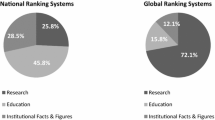
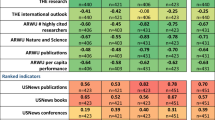
Abstract
Recently there are many organizations conducting projects on ranking world universities from different perspectives. These ranking activities have made impacts and caused controversy. This study does not favor using bibliometric indicators to evaluate universities’ performances, but not against the idea either. We regard these ranking activities as important phenomena and aim to investigate correlation of different ranking systems taking bibliometric approach. Four research questions are discussed: (1) the inter-correlation among different ranking systems; (2) the intra-correlation within ranking systems; (3) the correlation of indicators across ranking systems; and (4) the impact of different citation indexes on rankings. The preliminary results show that 55 % of top 200 universities are covered in all ranking systems. The rankings of ARWU and PRSPWU show stronger correlation. With inclusion of another ranking, WRWU (2009–2010), these rankings tend to converge. In addition, intra-correlation is significant and this means that it is possible to find out some ranking indicators with high degree of discriminativeness or representativeness. Finally, it is found that there is no significant impact of using different citation indexes on the ranking results for top 200 universities.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altbach, P. (2006). The dilemmas of ranking. International Higher Education, 42, 2–3.
Billaut, J. C., Bouyssou, D., & Vincke, P. (2009). Should you believe in the Shanghai ranking? An MCDM view. Scientometrics, 72(1), 25–32.
Bookstein, F. L., Seidler, H., Fieder, M., & Winckler, G. (2010). Too much noise in the times higher education rankings. Scientometrics, 85, 295–299.
Cybermetrics Lab, Centro de CienciasHumanas y Sociales, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (2011) Webometrics ranking of world universities. Retrieved March 10, 2011, from http://www.webometrics.info/.
Hazelkorn, E. (2008). Globalization, internationalization, and rankings. International Higher Education, 53, 8–10.
Higher Education Evaluation and Accreditation Council of Taiwan (2011) Performance ranking of scientific papers for world universities—2007, 2008, 2009, 2010. Retrieved March 10, 2011, from http://ranking.heeact.edu.tw/.
Holmes, R. (2006). The THES university rankings: are they really world class? Asian Journal of University Education, 2(1), 1–14.
Hou, Y. Q., Morse, R., & Jiang, Z. L. (2011). Analyzing the movement of ranking order in world universities’ rankings: how to understand and use universities’ rankings effectively to draw up a universities’ development strategy. Evaluation Bimonthly, 30, 43–49.
Huang, M. X. (2009). Exposing the black box of the ranking of the Times higher education supplement. Evaluation Bimonthly, 22, 31–36.
Huang, M. X. (2011). The comparison of performance ranking of scientific papers for world universities and other ranking systems. Evaluation Bimonthly, 29, 53–59.
International Ranking Expert Group (2006) Berlin principles on ranking of higher education institutions. Retrieved Nov 29, 2011, from http://www.che.de/downloads/Berlin_Principles_IREG_534.pdf.
Ioannidis, A., Patsopoulos, N., Kavvoura, F., Tatsioni, A., Evangenlou, E., Kouri, I., Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D., & Liberopoulous, G. (2007). International ranking systems for universities and institutions: a critical appraisal. BMC Medicine, 5 (30). Retrieved Nov 29, 2011, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2174504/.
Lawani, S. M. (1981). Bibliometrics: its theoretical foundations methods and applications. Libri, 31(4), 294–315.
Liu, W. Q. (2008). How to look upon universities’ rankings? Evaluation Bimonthly, 13, 6–7.
Marginson, S. (2007) Global university rankings: where to from here? Communication to the Asia-Pacific Association for International Education, National University of Singapore, 7–9, March, 2007. Retrieved Nov 22, 2011, from http://mt.educarchile.cl/mt/jjbrunner/archives/APAIE_090307_Marginson.pdf.
MINES ParisTech (2010) International professional ranking of higher education institutions: 2007, 2008, 2009. Retrieved Nov 22, 2011, from http://www.ensmp.fr/Actualites/PR/EMP-ranking.html.
Qiu, J. P. (2009). Practice, features, and analysis in evaluating 2009 world class universities and research institutions. Evaluation and Management, 7(2), 19–28.
RatER.(2010). Global universities ranking. Retrieved Jan 3, 2010, from http://www.globaluniversitiesranking.org/.
Shanghai Ranking Consultancy & Shanghai Jiao Tong University (2011) Academic ranking of world universities: 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010. Retrieved Nov 22, 2011, from http://www.arwu.org/.
The Times Higher Education Supplement (2011) World university rankings: 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010. Retrieved March 19, 2011, from http://www.timeshighereducation.co.uk/.
Van Raan, A. (2005). Fatal attraction: conceptual and methodological problems in the ranking of universities by bibliometric methods. Scientometrics, 62(1), 133–143.
Van Raan, A. F. J., Moed, H. F., & Van Leeuwen, T. N. (2006). License to Rank. Coimbra Group Annual MeetingUniversity of Tartu. Retrieved Nov 3, 2010, from http://www.ut.ee/coimbra2006/orb.aw/class=file/action=preview/id=166720/TartuWebsite.pdf.
Vo, B. T., Sreeram, V., & Vo, B. N. (2010). On the assessment of university research impact: towards simplicity, transparency and fairness. TECH REPT. Retrieved Nov 3, 2010, from http://www.highimpactuniversities.com/uwarpi2010-article.pdf.
Williams, R. (2008). Methodology, meaning, and usefulness of rankings. Australian Universities’ Review, 50(2), 51–58.
Yu, L., Pan, Y., & Wu, Y. (2008).Two new indicators to compare different evaluation methods’ effect. Journal of Nanjing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 3, 135–140. Retrieved Feb 24, 2012, from http://image.sciencenet.cn/olddata/kexue.com.cn/upload/blog/file/2008/10/200810592044466910.pdf.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank two anonymous reviewers for their insightful suggestions. The authors would like to thank Professor Szu-chia Lo for her invaluable help in reviewing the draft of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Kh., Liao, Py. A comparative study on world university rankings: a bibliometric survey. Scientometrics 92, 89–103 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-012-0724-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-012-0724-7