Abstract
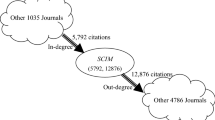
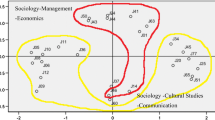
This paper aims to reveal the relationship and structure of library and information science (LIS) journals in China. 24 core LIS journals in China are selected and the relevant data of journal co-citation are retrieved from Chinese Journal Full-Text Database constructed by China National Knowledge Infrastructure during the period of 1999–2009. By calculating mean co-citation frequencies and correlation coefficients, we find that there is a strong relationship among LIS journals in China. Utilizing the methods of cluster analysis, multidimensional scaling analysis and factor analysis, we analyze the data of journal co-citation. LIS journals in China are divided into four clusters. The relatedness among journals is shown manifestly through their locations in the two-dimensional map. A three-factor solution is obtained with the factor loading of each journal. Finally, we interpret and discuss the results to get some conclusions and also expect to describe the network characters of journal co-citation in future research.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding, Y., Chowdhury, G., & Foo, S. (2000). Journal as markers of intellectual space: Journal cocitation analysis of information retrieval area, 1987–1997. Scientometrics, 47(1), 55–73.
Hung, R. L. (2004). The advanced tutorial for SPSS. Beijing: Higher Education Press.
Liu, L. Q. (2005a). Mapping knowledge domains of research with document co-citation. Studies in Science of Science, 23(2), 155–159.
Liu, Z. (2005b). Visualizing the intellectual structure in urban studies: A journal co-citation analysis (1992–2002). Scientometrics, 62(3), 385–402.
Ma, R. M., Qiu, J. P., Ni, C. Q., & Li, X. L. (2009). An author co-citation analysis of information science in China with Chinese Google Scholar search engine, 2004–2006. Scientometrics, 81(1), 33–46.
McCain, K. W. (1990). Mapping authors in intellectual space: A technical overview. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 41(6), 433–443.
McCain, K. W. (1991). Mapping economics through the journal literature: An experiment in journal co-citation analysis. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 42, 290–296.
Norusis, M. J. (1997). SPSS 7.5 guide to data analysis. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Small, H. (1973). Co-citation in the scientific literature: A new measure of the relationship between two documents. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 24(4), 265–269.
Small, H., & Griffith, B. C. (1974). The structure of scientific literatures I: Identifying and graphing specialties. Science Studies, 4(1), 17–40.
Small, H., Sweeney, E., & Greenlee, E. (1985). Clustering the science citation index using co-citations. II. Mapping science. Scientometrics, 8(5-6), 321–340.
Song, G., & Ye, J. Y. (2009). An analysis of network structures of mutual citation of library and information science journals based on SNA. Journal of Library Science in China, 35(3), 27–34.
Tian, D. F. (2009). Citing and cited network analysis on journals in library and information science. Journal of Intelligence, 28(6), 48–51.
Tsay, M. Y., Xu, H., & Wu, C. W. (2003). Journal co-citation analysis of semiconductor literature. Scientometrics, 57(1), 7–25.
White, H. D. (2003). Author cocitation analysis and pearson’s r. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 54(13), 1250–1259.
White, H. D., & McCain, K. W. (1998). Visualizing a discipline: An author co-citation analysis of information science, 1972–1995. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 49(4), 327–356.
Wu, X., & Yuan, F. (1994). Library and information education in the People’s Republic of China: The impact of reform and “opening-up”. Education for Information, 12, 247–257.
Yue, H. J., & Liu, S. F. (2008). Co-citation network analysis on journals in management sciences. Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information, 27(3), 400–406.
Zeng, J. X. (2009). Chinese journal highly cited indictors (2009). Beijing: Scientific and Technical Documents Publishing House.
Zhao, Y. Y., Cui, L., & Yang, H. (2009). Evaluating reliability of co-citation clustering analysis in representing the research history of subject. Scientometrics, 80(1), 91–102.
Zitt, M., Ramanana-Rahary, S., & Bassecoulard, E. (2003). Bridging citation and reference distributions: Part I—the referencing-structure function and its application to co-citation and co-item studies. Scientometrics, 57(1), 93–118.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, CP., Hu, JM., Gao, Y. et al. A journal co-citation analysis of library and information science in China. Scientometrics 86, 657–670 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-010-0313-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-010-0313-6