluid models of congestion collapse in overloaded switched networks. Queueing Syst. (2011, to appear)
Shah, D., Wischik, D.: Switched networks with maximum weight policies: Fluid approximation and multiplicative state space collapse. Ann. Appl. Probab. (2011, to appear)
Tassiulas, L., Bhattacharya, L.L.: Allocation of interdependent resources for maximal throughput. Stoch. Models 16, 27–48 (2000)
Tassiulas, L., Ephrimedes, A.: Stability properties of constrained queueing systems and scheduling policies for maximum throughput in multihop radio networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 37, 1936–1948 (1992)
Tekin, S.: Efficient system design: stability and flexibility. PhD thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology (2011)
Tekin, S., Andradóttir, S.: Inspection location in capacity-constrained serial lines. Working Paper (2011)
Weiss, G.: Jackson networks with unlimited supply of work. J. Appl. Probab. 42(3), 879–882 (2005)
Williams, R.J.: On dynamic scheduling of a parallel server system with complete resource pooling. Anal. Commun. Netw., Call Cent. Traffic Perform. 28 (2000)
Wu, C.-H., Lewis, M.E., Veatch, M.: Dynamic allocation of reconfigurable resources in a two-stage tandem queueing system with reliability considerations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 51, 309–314 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tekin, S., Andradóttir, S. & Down, D.G. Dynamic server allocation for unstable queueing networks with flexible servers. Queueing Syst 70, 45–79 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11134-011-9258-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11134-011-9258-6